
Trauma leaves deep imprints—not just in the mind but also in the body. For many living with Post-Traumatic Stress Disorder (PTSD), traditional treatments like therapy and medication are helpful but not always sufficient. Increasingly, research is pointing toward mind-body practices—especially yoga—as a gentle, complementary tool for trauma recovery.
In this post, we’ll take a detailed, practical look at how yoga can support PTSD healing, backed by science and informed by trauma-sensitive practices.
Why Yoga for PTSD?
PTSD affects how the brain and nervous system respond to perceived threats, even long after the traumatic event. Common symptoms include:
- Hyperarousal (constant alertness)
- Intrusive memories or flashbacks
- Emotional numbness or detachment
- Anxiety and depression
- Sleep disturbances
- Somatic symptoms (muscle tension, chronic pain, digestive issues)
Yoga can help address these symptoms on multiple levels:
- Physical regulation: calming the hyperactive stress response
- Emotional awareness: safely experiencing and processing feelings
- Mind-body reconnection: rebuilding trust in one’s own body
- Self-empowerment: regaining a sense of agency through mindful movement
What Does the Research Say?
Evidence Summary
Multiple studies and meta-analyses support yoga’s positive role in managing PTSD symptoms:
- A 2024 meta-analysis found yoga reduced PTSD and depressive symptoms with large effect sizes and minimal adverse effects.
- Trauma-Sensitive Yoga (TSY), developed at the Trauma Center in Brookline, MA, has shown promise in improving self-regulation and emotional resilience.
- A large clinical trial with veterans demonstrated significant PTSD symptom reduction with regular yoga practice.
- Yoga appears to help by modulating the autonomic nervous system, increasing parasympathetic tone (rest-and-digest state), and decreasing cortisol levels.
While more high-quality research is still needed, especially with diverse populations, the overall trend is very encouraging.
How Yoga Helps Heal Trauma
Yoga uniquely addresses PTSD by working directly with the nervous system and body awareness:
1️⃣ Regulation of the Stress Response
PTSD often involves chronic overactivation of the sympathetic nervous system (fight-flight-freeze). Yoga helps shift the nervous system into parasympathetic dominance (rest-digest-heal).
- Breathwork (Pranayama)
- Gentle, rhythmic movement
- Restorative poses
2️⃣ Interoception and Body Awareness
Trauma survivors often feel disconnected from their bodies. Yoga fosters safe, mindful reconnection:
- Observing sensations without judgment
- Recognizing tension or dysregulation early
- Learning how to release or soothe bodily discomfort
3️⃣ Emotional Resilience and Self-Regulation
By gently exposing the practitioner to present-moment experience, yoga can help build tolerance for emotional fluctuations without overwhelm.
- Mindful presence
- Grounding techniques
- Gradual exposure to sensations
Trauma-Sensitive Yoga: The Safest Approach
Not all yoga is equally safe for individuals with PTSD. Certain elements of traditional classes may unintentionally trigger distress.
Trauma-Sensitive Yoga (TSY) is specifically designed to create a safe and supportive space:
| Traditional Yoga | Trauma-Sensitive Yoga |
|---|---|
| Instructor-centered | Student-centered, invitational language |
| Hands-on adjustments | No physical touch without explicit consent |
| Closed eyes in poses | Choice to keep eyes open |
| Competitive or strenuous | Gentle, supportive, non-competitive |
| Fast-paced transitions | Slow, predictable pacing |
| Emphasis on alignment | Emphasis on choice and interoception |
Practical Guide: Safe and Gentle Yoga Practices for PTSD
Here’s a highly practical, step-by-step approach for anyone looking to integrate yoga into PTSD healing:
A. Breathwork (Pranayama)
Start here: Breath is the most accessible tool for regulating the nervous system.
- 3-Part Breath (Dirga Pranayama):
Inhale into belly → ribcage → upper chest; exhale slowly. - Extended Exhale:
Inhale for 4 counts, exhale for 6-8 counts. - Alternate Nostril Breathing (Nadi Shodhana):
Calms the mind, balances hemispheres.
Caution: Avoid breath-holding or forceful breathing if it feels destabilizing.
B. Gentle Movement
Purpose: Release physical tension without overwhelming the system.
Recommended Poses:
| Pose | Benefit |
|---|---|
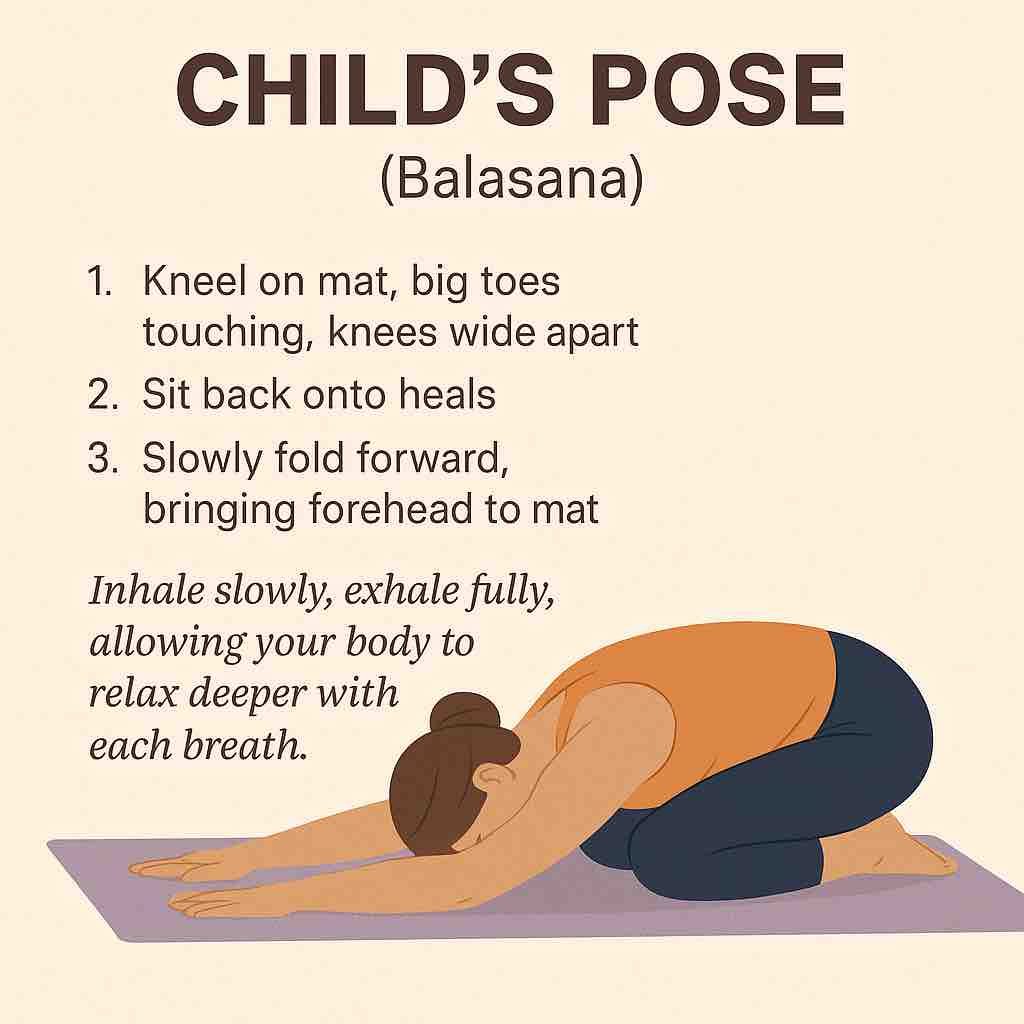
| Child’s Pose (Balasana) | Grounding, calming |
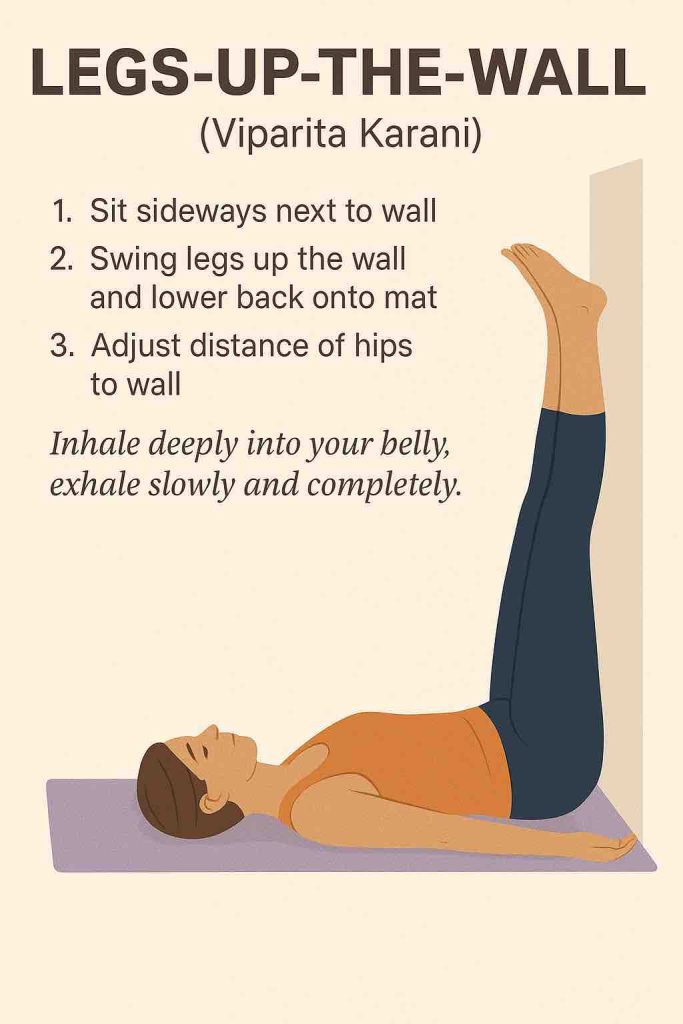
| Legs-Up-The-Wall (Viparita Karani) | Soothing, reduces anxiety |
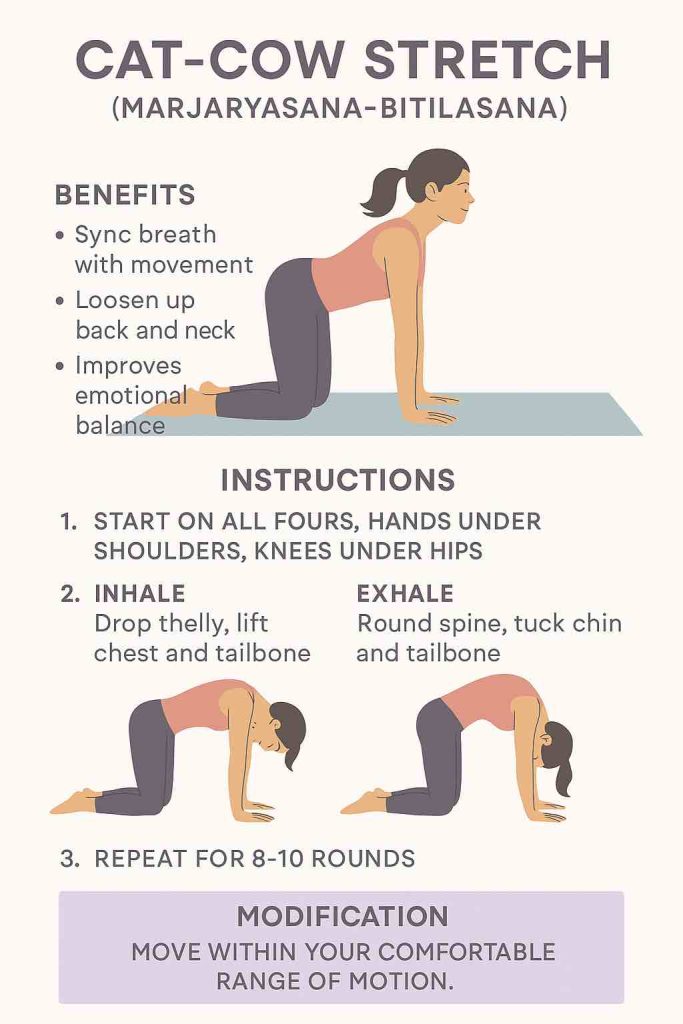
| Cat-Cow (Marjaryasana-Bitilasana) | Mobilizes spine, links breath with movement |
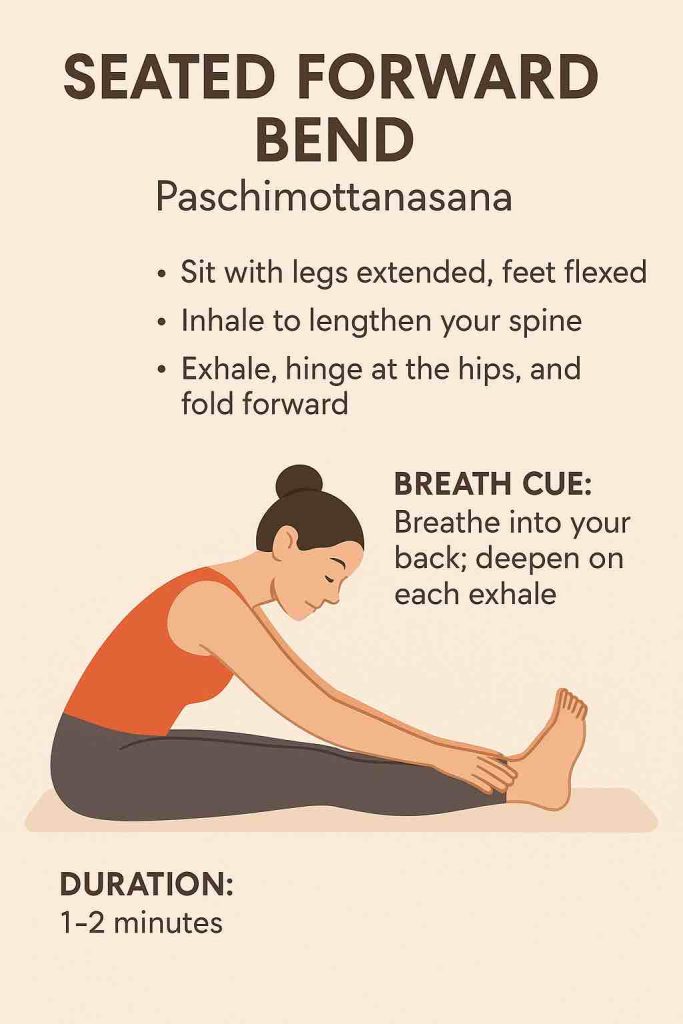
| Seated Forward Fold (Paschimottanasana) | Relaxes nervous system |
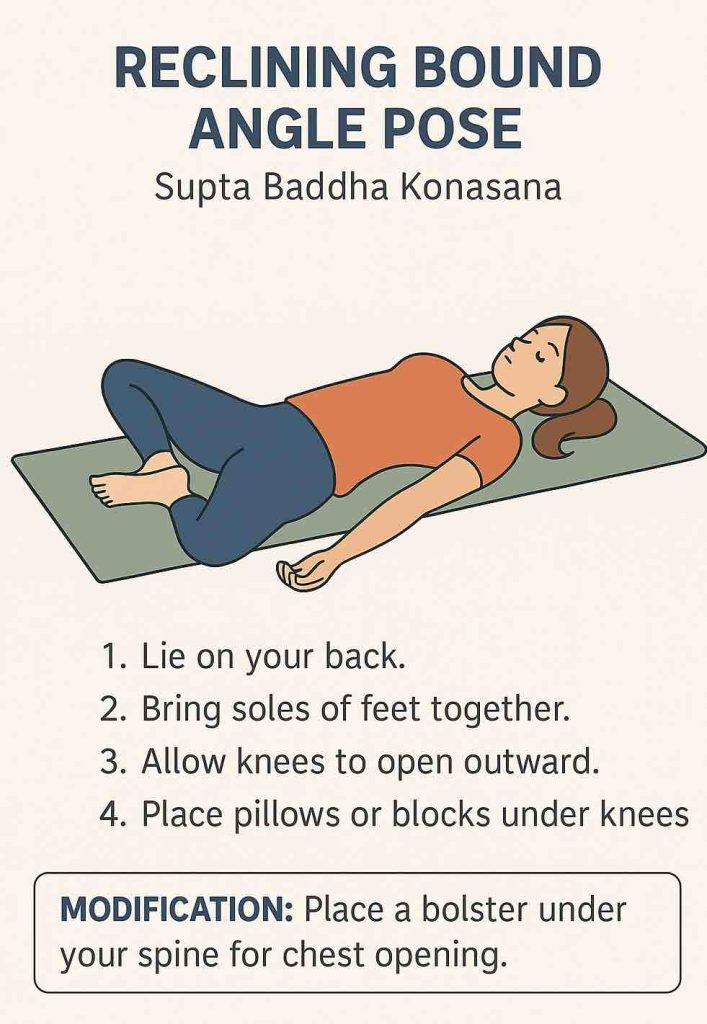
| Reclining Bound Angle (Supta Baddha Konasana) | Opens hips gently, calms mind |
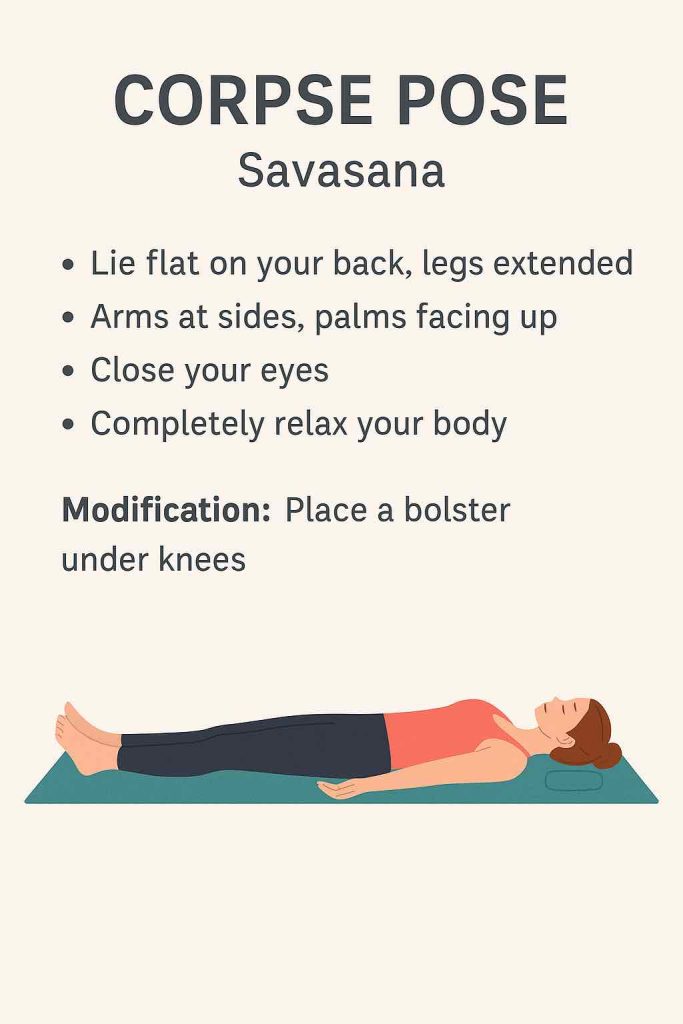
| Supported Savasana | Deep relaxation |
Safety Tips:
- Use props (bolsters, blankets, blocks) for support.
- Move slowly.
- Always offer choices: “If you like, you might explore…”
C. Mindfulness and Grounding
Mindfulness Techniques:
- Body scan meditation
- Naming five things you see, hear, feel (5-4-3-2-1 technique)
- Gentle anchoring in the breath or physical sensations
D. Restorative Yoga Sequence (20-30 mins)
- Supported Child’s Pose – 3 min
- Seated Cat-Cow – 5 rounds
- Legs-Up-The-Wall – 5-10 min
- Reclining Bound Angle with Bolster – 5 min
- Supported Savasana – 5-10 min
Finding the Right Teacher
- Look for instructors trained in Trauma-Informed Yoga.
- Verify experience with PTSD or mental health populations.
- Prioritize comfort, safety, and respect for personal boundaries.
- Small classes or private sessions may feel safer initially.
A Word on Combining Yoga with Therapy
Yoga is not a substitute for psychotherapy or medical care but works beautifully as an adjunct. Many trauma therapists now collaborate with yoga teachers to integrate mind-body work into a broader healing plan.
Always consult your healthcare provider before beginning any new practice.
Gentle Trauma-Sensitive Yoga Sequence (30-40 minutes)
✅ Focus: Nervous system regulation, grounding, gentle body awareness, and emotional safety.
📝 Before You Begin
- Find a quiet, safe space where you feel comfortable.
- Use props: bolster, pillow, blanket, blocks.
- Keep eyes open or closed, based on comfort.
- Always honor your body: skip or modify any posture that feels uncomfortable.
- Practice invitational language: “If you feel comfortable, you might explore…”
1️⃣ Grounding Breath (5 minutes)
- Sit comfortably (on floor, chair, or cushion).
- Place one hand on your chest, one on your belly.
- Inhale gently through the nose for 4 counts.
- Exhale slowly for 6-8 counts.
- Feel the rise and fall of your breath.
- Repeat for 5 minutes.
2️⃣ Seated Cat-Cow (3 minutes)
- Sit cross-legged or on a chair.
- On inhale: arch your back slightly, open chest.
- On exhale: round your spine, tuck chin gently.
- Flow slowly with your breath.
- 10-15 gentle rounds.
3️⃣ Supported Child’s Pose (3-5 minutes)
- Kneel on the floor, big toes together, knees apart.
- Rest torso on a bolster or pillow.
- Turn head to one side, switch halfway.
- Arms relaxed forward or alongside the body.
4️⃣ Legs-Up-The-Wall (5-8 minutes)
- Sit sideways against a wall.
- Gently swing legs up onto the wall.
- Place folded blanket under hips if helpful.
- Arms open to sides or resting on belly.
- Feel supported, grounded.
5️⃣ Reclining Bound Angle Pose (5-7 minutes)
- Lie back on the floor or bolster.
- Bring soles of feet together, knees falling outward.
- Support thighs with pillows/blocks for comfort.
- Rest hands on belly or sides.
6️⃣ 5-4-3-2-1 Grounding (2-3 minutes)
- Name aloud or silently:
- 5 things you see
- 4 things you hear
- 3 things you can touch
- 2 things you smell
- 1 thing you taste
- Brings you into the present moment.
7️⃣ Supported Savasana (5-10 minutes)
- Lie flat on back, support under knees and head.
- Cover with a blanket if desired.
- Rest hands gently on belly or sides.
- Option: Focus on the natural rhythm of breath.
✅ Optional Closing
End with a simple affirmation:
“I am safe. I am present. I honor my healing journey.”






🔄 Recommended Practice Schedule
- Frequency: 3-5 times per week.
- Time: Morning or evening.
- Goal: Consistency > duration. Even 10-15 minutes can be helpful.
Important Safety Reminders
- If distress arises, pause and return to grounding breath.
- Always consult your healthcare provider or therapist.
- Modify or stop any practice that feels uncomfortable.
- Seek certified trauma-sensitive yoga teachers if possible.
✅ Download this as PDF , which you can print as a 1-page handout for daily reference.
Closing Thought
Healing from trauma is not about “fixing” yourself — it’s about reclaiming safety, presence, and agency. Yoga offers a gentle, scientifically supported path toward this reclaiming.
Through mindful movement, breath, and self-compassion, you can learn to calm your nervous system, reconnect with your body, and gradually cultivate inner peace.
👉 If you found this article helpful, feel free to share or leave a comment below.
🧩 FAQs: Yoga for PTSD
1️⃣ Is yoga a replacement for therapy or medication for PTSD?
Answer:
No. Yoga is a complementary practice, not a replacement. It supports nervous system regulation, emotional resilience, and body awareness, but should be integrated alongside professional therapy, medication, or other evidence-based treatments as advised by healthcare providers.
2️⃣ Is it safe to practice yoga if I’m currently experiencing PTSD symptoms?
Answer:
Generally, yes — if practiced gently and with trauma-sensitive principles. Avoid intense, fast-paced, or forceful styles. Always listen to your body, start slowly, and consider working with a certified trauma-sensitive yoga instructor for maximum safety.
3️⃣ What style of yoga is best for PTSD?
Answer:
Trauma-Sensitive Yoga (TSY), Restorative Yoga, Gentle Hatha, Chair Yoga, and Somatic Yoga are most recommended. These focus on gentle movement, breathwork, and safety, avoiding potential triggers associated with certain other yoga styles.
4️⃣ How often should I practice yoga for PTSD benefits?
Answer:
Consistency is more important than duration. Practicing 3–5 times a week for 15–40 minutes can offer meaningful benefits over time. Even short, regular sessions (10-15 min daily) can help calm the nervous system.
5️⃣ Can certain yoga poses trigger PTSD symptoms?
Answer:
Yes. Some positions that feel vulnerable (e.g., backbends, closed-eye practices, inversions) can occasionally trigger discomfort. Always modify or skip poses. Trauma-sensitive yoga emphasizes choice, consent, and personal agency in every posture.
6️⃣ Do I need any special equipment to practice trauma-sensitive yoga?
Answer:
Basic props like a yoga mat, bolster, pillows, blocks, and blankets can make practice more comfortable and supportive. No advanced equipment is necessary, and many poses can even be done on a chair or bed.
7️⃣ What are the key principles of Trauma-Sensitive Yoga?
Answer:
- Invitational language (no commands)
- Offering choices in movement
- No hands-on adjustments without consent
- Creating a physically and emotionally safe space
- Encouraging present-moment awareness
8️⃣ How long before I might notice benefits from yoga practice?
Answer:
Some people feel more relaxed after just one session, but sustained benefits often build over weeks or months of regular practice. Improvements in sleep, mood, emotional regulation, and body awareness typically emerge gradually.
9️⃣ Can yoga trigger trauma memories?
Answer:
It can happen occasionally, especially when reconnecting with body sensations. This is why trauma-sensitive principles are crucial. If this occurs, pause, ground yourself (breath or grounding exercises), and seek support from a therapist.
🔟 Do I need an instructor, or can I practice at home?
Answer:
You can begin at home using safe, gentle sequences like the printable plan provided. However, working with a certified trauma-sensitive yoga teacher — even virtually — can provide additional safety, support, and individualized guidance.









