Introduction: Why Scalp Psoriasis vs Seborrheic Dermatitis Causes Confusion
If you’ve ever brushed flakes off your shoulders or scratched an itchy scalp, you may have wondered: Is this seborrheic dermatitis or scalp psoriasis? This is one of the most common scalp-related questions, and with good reason. At first glance, both conditions look similar. They both cause redness, itching, and skin shedding that ends up in your hair and on your clothes. The story changes when you look deeper. Scalp psoriasis vs seborrheic dermatitis is not just a matter of labels — it’s about two very different skin conditions.
Many people confuse scalp issues with other chronic skin conditions. There’s often confusion between eczema, psoriasis, and other forms of dermatitis — see Eczema vs Psoriasis vs Dermatitis for a full breakdown.
Seborrheic dermatitis is usually linked to yeast and excess oil, while psoriasis is driven by an overactive immune system. Because of this, each one responds to very different treatments. If you use antifungal shampoo on scalp psoriasis, it may not help at all. On the other hand, treating seborrheic dermatitis with only anti-inflammatory creams may leave the yeast component untouched. That’s why distinguishing the two is so important.
What This Guide Covers about Scalp Psoriasis vs Seborrheic Dermatitis
In this article, we’ll explore:
- What seborrheic dermatitis is, and how it behaves on the scalp.
- What scalp psoriasis is, and why it develops.
- The key differences between seborrheic dermatitis and psoriasis.
- How dermatologists diagnose them.
- Treatment paths for each condition.
- Lifestyle and self-care tips that make flare-ups easier to manage.
A Human Approach to Scalp Conditions
This isn’t just about medical facts. Your scalp health affects far more than your hair — it influences comfort, confidence, and even daily interactions. If you’ve been cycling through shampoos or searching forums for answers, you deserve clarity.
By the end, you’ll have a clear understanding of the difference between scalp psoriasis and seborrheic dermatitis, and know when it’s time to consult a dermatologist for tailored care.
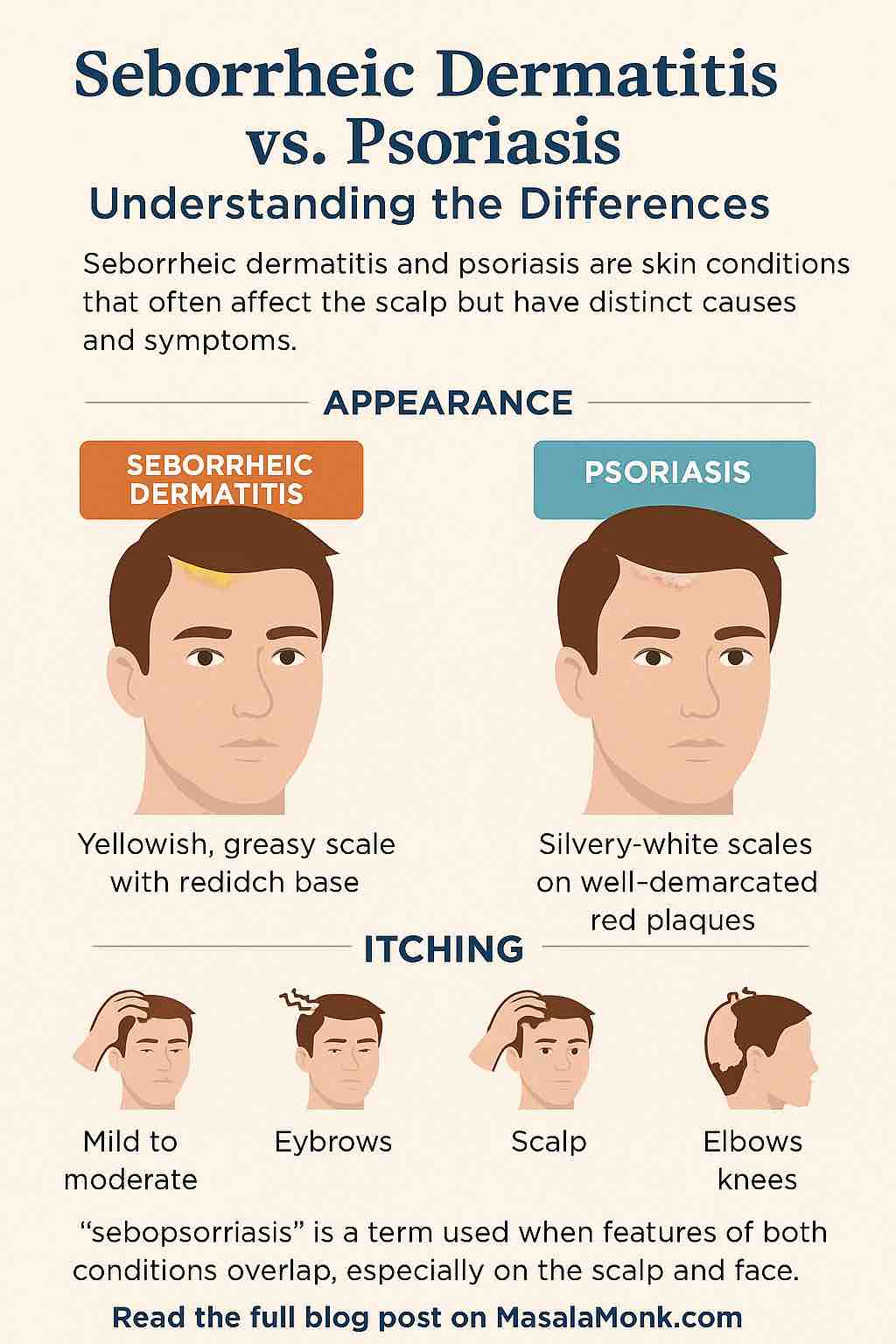
Seborrheic Dermatitis: When Oil and Yeast Cause Scalp Flakes
What Is Seborrheic Dermatitis?
Seborrheic dermatitis is a chronic inflammatory skin condition that often affects the scalp, but it can also appear on areas rich in oil glands such as the face, chest, and back. When it shows up on the scalp, it’s easy to confuse it with psoriasis — which is why so many people search for clarity on seborrheic dermatitis vs psoriasis on the scalp.
In fact, the mildest form of seborrheic dermatitis is simply known as dandruff — a condition often confused with psoriasis. Here’s a helpful guide on What’s the Difference Between Dandruff and Psoriasis? In more persistent cases, it leads to redness, greasy flakes, and uncomfortable irritation.
Causes of Seborrheic Dermatitis
Although the exact cause isn’t fully understood, several factors work together to trigger flare-ups.
Mayo Clinic notes that seborrheic dermatitis may be linked to yeast (Malassezia), excess oil, or immune responses. Verywell Health further highlights that in some people, an abnormal inflammatory response plays a key role.
- Yeast overgrowth: The skin naturally harbors Malassezia yeast, but too much of it irritates the scalp.
- Excess oil production: Extra oil provides the yeast with fuel and contributes to greasy buildup.
- Immune sensitivity: Some people’s skin reacts more strongly to yeast than others.
- Genetics: A family history of seborrheic dermatitis increases risk.
- Environmental triggers: Cold weather, stress, and lack of sleep often worsen symptoms.
This combination of yeast, oil, and sensitivity explains why seborrheic dermatitis is stubborn. It may not vanish overnight, but with consistent management, symptoms can usually be kept under control.

Symptoms of Seborrheic Dermatitis on the Scalp
Seborrheic dermatitis has a very distinct appearance when you look closely:
- Greasy, yellowish flakes that cling to the scalp or hair strands.
- Redness and irritation underneath the flakes.
- Mild to moderate itching, which often becomes worse during stressful periods.
- Seasonal flare-ups, especially in winter when the air is dry.
- Spread to oily facial zones, such as the eyebrows, sides of the nose, or behind the ears.
While it’s not a dangerous condition, seborrheic dermatitis can feel relentless. Many people describe the cycle of flakes returning no matter how often they wash their hair, which can be both frustrating and discouraging.
Living With Seborrheic Dermatitis
The impact of seborrheic dermatitis goes far beyond physical irritation. Constant flakes on clothing, visible redness along the hairline, and the persistent feeling of an “unclean” scalp can chip away at self-confidence. It’s important to remember, though, that this condition has nothing to do with hygiene. Seborrheic dermatitis is not caused by being “dirty” — it is a skin imbalance, and it can affect anyone.
Now that we’ve taken a closer look at seborrheic dermatitis, it’s time to turn to the other half of the picture: scalp psoriasis.
Scalp Psoriasis: When the Immune System Targets the Skin
What Is Scalp Psoriasis?
Psoriasis is very different from seborrheic dermatitis. Instead of being driven by yeast and oil, it is a chronic autoimmune condition. In scalp psoriasis, the immune system mistakenly speeds up the life cycle of skin cells, causing them to pile up far too quickly. This buildup creates the thickened, scaly patches known as plaques.
While psoriasis can appear anywhere on the body, the scalp is one of the most common sites. In fact, studies show that up to 80 percent of people with psoriasis will experience scalp involvement at some point in their lives. This makes the question of scalp psoriasis vs seborrheic dermatitis especially important, since the two can look deceptively alike in this area.
Why Does Scalp Psoriasis Happen?
The exact cause of psoriasis is still being studied, but experts agree it results from a combination of genetics, immune system overactivity, and environmental triggers. For scalp psoriasis specifically, the following are common contributors:
- Immune dysfunction: The immune system sends faulty signals, telling skin cells to grow and shed too quickly.
- Genetics: Having a close relative with psoriasis increases your risk.
- Stress: Emotional stress is a frequent trigger for scalp flares.
- Infections: Strep throat and other illnesses can spark new episodes.
- Skin injury: Even a small scratch or tight hairstyle can lead to plaques (a phenomenon called the Koebner response).
- Medications: Certain drugs, like beta blockers or lithium, can make psoriasis worse.
These factors don’t affect everyone in the same way, which is why psoriasis behaves differently from person to person.

Symptoms of Scalp Psoriasis
The symptoms of scalp psoriasis can range from mild to very severe. They often include:
- Thick, silvery-white scales that build up on top of red, inflamed plaques.
- Sharp, well-defined borders between affected skin and surrounding healthy areas.
- Itching and burning that can be intense, sometimes even painful.
- Extension beyond the hairline, with plaques spreading to the forehead, back of the neck, or around the ears.
- Nail changes, such as pitting, ridging, or discoloration — which Mayo Clinic explains are often strong clues pointing to psoriasis rather than seborrheic dermatitis.
- Joint pain or stiffness, which may signal psoriatic arthritis.
Unlike seborrheic dermatitis, which tends to create oily flakes that brush away more easily, psoriasis produces stubborn, thick scales that often cling tightly to the scalp. Removing them forcefully can cause bleeding or worsen irritation.
The Emotional Side of Scalp Psoriasis
Beyond physical discomfort, scalp psoriasis often has a heavy emotional burden. The plaques are highly visible, especially when they extend beyond the hairline, and the constant itching can interfere with sleep and concentration. Many people feel self-conscious about flakes on dark clothing or about others assuming they have “contagious dandruff.”
It’s worth repeating that psoriasis is not contagious. It is an immune-mediated condition, not an infection. Still, the stigma can be tough, and finding effective treatment makes a real difference not just for the skin but also for overall well-being.
Having explored the immune-driven nature of scalp psoriasis, it’s easier to see why it can look similar to — but behave very differently from — seborrheic dermatitis. That’s where a direct comparison helps.
Scalp Psoriasis vs Seborrheic Dermatitis: Key Differences
When you’re dealing with flakes, redness, and itching, it can feel almost impossible to tell which condition you’re experiencing. That’s why the question of scalp psoriasis vs seborrheic dermatitis comes up so often. Although they share some similarities, the differences are clearer once you break them down.
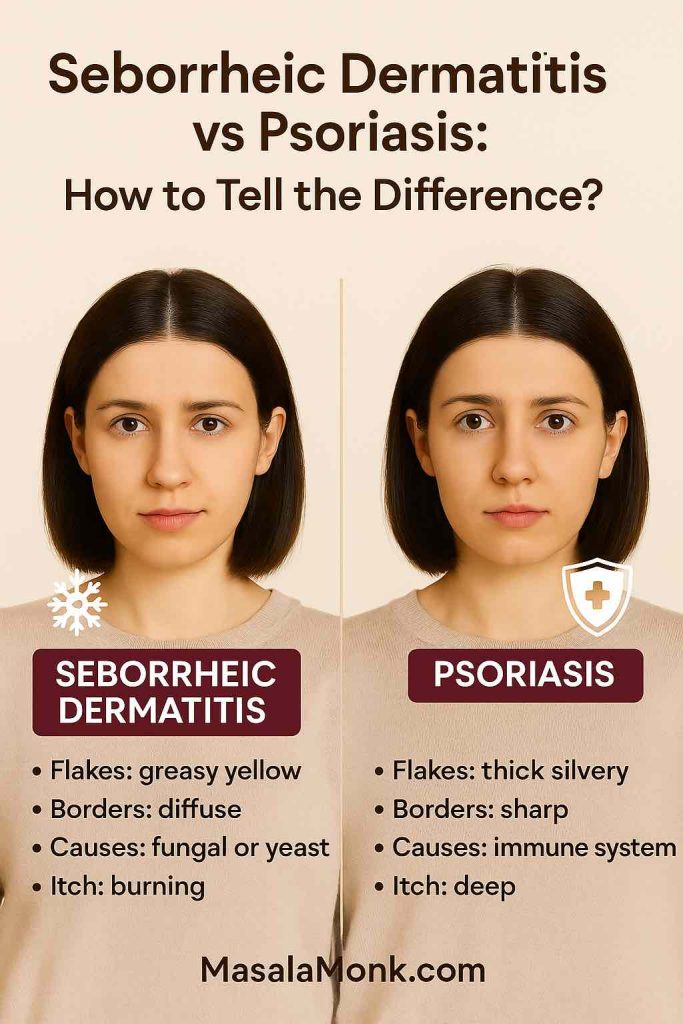
Quick Comparison: Seborrheic Dermatitis vs Psoriasis on the Scalp
| Feature | Seborrheic Dermatitis | Scalp Psoriasis |
|---|---|---|
| Scale Type | Greasy, yellowish, soft flakes | Dry, silvery, thick buildup |
| Redness | Mild to moderate, diffuse | Deep red, more inflamed |
| Edges | Ill-defined, patchy | Sharp, well-demarcated |
| Itching | Mild to moderate | Often moderate to severe |
| Common Sites | Scalp, eyebrows, sides of nose, behind ears | Scalp, elbows, knees, lower back, nails |
| Other Signs | Oily skin, dandruff | Nail pitting, possible joint pain |
What the Flakes Look Like
The texture and color of the scales are often the biggest clues. Seborrheic dermatitis produces flakes that are greasy and yellowish. They may feel soft and waxy to the touch and can sometimes stick to the hair. Psoriasis, on the other hand, creates dry, silvery scales that build up in layers. They feel thicker, drier, and more stubborn to remove. Medical News Today notes that psoriasis scales often look powdery and silver, whereas seborrheic dermatitis tends to appear yellow and greasy.
How the Redness Appears
Another difference is in the skin underneath. With seborrheic dermatitis, the redness tends to be mild to moderate and often looks patchy. In scalp psoriasis, the base skin is usually bright red and inflamed, making the contrast with the silvery scale even more pronounced.
Edges and Borders
Seborrheic dermatitis blends into the surrounding skin with fuzzy, ill-defined edges. Psoriasis almost always has sharp borders, where you can clearly see where the plaque begins and ends. This feature often helps dermatologists distinguish the two conditions at a glance.
The Itch Factor
Both conditions itch, but the intensity can vary. Seborrheic dermatitis usually causes mild to moderate itching, while psoriasis often produces intense itching or burning, sometimes severe enough to interfere with sleep.
Where Else It Shows Up
Seborrheic dermatitis prefers oily areas: the scalp, eyebrows, sides of the nose, beard area, and behind the ears. Psoriasis, by contrast, frequently affects the elbows, knees, lower back, and nails. If you notice thick plaques outside the scalp — or nail changes like pitting — psoriasis is far more likely.
Putting It Together
The tricky part is that both conditions can appear on the scalp at the same time, and their symptoms sometimes overlap. Still, by paying attention to the scale type, redness, and pattern, you can often get a good sense of which condition you may be dealing with.
Up next, we’ll look at what happens when the two overlap — a condition dermatologists call sebopsoriasis.
Sebopsoriasis: When Scalp Psoriasis and Seborrheic Dermatitis Overlap
Sometimes the question of scalp psoriasis vs seborrheic dermatitis doesn’t have a simple answer. That’s because some people experience a combination of both conditions at once. Dermatologists call this overlap sebopsoriasis.
What Is Sebopsoriasis?
Sebopsoriasis is a term used when the scalp (and sometimes the face) shows features of both seborrheic dermatitis and psoriasis. For example, the flakes may look greasy and yellowish like seborrheic dermatitis, but the plaques may also be thicker, sharper, and more inflamed like psoriasis.
It is not an entirely separate disease, but rather a description doctors use when the skin doesn’t fit neatly into one category.
Why Does Sebopsoriasis Happen?
Sebopsoriasis usually appears in people who have an underlying tendency toward psoriasis but also react strongly to yeast or oil imbalances on the skin. In other words, both mechanisms are active at the same time:
- Yeast and oil triggers create seborrheic-type irritation.
- Immune overactivity drives psoriatic scaling.
This explains why sebopsoriasis is often most visible on the scalp and face, where both conditions naturally thrive.
Symptoms of Sebopsoriasis
Because it’s a blend, sebopsoriasis can be confusing to recognize. Common signs include:
- Flakes that are greasy but also thick or silvery.
- Red patches that have both diffuse and well-defined edges.
- Itching that feels worse than typical dandruff but not always as severe as full psoriasis.
- Flare-ups that respond partially to dandruff shampoos but not fully.
How Sebopsoriasis Is Treated
Since sebopsoriasis has elements of both conditions, treatment often needs to combine approaches:
- Antifungal shampoos or creams help reduce yeast on the scalp.
- Topical corticosteroids or vitamin D analogues calm psoriatic inflammation.
- Coal tar or salicylic acid products can reduce scaling and soften buildup.
- Lifestyle support — reducing stress, sleeping well, and avoiding overly harsh products — helps minimize flare-ups.
Dermatologists may adjust treatments depending on which aspect (seborrheic vs psoriatic) seems more dominant at the time.
Why a Diagnosis Matters
For people who live with sebopsoriasis, self-diagnosis can be particularly tricky. One week the condition may look like seborrheic dermatitis, and the next week it may resemble psoriasis. Having a dermatologist’s guidance ensures you’re not chasing ineffective treatments or missing an underlying autoimmune component.
Although sebopsoriasis can feel frustrating, knowing it exists often brings relief. It helps explain why standard dandruff shampoos may only partly help, and why stronger psoriasis medications may also be needed.
Next, let’s look at how dermatologists distinguish between scalp psoriasis vs seborrheic dermatitis, especially in cases that aren’t straightforward.
How Dermatologists Diagnose Scalp Psoriasis vs Seborrheic Dermatitis
When flakes and redness on the scalp just won’t go away, the next step is often seeing a dermatologist. Because the signs of both conditions overlap, many people understandably wonder: How do dermatologists tell the difference between scalp psoriasis vs seborrheic dermatitis?
Clinical Examination
The first step is a detailed scalp examination. Dermatologists look at:
- Scale texture: greasy and yellow (seborrheic dermatitis) vs dry and silvery (psoriasis).
- Edges: fuzzy and diffuse (seborrheic) vs sharply defined (psoriasis).
- Redness: mild irritation vs deeper, more inflamed plaques.
By comparing these clues, dermatologists often spot the dominant condition fairly quickly.

Looking Beyond the Scalp
Another important part of diagnosis is checking other areas of the body. Psoriasis has certain “tell-tale” locations, such as the elbows, knees, and lower back. Nail changes — like pitting, ridging, or thickening — are also strongly associated with psoriasis.
Seborrheic dermatitis, by contrast, is more likely to appear on oily areas: the eyebrows, sides of the nose, beard, or chest. If these zones are affected with greasy scales, it leans more toward seborrheic dermatitis.
Medical History and Triggers
A dermatologist also considers your medical history:
- Family history of psoriasis is a strong clue.
- Stress, weather changes, or immune conditions may point toward psoriasis flare-ups.
- Flare-ups in winter or with excess oil production may favor seborrheic dermatitis.
These patterns often guide diagnosis, especially when the scalp appearance is ambiguous.
Response to Treatment
Sometimes the fastest way to confirm is to try treatment and observe the response. For instance:
- If antifungal shampoos (like ketoconazole) reduce symptoms significantly, seborrheic dermatitis is likely.
- If steroid lotions, vitamin D creams, or biologics help more, psoriasis may be the main driver.
Of course, dermatologists never want to delay relief, so treatment often begins alongside diagnosis.
Skin Biopsy (Rarely Needed)
In uncertain cases, a dermatologist may recommend a skin biopsy. This involves taking a very small sample of skin and analyzing it under a microscope. While not common, it provides a definitive answer if the condition refuses to declare itself clearly.

Why Getting the Right Diagnosis Matters
Understanding whether you have scalp psoriasis, seborrheic dermatitis, or both isn’t just a technical distinction. It directly affects:
- Which shampoos or medications will work best.
- How aggressively treatment should be pursued.
- What long-term monitoring may be necessary, especially since psoriasis can be linked to arthritis and other systemic issues.
In short, diagnosis is about more than naming the condition. It’s about giving you a clear path forward so that the endless cycle of flakes and discomfort doesn’t control your daily life.
Up next, we’ll dive into the heart of the matter: the different treatment approaches for scalp psoriasis vs seborrheic dermatitis, including over-the-counter remedies, prescription options, and lifestyle support.
Treatment for Scalp Psoriasis vs Seborrheic Dermatitis
When it comes to managing scalp psoriasis vs seborrheic dermatitis, the goal is always the same: reduce itching, control flakes, calm redness, and prevent flare-ups. But the way you get there depends on which condition you’re dealing with. Let’s break down the most effective treatment options.
Over-the-Counter (OTC) Treatments
For both conditions, many people start with non-prescription products. These are widely available and often bring noticeable relief.
Medicated Shampoos
- For seborrheic dermatitis: Shampoos with ketoconazole, selenium sulfide, or zinc pyrithione help control yeast overgrowth. They target one of the root causes and often reduce both flakes and redness. See this breakdown on Nizoral, T/Gel, and Selsun Blue for how different shampoos compare for dandruff and psoriasis.
- For scalp psoriasis: Shampoos with coal tar or salicylic acid soften thick scales and slow down the rapid turnover of skin cells.
Because the two conditions respond differently, trying one type of shampoo and observing the effect can provide important diagnostic clues.
Coal Tar Products
Coal tar is an age-old remedy that works especially well for psoriasis. It slows skin growth and reduces scaling. While it can also help seborrheic dermatitis, its effect is usually stronger for psoriasis plaques.
Salicylic Acid
This ingredient acts as a keratolytic, meaning it breaks down thick scale buildup. It’s very effective in scalp psoriasis, where plaques are stubborn. In seborrheic dermatitis, it can help loosen greasy flakes but usually works best when combined with antifungal agents.

Prescription Treatments
If OTC options aren’t enough, dermatologists may recommend prescription medications tailored to whether psoriasis or seborrheic dermatitis is the main culprit.
Topical Corticosteroids
These are often the first line for scalp psoriasis, as they reduce inflammation and redness quickly. They may also be prescribed for seborrheic dermatitis during flares, though usually for shorter periods. Healthline explains that treatments for psoriasis may also include light therapy or prescription vitamin D analogues to slow skin cell growth.
Vitamin D Analogues
Medications like calcipotriol (calcipotriene) work specifically on psoriasis by slowing skin cell growth and reducing scale thickness. These aren’t typically used for seborrheic dermatitis.
Antifungal Creams and Shampoos
For seborrheic dermatitis, prescription-strength antifungal creams or shampoos can make a huge difference. They directly target Malassezia, the yeast that fuels the condition.
Combination Therapy
Sometimes dermatologists prescribe treatments that combine antifungals and mild steroids for seborrheic dermatitis — helpful when inflammation is strong. In psoriasis, combinations of steroids plus vitamin D analogues are common.
Systemic Medications and Biologics
For moderate-to-severe scalp psoriasis, oral or injectable medications may be necessary. Biologics, such as adalimumab or secukinumab, work by calming the immune system. These are not used for seborrheic dermatitis, which is typically localized and less severe.
Wikipedia notes that while there is no cure for psoriasis, biologics can target specific immune pathways — and up to 30% of people with psoriasis may also develop psoriatic arthritis.
Natural and Home Remedies
Some people prefer to start with gentle, natural approaches, or use them alongside medical treatments. While these aren’t cures, they can help reduce irritation and improve comfort.
- Aloe vera gel: Soothes redness and itching.
- Coconut oil or olive oil: Softens scales so they can be washed out more easily. Read more about Coconut Oil for Psoriasis and Olive Oil and Psoriasis.
- Apple cider vinegar (diluted): Sometimes used for its antifungal properties in seborrheic dermatitis, though it should be applied carefully to avoid irritation. Here you might want to read Apple Cider Vinegar for Hair, Dandruff, and Scalp.
- Oatmeal soaks or shampoos: Calm itchiness and reduce irritation.
It’s important to note that natural remedies may help seborrheic dermatitis more consistently than psoriasis, but some people with psoriasis also find relief.
Lifestyle Support and Daily Habits
Treatment isn’t just about products. Daily habits can strongly influence flare-ups of both scalp psoriasis and seborrheic dermatitis.

Small lifestyle changes can make a BIG difference.
Here are 5 self-care tips to soothe your scalp and improve daily comfort. 💆♀️
MasalaMonk.com
Stress Management
Stress is a major trigger for both conditions. Incorporating stress-reducing practices such as meditation, gentle exercise, or journaling can help reduce flare frequency.
Scalp Care Routine
- Wash hair regularly with a gentle shampoo between medicated treatments.
- Avoid scratching or forcefully removing scales, which can worsen irritation.
- Use lukewarm water — hot water strips oils and aggravates symptoms.
Some people also explore essential oils — for example, diluted Tea Tree Oil for Scalp Eczema and Psoriasis has antifungal and soothing properties.
Diet and Overall Health
While no strict “psoriasis diet” or “seborrheic dermatitis diet” is universally proven, many people notice improvements by reducing:
- Alcohol, processed foods, and excess sugar (common psoriasis triggers).
- Very oily or greasy foods (sometimes linked with seborrheic dermatitis flare-ups).
A balanced diet rich in anti-inflammatory foods — vegetables, fruits, whole grains, and omega-3 fatty acids — supports skin health in general.
When to Seek Professional Help
If you’ve tried OTC shampoos and home remedies without success, or if your condition is severe, it’s important to consult a dermatologist. Here’s when you should definitely seek help:
- Symptoms are spreading beyond the scalp.
- You notice nail changes (possible psoriasis).
- OTC treatments only bring partial relief.
- Itching or pain interferes with sleep or daily life.
- You’re unsure whether it’s seborrheic dermatitis, scalp psoriasis, or both.
A professional diagnosis ensures you’re not wasting time — or worsening the condition — with the wrong approach.
Key Takeaway on Treatment
The bottom line is that while treatments for scalp psoriasis vs seborrheic dermatitis may overlap, the root causes are different. Psoriasis requires calming the immune system and slowing cell turnover. Seborrheic dermatitis requires reducing yeast and oil imbalances. Sometimes both need to be addressed together.
The best plan is usually a layered approach: start with OTC products, add prescription options if needed, and support everything with healthy daily habits.
Living With Scalp Psoriasis vs Seborrheic Dermatitis
Managing scalp psoriasis vs seborrheic dermatitis isn’t just about creams and shampoos. It’s also about learning how to live with a condition that may never fully go away. Both are chronic and tend to wax and wane. That means you’ll likely have periods where your scalp feels clear and comfortable, followed by flare-ups that test your patience. Knowing how to navigate this cycle — emotionally and practically — makes all the difference.
The Emotional Impact of Visible Scalp Conditions
Scalp issues aren’t always hidden by hair. Flakes can land on clothing, plaques may extend beyond the hairline, and itching can be obvious during social interactions. For many people, this creates:
- Embarrassment or self-consciousness in public or professional settings.
- Frustration when treatments only partly work.
- Anxiety about flare-ups appearing before important events.
- Isolation from avoiding situations like dark clothing, crowded places, or intimate relationships.
It’s important to acknowledge these feelings. You’re not alone — millions live with these conditions, and dermatologists are increasingly aware of the mental health burden.
Building Confidence Despite Symptoms
While you can’t always control when a flare-up strikes, there are ways to protect your confidence:
- Choose clothing strategically: lighter fabrics or patterned shirts camouflage flakes better than dark solids.
- Use styling tricks: looser hairstyles or hats can cover plaques near the hairline during severe flares.
- Be proactive: having a go-to shampoo or topical on hand helps you feel prepared rather than caught off guard.
- Practice self-kindness: remember that neither psoriasis nor seborrheic dermatitis is a reflection of hygiene — they are medical conditions.
The Cleveland Clinic emphasizes that it isn’t contagious, often comes and goes throughout life, and is generally well managed with medicated shampoos and creams.
Coping With Chronicity
Because both conditions are chronic, managing expectations is key. You may not always achieve perfect clearance, but you can often keep symptoms well under control.
Think of it as maintenance, not a cure:
- For seborrheic dermatitis, that often means sticking with antifungal shampoos once or twice a week even when the scalp looks clear.
- For psoriasis, it may mean cycling treatments to avoid tolerance or side effects while still preventing major flares.
The Role of Support Systems
Living with a visible skin condition is easier when you don’t do it alone. Support can come from different places:
- Dermatologists who take time to listen and adjust treatment.
- Support groups or online communities, where you’ll find others navigating the same frustrations.
- Friends and family who understand it’s not “just dandruff” but a real health issue.
Sometimes even talking about it openly helps reduce shame and clears up misconceptions.
Long-Term Outlook
- Seborrheic dermatitis: often lifelong but generally mild and controllable with the right routine. Symptoms usually improve with consistent antifungal use and tend to calm with age.
- Scalp psoriasis: more unpredictable. Some people have only mild patches for years, while others experience frequent severe flares. Because it’s part of a systemic condition, it can sometimes be linked to psoriatic arthritis or other immune-related issues. Early diagnosis and consistent management improve the outlook dramatically.
Lifestyle Integration
Ultimately, both conditions become part of your life rhythm. With time, many people learn to anticipate triggers, recognize early signs of flares, and adapt routines. What once felt overwhelming can become manageable — and even routine.
Living with scalp psoriasis vs seborrheic dermatitis doesn’t mean resigning yourself to discomfort. It means developing a toolkit of strategies — medical, practical, and emotional — that allow you to stay in control, rather than letting the condition control you.
Key Takeaway on Daily Life
Both conditions affect far more than just the skin. They touch confidence, daily choices, and long-term well-being. The good news? With consistent care, the right support, and patience, it is possible to live fully and confidently, even when flakes or plaques occasionally return.
When to See a Dermatologist for Scalp Psoriasis vs Seborrheic Dermatitis
While many people can manage mild scalp psoriasis vs seborrheic dermatitis with home care and over-the-counter products, there are times when it’s best to bring in a dermatologist. A professional can confirm the diagnosis, rule out other scalp conditions, and create a personalized treatment plan.

Here’s a simple recap to help you remember the key differences.
But remember — only a dermatologist can confirm your condition. 🩺
MasalaMonk.com
Signs You Should See a Dermatologist
- Persistent Symptoms: If flakes, redness, or itching continue despite weeks of treatment with medicated shampoos.
- Severe Discomfort: When itching or burning interferes with sleep, concentration, or daily activities.
- Uncertainty: If you can’t tell whether it’s seborrheic dermatitis, psoriasis, or another condition entirely.
- Spreading or Worsening: When plaques extend beyond the scalp to the forehead, ears, or body.
- Nail or Joint Changes: Thickened nails or joint stiffness may indicate psoriatic arthritis, which requires early treatment.
- Emotional Impact: If the condition significantly affects your self-esteem or quality of life.
What to Expect at an Appointment
Dermatologists will usually:
- Examine the scalp closely and may use a dermatoscope for detail.
- Ask about your medical history, stress levels, and family history.
- Sometimes take a small skin sample (biopsy) if the diagnosis isn’t clear.
- Recommend treatments such as prescription shampoos, topical medications, or — in the case of psoriasis — systemic options like biologics.
Importantly, they’ll help you develop a realistic, long-term plan rather than just a quick fix.
Final Thoughts: Taking Charge of Your Scalp Health
At first glance, scalp psoriasis vs seborrheic dermatitis may seem frustratingly similar. Both can cause flakes, redness, and itching, but their root causes, long-term outlooks, and treatment strategies are not the same.
- Seborrheic dermatitis is often driven by yeast and oil imbalances and responds best to antifungal and anti-inflammatory care.
- Scalp psoriasis stems from immune system overactivity and requires treatments that slow skin growth and calm inflammation.
The good news? Both conditions are manageable, and you don’t have to live in constant discomfort. With the right combination of treatments, lifestyle adjustments, and professional guidance, you can minimize flares and restore confidence.
Conclusion: Scalp Psoriasis vs Seborrheic Dermatitis
Understanding the differences between scalp psoriasis vs seborrheic dermatitis is the first step toward effective management. While they share similar symptoms, the underlying causes — and therefore the treatments — are different.
- Focus on symptom control with shampoos and topical care.
- Support your scalp with healthy habits and stress management.
- Seek medical guidance when symptoms are stubborn or life-impacting.
Living with a chronic scalp condition isn’t always easy, but it’s absolutely possible to live comfortably and confidently with the right support. Remember: clearer days for your scalp are ahead.
📖 Further Reading & Resources
If you’d like to learn more about related scalp and skin health topics, here are some helpful guides on MasalaMonk:
- What’s the Difference Between Dandruff and Psoriasis? – A detailed comparison between common dandruff (mild seborrheic dermatitis) and psoriasis, including key visual differences.
- Eczema vs Psoriasis vs Dermatitis – Explains how these conditions overlap and what makes them unique.
- Nizoral, T/Gel, Selsun Blue: Battling Psoriasis and Dandruff – A shampoo comparison to help you choose the right OTC product.
- Tea Tree Oil for Scalp Eczema and Psoriasis – Natural antifungal and soothing properties explained.
- Apple Cider Vinegar for Hair, Dandruff, and Scalp – Insights into ACV as a natural remedy for yeast-related flakes.
- Coconut Oil for Psoriasis, Olive Oil and Psoriasis, and Castor Oil for Psoriasis – Oils that nourish the scalp, soften plaques, and reduce irritation.
- Harnessing the Healing Power of Turmeric for Psoriasis – The role of turmeric’s anti-inflammatory compounds in skin care.
- Shea Butter for Scalp Psoriasis – Natural moisturization and flare-up relief for dry, irritated scalps.
These resources expand on treatment options, natural remedies, and comparisons, helping you build a well-rounded understanding of scalp health.
📚 References & Reading
If you’d like to explore more or see what the experts say, here are some trusted resources that guided this article:
- Mayo Clinic – Seborrheic Dermatitis – A clear explanation of seborrheic dermatitis, its causes, and common triggers.
- Verywell Health – Seborrheic Dermatitis Causes – A deeper look at inflammation, genetics, and lifestyle factors that may play a role.
- Mayo Clinic – Scalp Psoriasis FAQ – Helpful details about scalp psoriasis symptoms, including nail changes and common sites.
- Medical News Today – Psoriasis vs Seborrheic Dermatitis – A practical comparison of how the two conditions look and feel.
- Healthline – Psoriasis vs Seborrheic Dermatitis – Covers treatments, from shampoos to prescription therapies.
- Cleveland Clinic – Seborrheic Dermatitis – Highlights why the condition isn’t contagious and how it can be managed long-term.
- Wikipedia – Psoriasis – A broad overview of psoriasis, systemic treatments, and links to psoriatic arthritis.
👉 By linking to these expert-backed sources, you not only get clarity but also reassurance that what you’re experiencing is real, common, and manageable. If you’re still unsure about your own symptoms, remember — the best step is always a personalized chat with a dermatologist.
Here are answers to the most common questions people ask about scalp psoriasis vs seborrheic dermatitis — based on real search queries and expert guidance.
✅ FAQs: Scalp Psoriasis vs Seborrheic Dermatitis
1. What is the difference between scalp psoriasis and seborrheic dermatitis?
The main difference is in the cause and scale appearance. Scalp psoriasis is an autoimmune condition that speeds up skin cell turnover, creating thick, silvery plaques with sharp borders. Seborrheic dermatitis, on the other hand, is linked to yeast overgrowth and excess oil, causing greasy, yellowish flakes with ill-defined edges.
2. How do I know if I have scalp psoriasis vs seborrheic dermatitis?
Look at the flakes and borders. If the scales are thick, dry, silvery-white, and plaques extend beyond the hairline (often with nail changes), psoriasis is more likely. If flakes are greasy, yellow, and soft, affecting oily areas like eyebrows or behind the ears, seborrheic dermatitis is the more probable culprit.
3. Can you have both seborrheic dermatitis and scalp psoriasis at the same time?
Yes. This overlap is called sebopsoriasis. It shows features of both conditions — greasy flakes plus thick plaques. Because it doesn’t fit neatly into one category, dermatologists often recommend a combined treatment approach (antifungal shampoos + anti-inflammatory creams).
4. Is seborrheic dermatitis the same as psoriasis?
No, they are different conditions. Seborrheic dermatitis is a chronic inflammatory reaction to yeast and oil, while psoriasis is an autoimmune disease. They can look similar on the scalp, but their causes, triggers, and treatments differ.
5. Which itches more: scalp psoriasis or seborrheic dermatitis?
Both can cause itching, but scalp psoriasis often causes more intense itching and burning, sometimes severe enough to disturb sleep. Seborrheic dermatitis usually causes mild to moderate itchiness that worsens with stress or cold weather.
6. Can seborrheic dermatitis turn into psoriasis?
No. One does not “turn into” the other. However, because symptoms overlap, people may be misdiagnosed at first. It’s also possible to have both conditions (sebopsoriasis), which can make diagnosis tricky.
7. What is the best treatment for scalp psoriasis vs seborrheic dermatitis?
- Seborrheic Dermatitis: responds best to antifungal shampoos (ketoconazole, selenium sulfide, zinc pyrithione) and anti-inflammatory creams.
- Scalp Psoriasis: improves with coal tar, salicylic acid, topical corticosteroids, vitamin D analogues, or biologics in severe cases.
Because the treatments are different, getting the right diagnosis matters.
8. Can seborrheic dermatitis or scalp psoriasis go away on their own?
Both are chronic conditions. Seborrheic dermatitis tends to flare and calm over time, often improving with age. Scalp psoriasis is usually more persistent and may require ongoing treatment to prevent flares. Neither is contagious.
9. Where else do these conditions appear besides the scalp?
- Seborrheic Dermatitis: eyebrows, sides of nose, behind ears, chest, beard area.
- Psoriasis: elbows, knees, lower back, nails, and sometimes joints (psoriatic arthritis).
If you notice joint pain or nail pitting, it’s more likely psoriasis.
10. When should I see a dermatologist for scalp psoriasis vs seborrheic dermatitis?
Seek medical advice if:
- OTC shampoos haven’t helped after several weeks,
- The condition spreads beyond your scalp,
- You notice nail changes or joint pain,
- Itching or pain interferes with sleep or daily life.
A dermatologist can confirm the diagnosis and tailor treatment to your specific condition.









