Almond Nutrition Facts tell a fascinating story about why these nuts are so valued across the world. For centuries, almonds (or badam, as they’re called in India) have been symbols of nourishment, longevity, and even wisdom. Today, modern nutrition science confirms what tradition already knew: almonds are one of the most nutrient-dense foods you can add to your diet.
In every 100 grams of almonds, you’ll find a balance of protein, healthy fats, fiber, vitamins, and minerals — plus a surprisingly low glycemic index that makes them suitable even for people managing blood sugar. Whether you’re someone counting macros, looking for natural plant-based protein, or simply searching for smarter snacks, understanding almond nutrition facts per 100g is the key to appreciating what this nut can really do for your health.
Also Read: 7 Types of Almonds & How They Boosts Your Health
Let’s dive in and break down the numbers behind this nutritional powerhouse.
Almond Nutrition Facts per 100g: Breaking It Down
When you look at almond nutrition facts per 100g, what stands out first is how concentrated their nutrition is. A mere handful of almonds may not look like much, but in that small serving lies nearly 600 calories worth of clean, slow-burning fuel. Unlike empty calories from junk food, every one of those calories comes wrapped with nutrients that support your heart, muscles, digestion, and overall well-being.

Calories in Almond Nutrition Facts (100g)
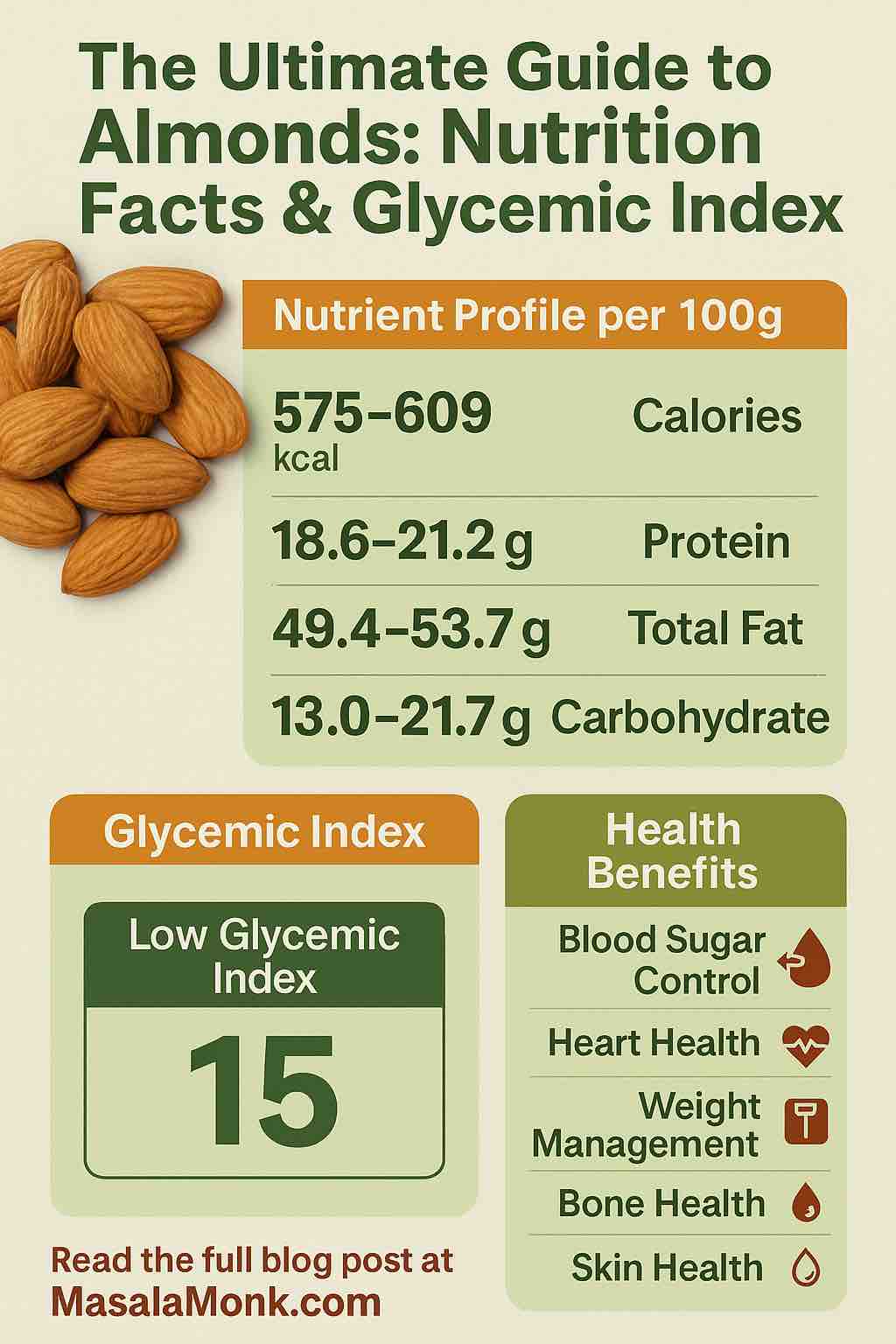
Almonds provide 575–609 calories per 100 g. That might sound like a lot, but context matters. Unlike a pastry or candy bar that delivers a similar calorie load with little benefit, almonds supply calories alongside protein, fiber, and micronutrients.
Think of almonds as premium fuel. Instead of a quick sugar rush and crash, they release energy slowly, keeping you satisfied for hours.
| Portion Size | Calories |
|---|---|
| 100 g (≈ 70–80 almonds) | 575–609 |
| 28 g (≈ 23 almonds, a standard serving) | ~164 |

👉 The takeaway: almond nutrition facts show that calories aren’t just about quantity — it’s about quality.
Protein in Almond Nutrition Facts (100g)
One of the highlights of almond nutrition is protein. In every 100 grams, almonds deliver 18.6–21.2 g of protein — roughly the same as three large eggs.

Protein is crucial for muscle repair, satiety, and overall metabolism. For vegetarians and vegans, almonds are an easy way to boost daily protein intake without relying on animal products.
| Portion Size | Protein |
|---|---|
| 100 g | 18.6–21.2 g |
| 28 g (serving) | ~6 g |
👉 Another reason why almond nutrition facts are impressive: they pack plant-based protein into every bite.
Healthy Fats in Almond Nutrition Facts
Almonds are sometimes criticized for being “high-fat,” but that misses the point. Out of the 49–54 g of fat per 100 g, most are the good fats — the kind that protect your heart.
| Type of Fat | Amount (per 100 g) | Why It Matters |
|---|---|---|
| Total Fat | 49.4–53.7 g | Dense energy source |
| Saturated Fat | 3.7–6.1 g | Should be limited, but minimal here |
| Monounsaturated Fat | ~30.9 g | Supports healthy cholesterol |
| Polyunsaturated Fat | ~12.1 g | Provides essential fatty acids |

These fats don’t just fuel your body — they actively reduce LDL (“bad”) cholesterol and improve cardiovascular health. That’s why nutritionists often group almonds with olive oil and avocados as staples of a heart-healthy diet.
Carbs, Fiber & Sugar in Almond Nutrition Facts
Almonds contain 13–21.7 g of carbohydrates per 100 g, but nearly half of this comes from fiber. That’s a game-changer.
| Nutrient | Amount (per 100 g) | Why It Matters |
|---|---|---|
| Carbohydrates | 13–21.7 g | Provides some energy |
| Fiber | ~12.2 g | Slows digestion, supports gut health |
| Sugars | 3.9–5 g (natural) | Minimal, and balanced by fiber |

The high fiber content means almonds don’t behave like carb-heavy foods such as bread or rice. Instead, they release glucose slowly, keeping blood sugar stable. This is one of the most overlooked yet powerful aspects of almond nutrition facts.
Quick Recap: Almond Nutrition Facts 100g
Here’s a bird’s-eye view of everything almonds pack into 100 grams:
| Nutrient | Amount (per 100 g) |
|---|---|
| Calories | 575–609 |
| Protein | 18.6–21.2 g |
| Total Fat | 49.4–53.7 g |
| Saturated Fat | 3.7–6.1 g |
| Monounsaturated Fat | ~30.9 g |
| Polyunsaturated Fat | ~12.1 g |
| Carbohydrates | 13–21.7 g |
| Fiber | ~12.2 g |
| Sugars | 3.9–5 g |
👉 Clearly, almond nutrition facts show us that almonds aren’t just calorie-dense — they’re nutrient-dense, delivering energy, protein, and heart-healthy fats in perfect balance.
Numbers are drawn from USDA composition data (compiled by MyFoodData) for raw almonds per 100 g—covering calories, protein, fats, carbs, fiber, vitamin E, magnesium, calcium and potassium. (My Food Data)
Almond Nutrition Facts: Vitamins & Minerals in 100g
The macronutrients — protein, fats, and fiber — often grab the spotlight, but when we look deeper into almond nutrition facts per 100g, what’s truly striking is the wealth of micronutrients they provide. Think of almonds as a compact multivitamin: small in size, yet rich in essential vitamins and minerals that play a role in everything from energy production to skin glow.
Vitamin E: The Antioxidant Superstar
One of the most celebrated aspects of almond nutrition facts is their exceptionally high Vitamin E content — around 26.2 mg per 100 g, which covers more than 100% of your daily needs.
Vitamin E is a fat-soluble antioxidant, meaning it protects the fats in your body (including cell membranes and cholesterol particles) from oxidative damage. In everyday terms, it helps slow down cellular aging, keeps your skin supple, and reduces the oxidative stress linked to heart disease.
If you’ve ever wondered why almonds are so often called a “beauty food,” this is the reason: Vitamin E nourishes your skin from within.
Magnesium: The Metabolism Regulator
Another standout in the almond nutrient profile is magnesium. At 268 mg per 100 g, almonds provide nearly two-thirds of your daily requirement.

Why does this matter? Magnesium is involved in more than 300 biochemical reactions — from muscle contractions to nerve impulses to blood sugar regulation. Low magnesium intake is surprisingly common, and it’s strongly linked with insulin resistance and type 2 diabetes.
Adding almonds to your diet is a simple, natural way to improve magnesium levels — and by extension, improve metabolic health.
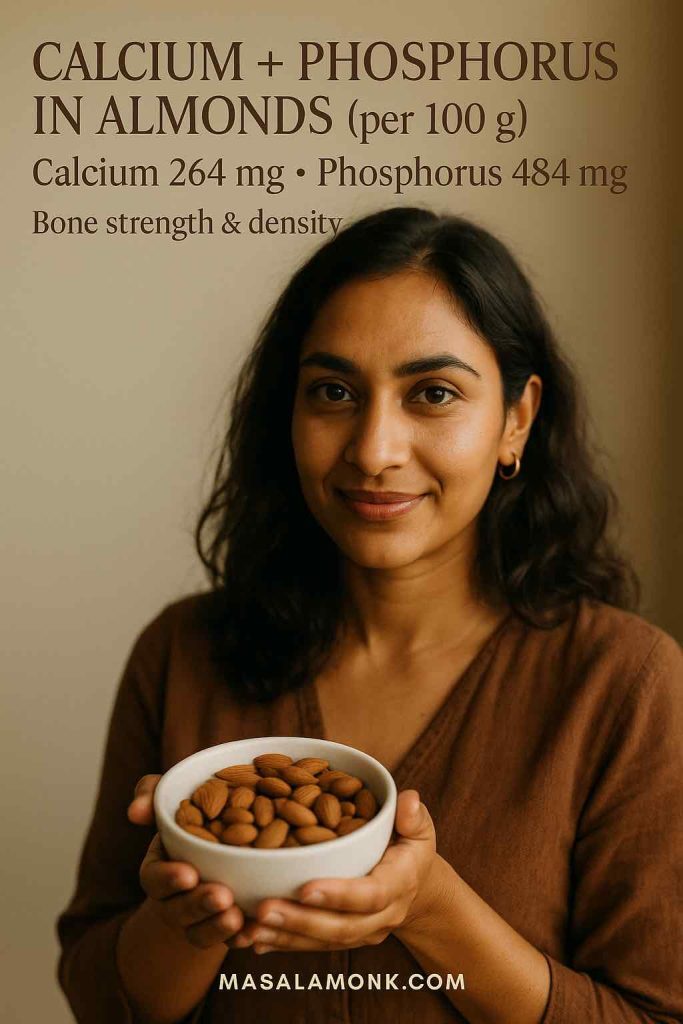
Calcium & Phosphorus: The Bone-Building Duo
Dairy often gets the credit for bone health, but almond nutrition facts prove that nuts can compete. With 264 mg of calcium and 484 mg of phosphorus per 100 g, almonds provide the raw materials your bones and teeth rely on.
Calcium builds the structure, while phosphorus ensures density and strength. For people who avoid dairy, almonds (and almond milk, if fortified) are a reliable plant-based option to keep bones strong.

Potassium: Balancing the Sodium
With 705 mg of potassium per 100 g, almonds help maintain fluid balance and regulate blood pressure. In a world where sodium intake is often too high, potassium-rich foods like almonds restore balance, easing the burden on the heart.

Iron, Zinc, Copper & Manganese: The Silent Helpers
Almonds also contain smaller but still significant amounts of other minerals:
- Iron (3.7 mg): Carries oxygen in your blood, preventing fatigue.
- Zinc (3.1 mg): Strengthens immunity and aids wound healing.
- Copper (1.0 mg): Supports energy production and iron absorption.
- Manganese (2.3 mg): Works with antioxidants to neutralize free radicals.
Individually these may seem minor, but together they form the quiet backbone of daily health.
Snapshot: Vitamins & Minerals in Almonds (per 100 g)
| Nutrient | Amount | Key Benefit |
|---|---|---|
| Vitamin E | 26.2 mg | Antioxidant, skin & heart health |
| Magnesium | 268 mg | Blood sugar control, nerves, muscles |
| Calcium | 264 mg | Bones & teeth |
| Phosphorus | 484 mg | Bone strength |
| Potassium | 705 mg | Blood pressure regulation |
| Iron | 3.7 mg | Oxygen transport |
| Zinc | 3.1 mg | Immune function |
| Copper | 1.0 mg | Energy production |
| Manganese | 2.3 mg | Antioxidant defense |
Why Micronutrients Matter in Almond Nutrition Facts
When people think about snacks, they often reach for options that satisfy hunger in the short term but leave the body starved of nutrients. Almonds, on the other hand, bring far more to the table. Their vitamin E protects your cells, magnesium supports metabolism, calcium and phosphorus build bones, potassium stabilizes blood pressure, and trace minerals keep your immune system strong.
In short: the micronutrient profile in almond nutrition facts is one of the reasons why a simple handful of almonds has such far-reaching benefits.
Glycemic Index & Glycemic Load in Almond Nutrition Facts
One of the most remarkable details in almond nutrition facts per 100g is not just the calories, protein, or fat — but their impact on blood sugar. Unlike many snack foods that cause spikes and crashes, almonds have a glycemic index (GI) so low it barely registers, making them a fantastic choice for people who want stable energy. Understand more about GI and Gl in our post – Glycemic Index (GI) VS Glycemic Load (GL).
Nuts, including almonds, are consistently classified as low-GI foods in the International Tables of Glycemic Index; this underpins almonds’ very small impact on post-meal glucose. (ScienceDirect)
What is Glycemic Index (GI)?
The glycemic index is a scale from 0 to 100 that measures how quickly a food raises blood sugar after eating.
- High GI (70–100): Foods like white bread, potatoes, and candy cause rapid spikes in blood glucose.
- Medium GI (56–69): Foods like sweet potatoes or basmati rice raise blood sugar moderately.
- Low GI (0–55): Foods like legumes, vegetables, and nuts lead to a slow, steady release of glucose.
Glycemic Index of Almonds
Almonds score around 15 on the GI scale, putting them firmly in the very low category. This means even a generous portion of almonds has almost no immediate impact on blood sugar.
Here’s how almonds compare with other common foods:
| Food | GI Value | Category |
|---|---|---|
| Almonds | ~15 | Very Low |
| Walnuts | ~15 | Very Low |
| Cashews | ~25 | Low |
| Apple | ~38 | Low |
| Banana | ~51 | Low |
| Brown Rice | ~55 | Low/Medium |
| White Bread | ~75 | High |
| Glucose (reference) | 100 | High |
👉 Clearly, almond nutrition facts stand out here: they are one of the most blood-sugar-friendly foods you can snack on.
Glycemic Load (GL) of Almonds
GI tells us how fast carbs raise blood sugar, but glycemic load (GL) considers the amount of carbs in a typical serving.
Almonds contain very few digestible carbs thanks to their high fiber content, so their glycemic load is only about 1.9 per 100 g — practically negligible.
To put that into perspective:
| Food | Serving Size | Glycemic Load |
|---|---|---|
| Almonds | 100 g | ~1.9 |
| Banana | 118 g (1 medium) | ~12 |
| White Rice | 150 g (1 cup cooked) | ~29 |
| White Bread | 60 g (2 slices) | ~20 |
Even when eating a full handful of almonds, your blood sugar barely moves. That’s why they’re often recommended for people with diabetes, prediabetes, or insulin resistance.
Why Almonds Have Such a Low Glycemic Impact
The reason behind this benefit comes down to the unique nutrient synergy we saw earlier in the almond nutrition facts:

- Fiber: With ~12 g per 100 g, fiber slows digestion and glucose absorption.
- Healthy fats: Delay stomach emptying, keeping glucose release gradual.
- Protein: Further slows carbohydrate breakdown, while boosting satiety.
Together, these elements turn almonds into a “slow-energy” food, giving you steady fuel without crashes.
Practical Takeaways
- For people with diabetes: Almonds are a safe snack that won’t cause glucose spikes. Pairing them with higher-GI foods (like fruit or rice) can even lower the meal’s overall GI.
- For steady energy: Eat almonds as a mid-morning or afternoon snack to avoid “sugar crashes.”
- For weight control: Stable blood sugar means fewer cravings, making almonds a natural appetite regulator.
Health Benefits of Almond Nutrition Facts
When you take a closer look at almond nutrition facts, it’s clear that the numbers aren’t just abstract data — they translate directly into powerful health benefits. Every calorie, gram of protein, and milligram of micronutrients contributes to long-term well-being. Here’s how almonds support your body in practical, everyday ways.
Almond Nutrition Facts and Heart Health
Almonds are rich in monounsaturated fats, the same type of “good fat” found in olive oil, known to protect the heart. Studies consistently show that diets including almonds help lower LDL (“bad”) cholesterol and improve HDL (“good”) cholesterol.

Add to that the Vitamin E content, which prevents oxidative damage to arteries, and you’ve got a food that actively supports cardiovascular health. Swapping a processed snack for a handful of almonds isn’t just a minor diet tweak — it’s a step toward lowering the risk of heart disease.
This isn’t just theory—randomized-trial meta-analyses show almond intake reduces LDL-cholesterol and other atherogenic lipids, supporting cardiovascular risk reduction. (PubMed)
Almond Nutrition Facts and Blood Sugar Control
With a glycemic index of just 15 and a glycemic load under 2, almonds barely budge blood sugar. This makes them ideal for people with diabetes or anyone watching glucose levels.
But it’s not just the GI number — almonds also deliver magnesium, which improves insulin sensitivity. In fact, people who eat almonds regularly tend to have steadier blood sugar throughout the day, especially when almonds are paired with higher-carb foods.
Practical example: add a handful of chopped almonds to your morning oatmeal, and you’ll notice you stay full longer and avoid the mid-morning crash.
Almond Nutrition Facts and Weight Management
Here’s where almond nutrition gets fascinating. Despite being calorie-dense (~600 kcal per 100 g), almonds actually help with weight management.

Why?
- The protein + fat + fiber trio triggers satiety hormones, making you feel full for hours.
- Not all almond calories are absorbed — some fat remains trapped in the nut’s fibrous walls.
- Regular almond eaters often naturally eat fewer total calories over the course of a day.
A controlled feeding study measured the metabolizable energy of almonds at ~129 kcal per 28 g (≈ 20% below Atwater label values), likely due to fat being trapped in the nut matrix—helping explain real-world satiety vs. calories. (American Journal of Clinical Nutrition)
This means almonds are both a filling snack and a supportive food for weight loss or maintenance. Read more about their weight management impact in our post Almonds for Weight Loss and Belly Fat Reduction: How to Eat, How Many to Eat, When to eat, and Why to Eat.
Almond Nutrition Facts and Bone Health
A look at the micronutrient side of almond nutrition facts reveals calcium, magnesium, and phosphorus — a trio essential for strong bones and teeth.
For people who avoid dairy, almonds become especially important. A daily handful contributes to bone density and may help lower the risk of osteoporosis over time.
Almond Nutrition Facts and Skin Vitality
Traditionally, almonds have been linked to beauty, and modern science backs it up. Their Vitamin E acts as an antioxidant, reducing skin damage from UV rays and pollution.
In one study, women who ate almonds daily showed visible reductions in facial wrinkles and pigmentation compared to those who didn’t. Simply put: almond nutrition supports healthy, youthful skin from the inside out.
Do not miss reading our post – Nuts About Beauty: 5 Benefits of Almonds for Skin Care.
Almond Nutrition Facts and Brain Health
In many Indian households, children are given soaked almonds before school — and for good reason. Almonds contain riboflavin (Vitamin B2) and L-carnitine, nutrients linked with cognitive performance.
Combined with steady glucose release, almonds fuel the brain without the highs and lows caused by sugary snacks. They’re the perfect study or workday snack for sustained focus.
Read our full post about Almonds for Brain, Memory, and Concentration.
Almond Nutrition Facts and Gut Health
Finally, let’s not forget digestion. With 12 g of fiber per 100 g, almonds act as prebiotics, feeding beneficial gut bacteria.
Studies show that almond consumption increases levels of Bifidobacteria and Lactobacillus, both linked to better immunity, digestion, and even mood.
So, a handful of almonds doesn’t just feed you — it nourishes your gut microbiome as well.
Do read: Almonds and Digestion: 5 Ways Eating Almonds Promotes Healthy Digestion
The Big Picture
When you piece it all together, the health benefits of almond nutrition facts are extraordinary:
- They protect your heart.
- They stabilize your blood sugar.
- They help with weight management.
- They strengthen your bones.
- They keep your skin youthful.
- They sharpen your brain.
- They support your gut.
It’s rare for a single food to tick so many boxes, which is why almonds have stood the test of time as both a cultural staple and a modern “superfood.”
Practical Tips for Adding Almonds to Your Diet
Knowing the almond nutrition facts is one thing, but putting them into practice is where the real benefits show up. Since almonds are calorie-dense, the key is enjoying them regularly but mindfully. Here’s how to make almonds part of your daily routine in delicious, sustainable ways.
Portion Control: The “23 Almond Rule”
Nutritionists often recommend 28 grams of almonds per day — about 23 whole almonds. One ounce (≈ 28 g) is about 23 almonds and provides ~165 kcal, ~6 g protein and ~14 g fat—useful for setting daily portions without overdoing calories. (The Nutrition Source, Harvard T.H. Chan School of Public Health)
This serving size provides:
- ~164 calories
- 6 g protein
- 14 g fat (mostly healthy monounsaturated)
- 3.5 g fiber

That’s just enough to deliver the health benefits we’ve discussed without going overboard on calories.
👉 A good trick: pre-portion almonds into small jars or snack bags so you don’t lose track and end up eating half a bag mindlessly.
Raw, Soaked, or Roasted?
The way you eat almonds can change both flavor and digestibility:
- Raw almonds → Crunchy, nutrient-rich, and perfect for quick snacking.
- Soaked almonds → A tradition in India and Ayurveda. Soaking overnight softens the nuts, makes them easier to digest, and may improve nutrient absorption. Many families give soaked almonds to children for memory and focus.
- Dry-roasted almonds → Keep the crunch, but make sure they’re unsalted and oil-free to avoid hidden calories or sodium.
- Flavored almonds → Fun occasionally, but watch out for honey coatings, chili flavorings, or added sugars — they reduce the health edge of plain almonds.
Best Times to Eat Almonds
Almonds are versatile, but timing can make them even more effective:
- Morning kickstart: Eat soaked almonds on an empty stomach for digestion and brain sharpness.
- Mid-morning snack: Stops energy dips and sugar cravings before lunch.
- Pre-workout fuel: Provides steady energy without feeling heavy.
- Evening munchies: A handful of almonds beats chips or cookies any day.
Almonds in Your Meals
They aren’t just a snack — they can transform meals:
- Breakfast: Sprinkle chopped almonds on oatmeal, muesli, or yogurt. Blend them into smoothies for creaminess and protein.
- Lunch: Add roasted almonds to salads, wraps, or grain bowls for extra crunch.
- Snacks: Make homemade trail mix with almonds, walnuts, raisins, and dark chocolate chips.
- Dinner: Use ground almonds instead of breadcrumbs to coat chicken or fish. Add almond slivers to rice or couscous dishes.
- Desserts: Bake with almond flour, or top fruit with almond butter for a nutrient boost.
Almond Milk and Almond Butter
Two modern staples have made almonds even more versatile:
- Almond Milk: A lactose-free, plant-based alternative to dairy milk. Unsweetened almond milk is low-calorie, while fortified versions add calcium and Vitamin D.
- Almond Butter: Creamy, protein-rich, and just as versatile as peanut butter. Spread it on toast, blend into shakes, or use as a dip for apple slices.
Both are excellent ways to enjoy almond nutrition facts if you don’t want to munch on plain nuts every day. Understand more about Almond milk when you read: Is Almond Milk Good for Diabetics? Here’s What the Science Says.
Also learn How to make Almond Milk at Home.
Almonds Across Cultures
Almonds appear in kitchens around the world, showing just how universal their appeal is:
- India: Soaked almonds for kids, almond paste in sweets like badam halwa and kheer.
- Mediterranean: Almonds in sauces like Spain’s romesco or ground into marzipan.
- Middle East: Almonds in pilafs, stews, and baklava.
- Western diets: Almond flour in gluten-free baking, almond milk in lattes, protein bars with almonds.
This global presence proves that almonds adapt to any cuisine — whether savory, sweet, traditional, or modern.
Things to Watch Out For
Even with all their benefits, almonds come with a few caveats:
- Calories add up: Stick to the ~23-almond serving unless you’re very active.
- Nut allergies: Almonds are tree nuts and can trigger severe reactions in sensitive people.
- Storage: Keep almonds in a cool, airtight container. In hot climates, refrigerate to avoid spoilage or aflatoxin (a mold toxin).

Almond Nutrition Facts in Everyday Life
At the end of the day, almonds are more than numbers on a nutrition chart. They’re a food you can enjoy in countless ways — raw, soaked, roasted, as butter or milk, in sweet or savory dishes, across cultures and traditions.
The secret is consistency. A handful a day may not feel like much, but over months and years, the benefits to your heart, blood sugar, bones, skin, and overall health truly add up. Almonds prove that sometimes the smallest daily habits create the biggest long-term results.
A Day with Almonds: Putting Nutrition into Practice
Understanding almond nutrition facts is valuable, but the real magic happens when you bring them into your daily routine. To see just how versatile almonds can be, let’s imagine a simple day powered by these nutrient-packed nuts.
Morning: Soaked Almonds for a Fresh Start
The day begins with a small handful of soaked almonds, peeled and eaten on an empty stomach. In many Indian households, this is a cherished ritual believed to sharpen memory and aid digestion. Science backs it up: soaked almonds are easier on the stomach, and the combination of protein, magnesium, and Vitamin E gives you a gentle but lasting energy boost.
Instead of reaching for a sugary breakfast cereal, this mindful start provides steady fuel and helps prevent mid-morning hunger pangs.
Talking about soaked almonds, do read out detailed post on them here: 10 Benefits of Eating Soaked Almonds Everyday.
Mid-Morning: Almonds in a Smoothie Bowl
A few hours later, it’s time for a smoothie bowl topped with chopped almonds and almond butter. This isn’t just decoration — those almonds add crunch, flavor, and a serious nutritional upgrade. The protein keeps you full, the fiber supports digestion, and the healthy fats prevent the sugar from fruit from spiking your blood sugar.
At this point, you’ve already enjoyed at least half of your recommended daily serving of almonds without even thinking about it.
Lunch: Almonds in a Salad
For lunch, imagine a colorful quinoa salad with roasted vegetables and a sprinkle of slivered almonds. Here, almonds do double duty — they add crunch to every bite and provide healthy fats that help your body absorb fat-soluble vitamins from the vegetables.
This is where almond nutrition facts shine in context: by pairing them with other foods, almonds amplify the benefits of your whole meal.
Afternoon: Almonds as a Smart Snack
The mid-afternoon slump is when most people crave chips or cookies. Instead, a small jar of 23 raw almonds comes to the rescue. This handful provides ~164 calories, 6 grams of protein, and 3.5 grams of fiber.
Instead of a sugar crash, you get sustained energy that carries you to dinner without gnawing hunger.
Dinner: Almond-Crusted Chicken or Veggies
At dinner, almonds can even take center stage. Try using ground almonds as a crust for chicken, tofu, or even roasted cauliflower. It’s a healthier alternative to breadcrumbs, adding crunch along with protein and healthy fats.
Paired with leafy greens and a drizzle of olive oil, this meal brings together the best of Mediterranean nutrition — where almonds have been cherished for centuries.
Evening: A Sweet Almond Finish
Finally, if you’re in the mood for something sweet, a dessert made with almond flour or a simple baked apple topped with warm almond butter is a perfect finish. Unlike refined sweets, this dessert doesn’t wreak havoc on your blood sugar. Instead, it satisfies your sweet tooth while still fitting into a nutrient-rich day.
Final Thoughts: Almond Nutrition Facts in Real Life
By the end of this single day, you’ve seen how easy it is to integrate almonds into meals and snacks without overthinking. From soaked almonds in the morning to almond butter at night, every bite delivers protein, fiber, vitamins, minerals, and those heart-healthy fats.
This is what makes almond nutrition facts so powerful: they’re not just numbers on a chart, they’re tools for building healthier habits. Whether you’re aiming for better heart health, stable blood sugar, glowing skin, or just smarter snacking, almonds can play a role — one handful at a time.
Frequently Asked Questions About Almond Nutrition Facts
1. What are the almond nutrition facts per 100g?
According to almond nutrition facts per 100 g, almonds provide about 575–609 calories, 18–21 g protein, 49–54 g fat, 13–22 g carbohydrates, and 12 g fiber. They are also rich in Vitamin E, magnesium, calcium, and potassium.
2. How many calories are in 100 grams of almonds?
100 g of almonds contains around 575–609 calories. These are nutrient-dense calories, coming mainly from healthy fats and protein.
3. How much protein is in 100 grams of almonds?
The protein in almonds per 100 g is about 18.6–21.2 g. That’s comparable to the protein in three large eggs, making almonds a valuable plant-based protein source.
4. How many carbs are in almonds per 100g?
Almond nutrition facts 100 g show 13–21.7 g of carbohydrates, nearly half of which is fiber. Net digestible carbs are therefore relatively low.
5. How much fat is in almonds per 100g?
Almonds provide 49–54 g of total fat per 100 g, mostly heart-healthy monounsaturated fats (~31 g) and polyunsaturated fats (~12 g). Saturated fat is minimal at 3.7–6.1 g.
6. How much sugar is in almonds per 100g?
Almond nutrition per 100 g includes only 3.9–5 g of natural sugar. Since this sugar is paired with fiber and healthy fats, it has little impact on blood sugar.
7. What is the glycemic index of almonds?
The glycemic index of almonds is about 15, which is considered very low. This means almonds have minimal impact on blood glucose levels.
8. What is the glycemic load of almonds?
The glycemic load (GL) of almonds per 100 g is ~1.9, which is negligible. Even larger servings have almost no effect on blood sugar compared to high-GL foods like rice or bread.
9. What is the almond GI index compared to other nuts?
Almonds have a GI of ~15, similar to walnuts (GI 15) and lower than cashews (GI ~25). This makes them one of the best nuts for stable blood sugar.
10. What is the badam glycemic index?
“Badam” is simply the Hindi word for almonds. The badam glycemic index is the same as almonds — around 15 (very low).
11. What is the glycemic index of almond nuts?
The glycemic index of almond nuts is ~15, and the glycemic load is under 2. Together, these values confirm almonds are blood-sugar friendly.
12. What is the glycemic index of almonds and walnuts?
Both almonds and walnuts score ~15 on the GI scale, placing them among the lowest-GI foods. This makes them excellent for people with diabetes or insulin resistance.
13. How many almonds are in 100 grams?
On average, 100 g of almonds equals 70–80 whole almonds. For daily health, a standard serving is ~28 g (23 almonds).
14. How many calories are in 100 almonds?
Since 100 g (≈ 70–80 almonds) contains ~600 calories, 100 almonds would provide roughly 700–800 calories, depending on size.
15. What is the nutritional value of almonds per 100g?
The nutritional value of almonds per 100 g includes:
- Calories: 575–609
- Protein: 18–21 g
- Fat: 49–54 g
- Carbs: 13–22 g
- Fiber: ~12 g
- Sugar: 4–5 g
Plus minerals like magnesium, calcium, and potassium.
16. How much protein is in badam per 100g?
Badam (almonds) contain 18–21 g of protein per 100 g. This makes them a strong protein source in vegetarian diets.
17. How many carbs are in badam per 100g?
Badam nutrition facts 100 g show about 13–22 g carbs, with ~12 g fiber. This explains why their glycemic index is so low.
18. How much fat is in badam per 100g?
Badam (almonds) contain about 49–54 g of fat per 100 g, most of which are heart-healthy unsaturated fats.
19. How much sugar is in almonds per 100g?
Almonds contain just 4–5 g of naturally occurring sugar per 100 g. Since this is balanced with fiber, it doesn’t cause blood sugar spikes.
20. Why are almond nutrition facts important for health?
Almond nutrition facts per 100 g highlight why almonds are considered a superfood: they deliver protein, fiber, healthy fats, vitamins, minerals, and a very low GI. This combination supports heart health, blood sugar control, weight management, and overall well-being.













