If you’ve ever wondered whether eating boiled eggs at night is a smart choice for your health and weight loss goals, you’re not alone. Many people trying to shed extra pounds ask if a simple boiled egg before bed can really help reduce late-night cravings, support fat loss, and even improve muscle recovery — or if it might cause unwanted side effects like indigestion or cholesterol concerns.
The truth is, eggs are one of the most versatile, nutrient-packed foods you can eat. They provide high-quality protein, essential vitamins, and healthy fats — all for fewer than 80 calories each. When eaten at night, especially in boiled form, they can satisfy hunger, stabilize blood sugar, and fuel your body while you sleep.
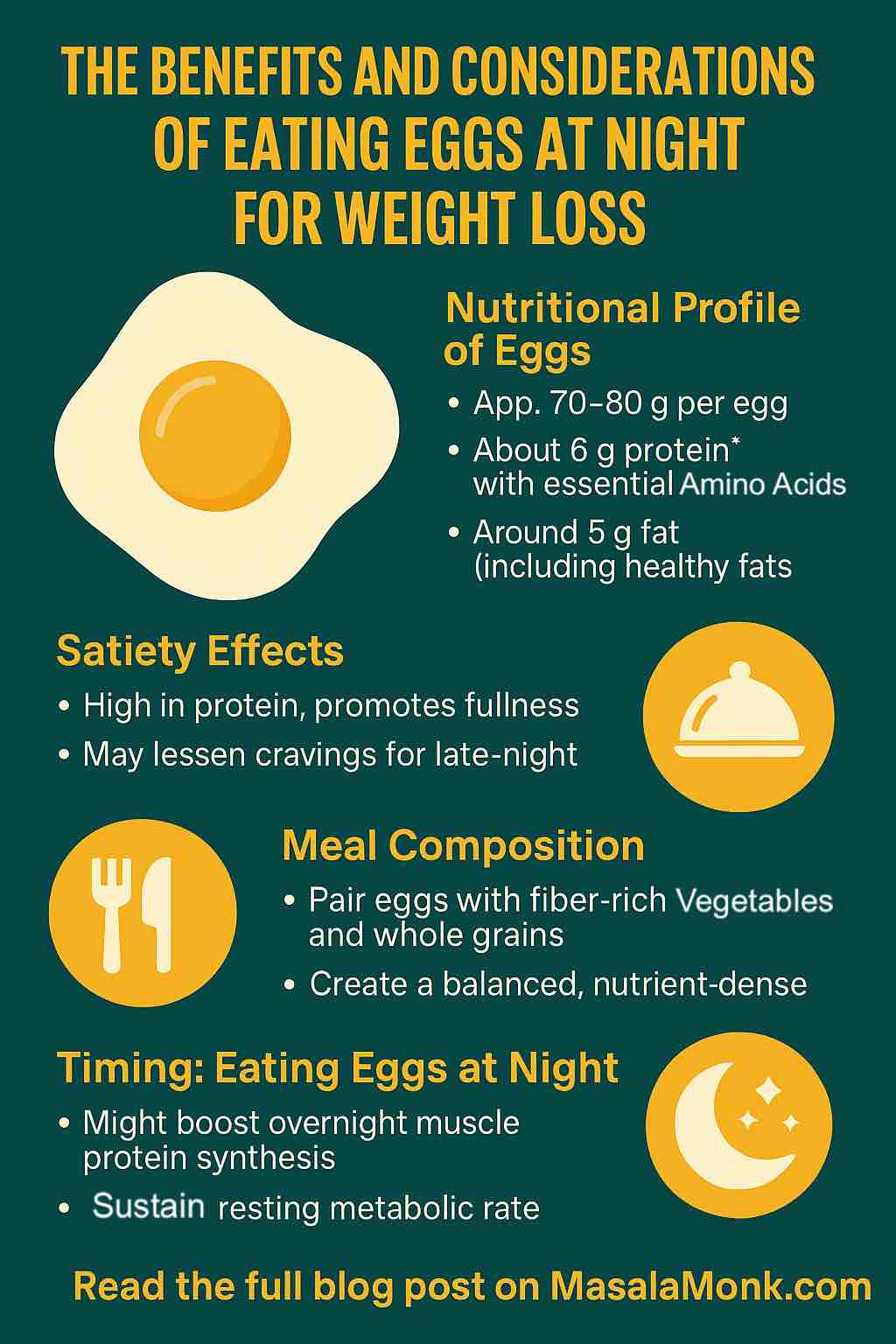
In this article, we’ll break down the science and practicality of eating boiled eggs at night. From their nutritional profile and satiety benefits to the best timing, meal ideas, and potential drawbacks, you’ll get a clear guide on how to use eggs to support weight loss without guilt or confusion.
🍳 Quick Takeaways: Eating Boiled Eggs at Night
- Yes, it’s safe: For most people, eating boiled eggs at night is perfectly fine and can support weight loss.
- Helps with weight loss: High protein keeps you full, reduces cravings, and helps you avoid late-night snacking.
- Supports muscle repair: Protein in eggs fuels overnight recovery and preserves muscle while losing fat.
- Low-calorie choice: One boiled egg has only 70–80 calories but is packed with nutrients like vitamin D, B12, and choline.
- Best timing: Eat them 1–2 hours before bed, or after an evening workout for recovery.
- Watch out for: Overeating (stick to 1–2 eggs), digestive discomfort if eaten too close to bedtime, and cholesterol if you have specific health concerns.
- Better than junk food: Compared to chips, ice cream, or sugary snacks, boiled eggs are healthier, more filling, and weight-loss friendly.
| ✅ Benefit / Insight | 📖 Details |
|---|---|
| 🥚 Safe & Healthy | For most people, eating boiled eggs at night supports weight loss and overall health. |
| ⚖️ Weight Loss Friendly | High protein reduces cravings and late-night snacking. |
| 💪 Muscle Recovery | Amino acids support overnight muscle repair and growth. |
| 🔥 Low-Calorie Snack | Only 70–80 calories per egg, but nutrient-dense. |
| ⏰ Best Timing | Eat 1–2 hours before bed or after an evening workout. |
| ⚠️ Considerations | Don’t overeat; watch cholesterol and digestion if sensitive. |
| 🍟 Better Choice | A healthier alternative to chips, ice cream, or sweets. |

Can You Eat Boiled Eggs at Night?
The short answer is yes — eating boiled eggs at night is perfectly safe for most people and can even be beneficial. Unlike carb-heavy snacks or sugary desserts that can spike blood sugar and leave you hungry again, boiled eggs provide steady energy and long-lasting fullness.
Boiled eggs are especially handy because they’re easy to prepare, portable, and digestible. They won’t weigh you down like a greasy takeaway meal or disrupt your sleep the way caffeine or sugar might. For anyone struggling with late-night snacking habits, they’re a healthier swap that still feels satisfying.
Benefits of Eating Boiled Eggs at Night for Weight Loss
Satiety and Craving Control
Late-night hunger is one of the biggest challenges for people trying to lose weight. That’s when cravings for chips, cookies, or ice cream usually strike. The problem is, these snacks are calorie-dense and nutrient-poor — they satisfy temporarily but leave you hungrier later.
Boiled eggs flip that script. Thanks to their high protein content, they provide satiety — the feeling of fullness that suppresses the hunger hormone ghrelin and reduces the urge to snack. Eating one or two boiled eggs in the evening can help you cut back on mindless snacking without feeling deprived. If you’re curious about protein numbers, here’s exactly how much protein is in two boiled eggs.

One randomized study compared an egg-based breakfast with a bagel-based one and found that eggs led to greater satiety and reduced calorie intake later in the day, highlighting their hunger-fighting power (PubMed)
Muscle Repair While You Sleep
If you exercise in the evening, eating boiled eggs at night can directly support your recovery. Protein is essential for muscle repair, and eggs are a complete protein source with all nine essential amino acids.
Research shows that protein eaten before bed is well digested and directly enhances overnight muscle protein synthesis, helping your body repair and adapt after exercise (NIH – National Library of Medicine).
This means that while you rest, your muscles are repairing and growing stronger — making your workouts more effective and helping you maintain lean muscle while losing fat. Pairing eggs with veggies or whole grains mimics the principles of high protein, high fiber diets for weight loss, which keep you full while supporting metabolism.

Low-Calorie, Nutrient-Dense Snack
At about 70–80 calories per large boiled egg, you’re getting an incredible nutrient-to-calorie ratio. Each egg delivers protein, healthy fats, and micronutrients like vitamin D, vitamin B12, selenium, and choline.
Compare that to a handful of chips or a chocolate bar, which can easily top 200 calories with little nutritional value. Boiled eggs fill you up without tipping your daily calorie balance, making them a smart tool for creating a calorie deficit. Don’t forget the nutritional profile of egg yolks, which adds vitamins and antioxidants many people mistakenly skip.
Nutrition experts also emphasize that choosing nutrient-dense late-night snacks like protein or casein-rich foods supports metabolism and better sleep, unlike processed snacks that can disrupt recovery (The Times)
Nutritional Profile of Boiled Eggs
Here’s a quick breakdown of what you get in one large boiled egg:
- Calories: 70–80 kcal
- Protein: ~6 grams
- Healthy Fats: ~5 grams (including omega-3s if you choose enriched eggs)
- Micronutrients: Vitamin D, vitamin B12, riboflavin, selenium, lutein, and choline
This compact nutrient package makes eggs a powerful option for weight loss, muscle maintenance, and general health. They’re proof that small, simple foods can pack a big nutritional punch. If you’re curious about whether price matters, here’s a guide on choosing the right eggs for nutrition and value.

Best Time for Eating Boiled Eggs at Night
While eggs are safe and healthy at night, timing can influence how well your body digests and uses the nutrients.
- 1–2 Hours Before Bed: The sweet spot. This gives your body enough time to digest without feeling heavy or uncomfortable when you lie down.
- After Evening Workouts: Eggs are ideal as a post-exercise recovery snack, especially when paired with a small portion of complex carbs. For those following fasting routines, they’re also one of the best foods during intermittent fasting.
- As a Late-Night Snack Alternative: If you usually reach for cookies or chips, swap them for boiled eggs. You’ll still feel satisfied but without the blood sugar spikes.

In fact, studies suggest that a moderate serving of protein (about 20–40 grams) within 30 minutes of bedtime supports muscle recovery and even improves strength over time (PubMed).
⚠️ If you find that eating right before bed causes indigestion, simply move your egg-based snack earlier in the evening. Everyone’s digestion is unique.
How to Eat Eggs at Night: Practical Meal Ideas
Eating plain boiled eggs works, but let’s face it — it can get boring. Luckily, eggs are versatile enough to keep things interesting. Here are some simple, healthy ways to include them at night:
- Classic Boiled Eggs with Veggies
Pair one or two boiled eggs with cucumber slices, cherry tomatoes, or baby carrots for a balanced, low-calorie plate. - Veggie Omelette
Cook a quick omelette with spinach, mushrooms, and bell peppers. Add herbs or chili flakes for flavor without adding calories. - Scrambled Eggs with Avocado
Lightly scramble eggs in a non-stick pan and serve with avocado for extra healthy fats and creaminess. - Egg Salad Lettuce Wraps
Mash boiled eggs with a spoonful of Greek yogurt (instead of mayo), season with herbs, and wrap in lettuce leaves for a crunchy, protein-packed option. - Eggs with Complex Carbs (If Needed)
If you’re especially hungry or have exercised, pair boiled eggs with a small serving of sweet potato, quinoa, or whole grain toast. This balances satiety with slow-release energy.

For those who train late in the evening, pre-sleep protein also boosts mitochondrial and muscle protein synthesis rates, which can improve endurance adaptations and overnight recovery (BCBSM Health).
Side Effects of Eating Boiled Eggs at Night
While eating boiled eggs at night is generally beneficial, here are a few considerations to keep in mind:
Cholesterol and Heart Health
Eggs do contain cholesterol — around 186 mg per large egg. For most people, this doesn’t raise blood cholesterol significantly. But if you’ve been advised by your doctor to limit cholesterol, keep your intake moderate.
Digestive Discomfort at Night
Some people may feel bloated or heavy if they eat too close to bedtime. If that’s you, shift your egg-based snack earlier, or try lighter preparations like poached instead of fried or scrambled.
Allergies and Intolerance
Eggs are a common allergen. If you experience reactions like stomach upset, rashes, or breathing issues, avoid them altogether and speak with a healthcare provider.
Calories Still Count
Even healthy foods add up. Eating five or six eggs at once can easily exceed 400 calories, which isn’t ideal before bed if you’re aiming for weight loss. Stick to 1–2 eggs unless you’ve planned them into your calorie allowance.
Eating Boiled Eggs at Night vs Other Snacks
Sometimes it helps to see the comparison clearly. Here’s how boiled eggs stack up against common late-night snack options:
| Snack | Calories (approx) | Nutrition | Effect on Hunger | Weight Loss Friendly? |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| Boiled Egg (1 large) | 70–80 | Protein, healthy fats, vitamins | High satiety | ✅ Yes |
| Chips (1 small bag) | 150–200 | Refined carbs, unhealthy fats | Low satiety | ❌ No |
| Ice Cream (1 cup) | 250+ | Sugar, saturated fats | Low satiety | ❌ No |
| Greek Yogurt (unsweetened) | 100–120 | Protein, probiotics | High satiety | ✅ Yes |
| Nuts (small handful) | 180–200 | Healthy fats, some protein | Medium satiety | ✅ In moderation |

Even a small protein-rich snack of around 150 calories before bed has been shown to help with muscle recovery and boost metabolism without promoting weight gain (Health.com).
It’s easy to see why eating boiled eggs at night is a winning choice. They provide more nutrition, better satiety, and fewer calories than most snack alternatives. To balance your diet further, here’s a look at foods that help reduce belly fat.
Final Thoughts: Should You Eat Boiled Eggs at Night?
So, is eating boiled eggs at night good for weight loss? The answer is a clear yes — when done in moderation and prepared the right way.
Eggs are nutrient-dense, low in calories, and packed with protein that curbs hunger, supports muscle repair, and helps reduce late-night snacking. They’re also simple, affordable, and versatile, making them one of the most practical foods to include in your diet.
That said, remember the basics: stick to 1–2 eggs, pair them with veggies or light sides, and avoid heavy cooking methods with lots of oil or butter. If you pay attention to how your body feels and make eggs part of an overall balanced diet, they can become a powerful ally in your weight loss journey. For a broader plan, check out these tips on how to eat 100 grams of protein a day.
If you’re looking for a satisfying nighttime snack that won’t derail your progress, boiled eggs may be exactly what you need.
🥚 Should You Try Eating Boiled Eggs at Night?
If you’re serious about weight loss, muscle recovery, or just kicking late-night cravings, eating boiled eggs at night can be one of the simplest, most effective changes you make. They’re nutrient-dense, satisfying, and far healthier than most evening snack options.
- Try adding 1–2 boiled eggs to your nighttime routine this week.
- Notice how your hunger, energy, and sleep feel.
- Share your experience in the comments — we’d love to hear if this small change makes a big difference for you!
🍴 Related Reads: Protein & Weight Loss Guides
Looking to expand your nutrition knowledge beyond eggs? Here are some practical, science-backed reads that pair perfectly with your weight-loss journey:
- How Much Protein in Two Boiled Eggs?
Find out exactly how much protein is in two boiled eggs and why it matters for satiety, muscle growth, and weight management. - Egg Yolks or Yellow: Nutritional & Protein Profile
Should you eat the yolk or skip it? Learn the truth about egg yolk nutrition, cholesterol myths, and what science really says. - Are Expensive Eggs Worth Your Money?
Omega-3 enriched, free-range, organic — are pricey eggs really healthier, or just marketing hype? Here’s how to choose wisely. - How to Eat 100 Grams of Protein a Day
Simple, practical strategies to hit your daily protein goals without stress — including snacks, meal ideas, and timing tips. - Foods to Eat During 16:8 Intermittent Fasting
If you practice intermittent fasting, discover which foods — including eggs — support energy, fat loss, and metabolic health. - 5 Foods that Help Reduce Belly Fat
Explore other fat-burning superfoods that work alongside protein to reduce belly fat and improve overall health.
❓ Frequently Asked Questions
1. Is it okay to eat boiled eggs at night for weight loss?
Yes, absolutely. For most people, eating boiled eggs at night is not only safe but also beneficial for weight loss. Their high protein content keeps you full, reduces late-night cravings, and supports muscle repair while you sleep. Unlike sugary or carb-heavy snacks, boiled eggs provide steady energy without spiking blood sugar.
2. How many boiled eggs should I eat at night?
Portion control matters. Most people do well with 1–2 boiled eggs at night as part of a balanced meal or snack. This gives you enough protein and nutrients without adding unnecessary calories. If you’re active, you may pair them with fiber-rich veggies or a small serving of complex carbs for extra satiety.
3. Does eating boiled eggs at night cause weight gain?
Not directly. Boiled eggs are low in calories — about 70–80 per egg — and rich in nutrients. Weight gain only happens if you consistently eat more calories than your body burns. If you stick to 1–2 eggs and keep your daily calories in check, eating boiled eggs at night won’t make you gain weight. In fact, they may help you avoid higher-calorie snacks.
4. Can eating boiled eggs at night help reduce late-night cravings?
Definitely. The protein and healthy fats in eggs promote satiety and calm hunger hormones, making you feel full longer. This makes them an excellent swap for chips, cookies, or ice cream. If late-night snacking is your weakness, boiled eggs are a much healthier way to stay satisfied.
5. Is it bad to eat boiled eggs right before bed?
For most people, no — but it depends on your digestion. If you eat eggs 1–2 hours before bed, your body has enough time to digest comfortably. Some people may feel heavy or bloated if they eat too close to bedtime, so listen to your body. A lighter option like poached or scrambled eggs may be easier if you’re sensitive.
6. Are eggs at night good for muscle growth?
Yes! Eating protein before sleep, like boiled eggs, can boost overnight muscle repair and growth. Studies show that consuming protein before bed enhances muscle protein synthesis, which is especially important if you train in the evening. Eggs are a convenient, complete protein source that fits perfectly here.
7. Can people with high cholesterol eat boiled eggs at night?
Moderation is key. One large egg contains about 186 mg of cholesterol, but research shows that for most healthy people, moderate egg consumption does not significantly raise blood cholesterol. If you have specific cholesterol concerns, it’s best to consult your doctor and consider egg whites or other protein-rich foods at night.
8. Are boiled eggs better than other late-night snacks?
Yes — in most cases. Compared to chips, cookies, or ice cream, boiled eggs offer far more nutrition with fewer calories. They’re rich in protein and essential vitamins, while most late-night snacks are high in sugar, refined carbs, or unhealthy fats. If you want something filling, nourishing, and weight-loss friendly, boiled eggs are a smarter choice.
9. Can I eat boiled eggs every night?
Yes, if you enjoy them and tolerate them well. Eating boiled eggs at night regularly can be part of a healthy, balanced diet. However, variety is important — rotate eggs with other protein sources like Greek yogurt, cottage cheese, nuts, or legumes to cover a wider nutrient spectrum.
10. Do boiled eggs improve sleep quality?
For some people, yes. Eggs contain tryptophan (an amino acid linked to better sleep) and can help stabilize blood sugar overnight. By preventing hunger spikes, they may even support deeper rest. If you notice digestive discomfort, just have them a little earlier in the evening to keep sleep smooth.










