Navigating dietary choices can be a complex task for people living with diabetes. One question that often arises is, “Are grapes good for diabetics?” This article aims to provide a comprehensive answer to this question, exploring the relationship between grapes and diabetes in detail.
Understanding Diabetes: Types and Impact on Diet 🩺
Diabetes is a chronic health condition that affects the body’s ability to process sugar. The sugar (glucose) obtained from the food we eat is used by the body’s cells for energy. However, in diabetes, the body either doesn’t produce enough insulin or can’t effectively use the insulin it does produce, leading to high blood sugar levels.
There are primarily two types of diabetes:
- Type 1 Diabetes: This is an autoimmune condition where the body’s immune system attacks and destroys insulin-producing cells in the pancreas. People with type 1 diabetes need to take insulin every day.
- Type 2 Diabetes: This is the most common type of diabetes. It occurs when the body becomes resistant to insulin or doesn’t produce enough insulin. It’s often associated with obesity and an unhealthy lifestyle.
Diet plays a crucial role in managing both types of diabetes. The goal is to balance the intake of carbohydrates, proteins, and fats to maintain stable blood sugar levels.
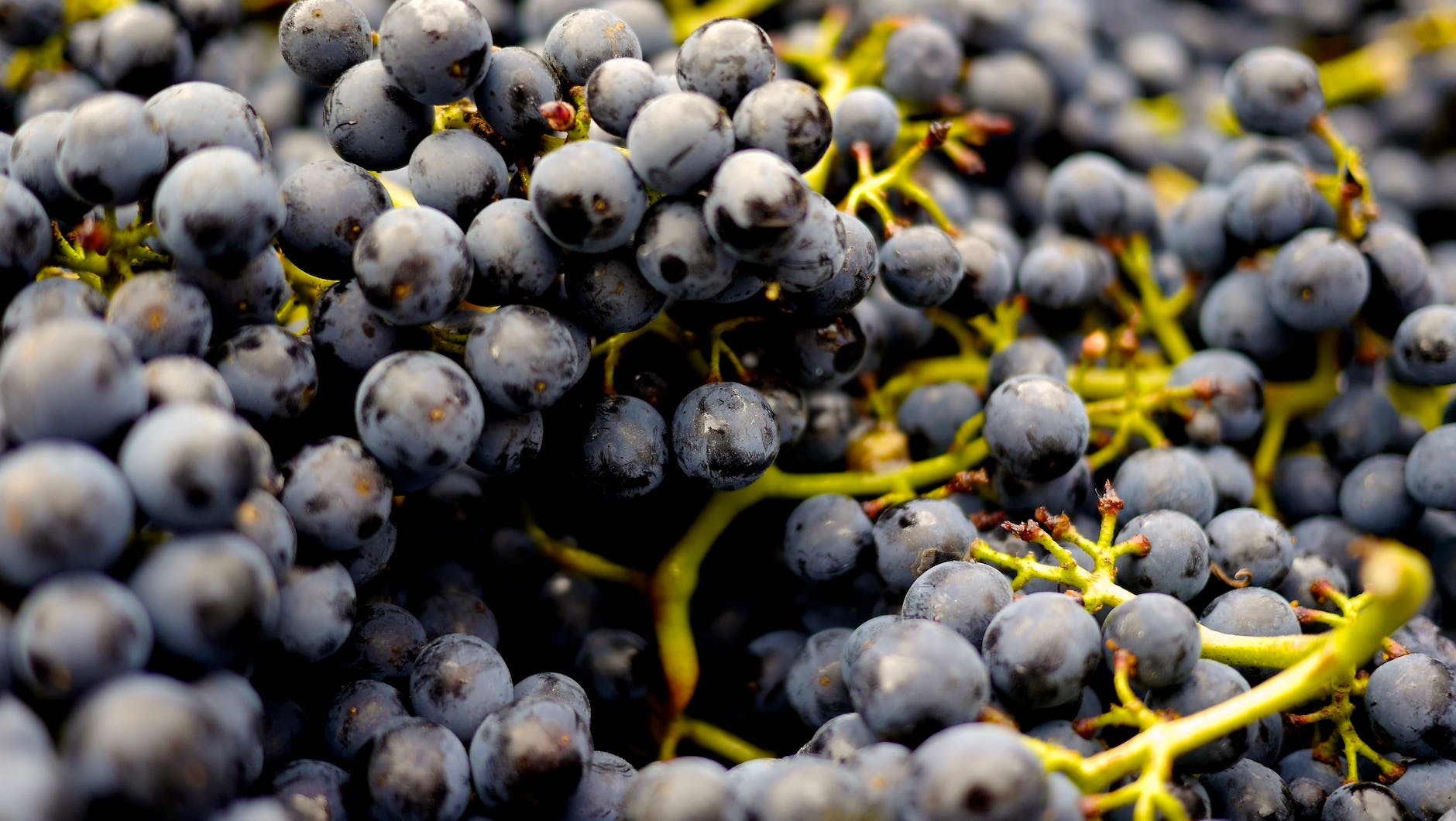
Grapes: Nutritional Profile and Health Benefits 🍇
Grapes, both red and green, are packed with nutrients and offer several health benefits. They are low in calories and high in vitamins C and K. Grapes also contain several antioxidants, including flavonoids and resveratrol, which have been linked to heart health.
The fiber content in grapes can help maintain a healthy digestive system and also slow the absorption of sugar into the bloodstream, preventing spikes in blood sugar levels.
The Relationship Between Grapes and Diabetes 🍇➕🩺
So, are grapes good for diabetics? Yes, when consumed in moderation, grapes can be a part of a healthy diet for people with diabetes. The key is to account for the carbohydrates they provide in your total daily intake.
Grapes do contain sugar, but they have a low glycemic index (GI), which means they have less impact on blood sugar levels than other high-GI foods.
Green Grapes vs Red Grapes: Which is Better for Diabetics? 🟢🔴
Both green and red grapes can be included in a diabetic diet. However, there are slight differences between the two:
- Sugar Content: Green grapes contain a slightly higher amount of sugar compared to red grapes. However, the difference is minimal and should not significantly impact blood sugar levels when consumed in moderation.
- Antioxidant Content: Red grapes have higher levels of certain antioxidants, including resveratrol, which may provide additional health benefits.
- Taste: Green grapes are often more tart, while red grapes are sweeter. This difference in taste might affect how many grapes you eat at a time.
Tips for Incorporating Grapes into a Diabetic Diet 🍇
Here are some tips for including grapes in a diabetic-friendly diet:
- Portion Control: A small bunch of grapes can make a satisfying snack. However, remember to count them as part of your daily carbohydrate intake.
- Pair with Protein: Eating grapes with a source of protein, such as cheese or nuts, can help slow the absorption of sugar and prevent blood sugar spikes.
- Choose Fresh Over Dried: Fresh grapes are a better choice than dried grapes (raisins), which have a higher concentration of sugar.
- Mix It Up: Add grapes to salads or use them in cooking to add a touch of natural sweetness to your meals.
In conclusion, grapes, when eaten in moderation, can be a part of a balanced diet for people with diabetes. They offer several health benefits and can add variety to your meals. As always, it’s important to monitor your blood sugar levels and consult with your healthcare provider or a dietitian to determine the dietary choices that work best for you.
Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs) 🙋♀️
In this section, we will address some of the most commonly asked questions about the relationship between grapes and diabetes.
1. What is the relationship between grapes and diabetes?
Grapes can be a part of a healthy diet for people with diabetes. They are low in calories, high in fiber, and packed with antioxidants. However, they do contain sugar, so they should be consumed in moderation and accounted for in your daily carbohydrate intake.
2. Are red grapes suitable for people with diabetes?
Yes, red grapes can be included in a diabetic diet. They have a slightly lower sugar content compared to green grapes and are rich in antioxidants, which can provide additional health benefits.
3. What is the glycemic index of green grapes?
The glycemic index (GI) of green grapes is around 46, which is considered low. This means that they have less impact on blood sugar levels compared to high-GI foods.
4. Do grapes affect blood sugar levels?
Yes, like all fruits, grapes contain carbohydrates and will affect blood sugar levels. However, due to their fiber content and low GI, they have a slower and less significant impact on blood sugar levels compared to other high-GI foods.
5. Is it okay for a person with diabetes to eat green grapes?
Yes, green grapes can be a part of a diabetic diet. However, they contain a slightly higher amount of sugar compared to red grapes, so portion control is essential.
6. How many grapes can a person with diabetes have?
The exact number can vary depending on individual dietary needs and blood sugar control. However, a small bunch of grapes (about 15 grapes) can be a good starting point. Always remember to account for them in your daily carbohydrate intake.
7. How many grapes are in a serving for diabetics?
A serving of grapes for a person with diabetes is typically around 15 grapes. This provides about 15 grams of carbohydrates, which is the equivalent of one carbohydrate serving.
8. Are black grapes good for diabetes?
Black grapes, like red and green grapes, can be included in a diabetic diet. They are rich in antioxidants and have a similar carbohydrate content. As always, portion control is key.
Remember, everyone’s body responds differently to different types of foods and diets, so it’s essential to monitor your blood sugar levels and work with your healthcare provider or a dietitian to determine what works best for you.
Blog tags: Diabetes, Type 1 Diabetes, Type 2 Diabetes, Grapes, Green Grapes, Red Grapes, Glycemic Index, Antioxidants, Sugar Content, Diabetic Diet, Portion Control, Pairing with Protein, Fresh Grapes, Cooking with Grapes, Blood Sugar Management.