If you’ve ever felt that burning sensation creeping up your chest after a meal, you know how frustrating acid reflux and heartburn can be. It can turn a simple dinner into hours of discomfort, rob you of sleep, and leave you wondering if every bite is worth the pain.
Naturally, people look for simple remedies — and one of the most common questions typed into Google is: “Is ginger good for acid reflux?” For some, a warm cup of ginger tea after a heavy meal feels like a lifesaver. For others, even a small piece of raw ginger seems to make things worse.
Why such a split experience? Ginger has been praised in traditional medicine for centuries, but when it comes to reflux and GERD (gastroesophageal reflux disease), the truth is more complicated. Some research shows it helps digestion and calms irritation, while other evidence (and real-world stories) point to it triggering more burn.
This article explores the science, the tradition, and the practical reality of ginger for reflux. We’ll look at whether ginger can relieve heartburn or if it’s just another wellness myth, and we’ll give you clear, actionable ways to use it safely. As MasalaMonk’s guide on ginger’s stunning health benefits notes, this root is powerful — but powerful foods demand some respect.
What Really Causes Acid Reflux and Heartburn?
Before we can answer whether ginger helps or hurts, it’s important to understand what’s actually going on in your body when reflux strikes.
The Basics of Reflux
Acid reflux happens when stomach acid escapes upward into the esophagus (the tube that carries food from your mouth to your stomach). Normally, a small muscle called the lower esophageal sphincter (LES) acts like a gatekeeper. It opens to let food in, then closes tightly to keep acid where it belongs.
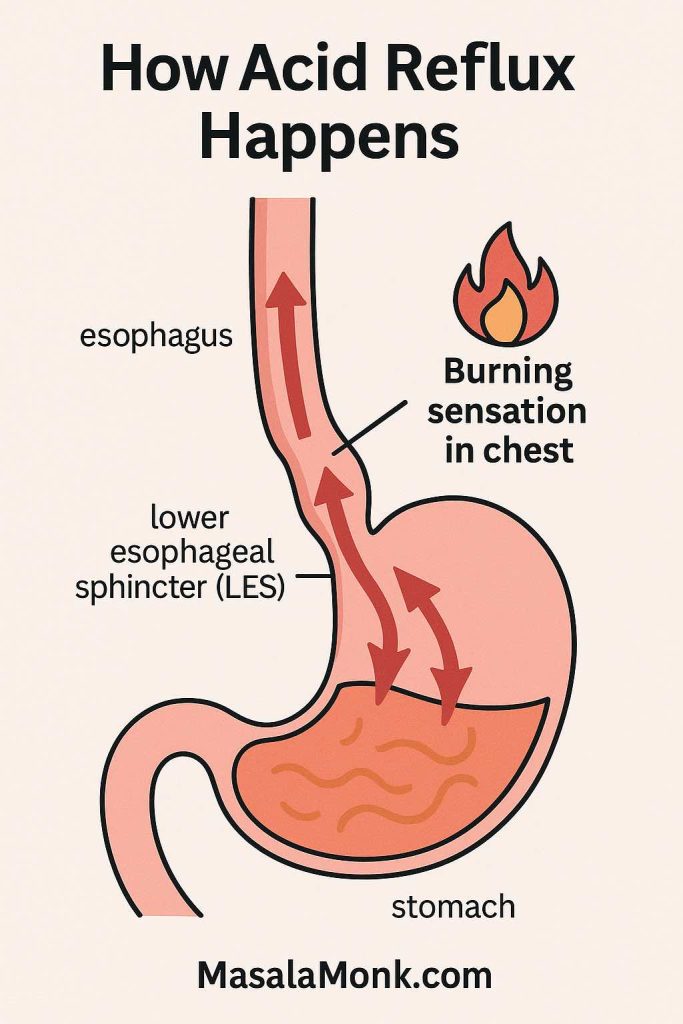
When that gate weakens, relaxes at the wrong time, or faces too much pressure, acid sneaks upward. The result? A burning, sometimes bitter sensation in the chest or throat — what we call heartburn. If reflux becomes frequent, it’s known as GERD (Gastroesophageal Reflux Disease).
Also Read: Is Popcorn Safe for Acid Reflux, Heartburn, and GERD?
Common Triggers You Might Recognize
- Foods: Tomatoes, citrus fruits, chocolate, fried foods, alcohol, coffee, and spicy dishes are classic culprits.
- Habits: Eating large meals, lying down right after eating, or eating too quickly.
- Lifestyle factors: Stress, poor sleep, smoking, or excess weight.
- Medications: Some painkillers, blood pressure drugs, and muscle relaxants can worsen reflux by relaxing the LES.
If you’ve ever wondered why one meal goes down fine but another makes you miserable, it’s often these factors at play. And as MasalaMonk’s article on foods that help with reflux and heartburn explains, the wrong food choices can set the stage for irritation — while the right ones can soothe.
Where Ginger Fits Into This Picture
Ginger is a bit of a wildcard. On one hand, it’s been shown to help the stomach empty faster and calm digestive spasms, which could reduce reflux risk. On the other hand, some people find it relaxes the LES too much, making heartburn worse. That’s why you’ll find so many conflicting experiences online — and why dosage, form (tea vs raw root), and timing matter more than you might think.
Is Ginger Good for Acid Reflux?
This is the million-dollar question. If you search “ginger for acid reflux” or “does ginger help with heartburn,” you’ll find both glowing recommendations and stern warnings. The truth is somewhere in the middle.
Why Ginger Can Be Helpful
Ginger is packed with active compounds like gingerols and shogaols, which have been shown to:
- Calm inflammation: Heartburn often comes from acid irritating the esophagus. Ginger’s natural anti-inflammatory effect may soothe that irritation.
- Support digestion: Ginger helps food move through the stomach faster (a process called gastric emptying), which means less time for acid to pool and reflux upward.
- Ease nausea and bloating: Many people with GERD also feel bloated or nauseated. Ginger is one of the best natural remedies for both.
That’s why you’ll often see it listed in natural reflux remedies. In fact, MasalaMonk includes ginger in 5 Highly Alkaline Foods for Acid Reflux, highlighting how it can help balance stomach acid when used in moderation.
When Ginger Works Best
- Mild, occasional reflux: A warm cup of ginger tea after a heavy or spicy meal can make digestion feel smoother.
- Mixed symptoms: If you struggle with nausea and reflux, ginger may ease both.
- As part of a reflux-friendly diet: Pairing ginger with other calming foods like bananas or fennel (also listed in MasalaMonk’s alkaline foods guide) may give a gentle, synergistic effect.
👉 Practical tip: Start small — a thin slice of ginger brewed in tea or about 1 gram in cooking. See how your body responds before adding more.
Also Read: Bananas Good or Bad for Heartburn and Acid Reflux
Can Ginger Cause Heartburn or Make GERD Worse?
Here’s the other side of the story: ginger isn’t a guaranteed reflux cure. In fact, for some people, it can actually be a trigger.
Why Ginger Backfires for Some
- Relaxing the LES too much: If your reflux is caused by a weak valve, ginger’s effect on muscle relaxation might allow acid to escape upward more easily.
- Acidic combos: Lemon-ginger water or concentrated ginger shots may be too harsh, especially for sensitive stomachs.
- High doses: More than 4–6 grams a day can increase the risk of heartburn, diarrhea, or stomach upset.
MasalaMonk touches on this in Benefits of Cucumber, Lemon, and Ginger Water, where they note that while refreshing, lemon-ginger drinks can actually aggravate reflux symptoms in some people.

Who Should Use Ginger Cautiously
- People with chronic GERD: Regular, high amounts of ginger may worsen irritation instead of easing it.
- Nighttime sufferers: Having ginger too close to bedtime (especially in large meals or teas) may fuel nighttime reflux.
- Those sensitive to acidic foods/drinks: If you already struggle with citrus, vinegar, or tomatoes, concentrated ginger drinks may fall into the same category for you.
It’s worth remembering, as MasalaMonk’s article on Foods That Worsen Acid Reflux and Heartburn explains, that even healthy, natural foods can become problematic if eaten the wrong way or in the wrong amounts. Ginger is no exception.
Best Ways to Use Ginger for Heartburn Relief
If you’ve ever typed “how do you use ginger for acid reflux” into Google, you’re not alone. Ginger can be soothing, but how you use it makes all the difference between relief and regret.
Ginger Tea: Gentle and Calming
One of the best ways to take ginger is in tea. Warm water extracts its soothing compounds while diluting any harshness. A thin slice of fresh ginger brewed for 5–10 minutes can calm the stomach without overwhelming it.
- When to drink: About 20–30 minutes after meals.
- What to avoid: Don’t go overboard with concentrated ginger shots or heavily spiced teas before bed.
For more soothing beverage ideas, check MasalaMonk’s post on What to Drink for Acid Reflux and Heartburn Relief, which includes ginger tea alongside other calming options like licorice root tea and aloe vera juice.
Fresh Ginger in Cooking
Adding small amounts of ginger to stir-fries, soups, or curries can enhance digestion without being too intense. The heat of cooking also mellows out its spiciness, making it gentler for sensitive stomachs.
Ginger Infused Water
If you like refreshing drinks, ginger water can be a good option — but keep it simple. Just slice a bit of fresh ginger into warm water and sip slowly. Avoid pairing it with lemon if reflux is your main issue (that combo can backfire).
Moderation Is Key
Doctors and herbalists often suggest limiting ginger to 1–2 grams a day if you’re using it for reflux. This is consistent with advice in MasalaMonk’s article on What Foods Neutralize Stomach Acid Immediately?, which reminds readers that ginger is safe in small doses but may irritate in excess.
👉 Practical takeaway: Ginger works best in mild, diluted forms — teas, small amounts in food, or light infusions. Skip raw ginger chunks or spicy ginger shots if reflux is your struggle.

Is Ginger Acidic?
Another common search is: “is ginger acidic?” or “is ginger root acidic in nature?”
The short answer: yes, ginger is mildly acidic — but acidity isn’t the whole story.
Ginger’s pH vs Its Effect in the Body
On the pH scale, ginger leans slightly acidic. But that doesn’t necessarily mean it worsens reflux. Many foods with mild acidity don’t trigger reflux at all, while others with neutral pH (like fatty fried foods) can be major triggers because they relax the LES.
In fact, ginger’s digestive benefits often outweigh its mild acidity. By reducing inflammation and supporting motility, it may actually lower your risk of reflux symptoms — as long as you don’t consume it in irritating forms or huge quantities.
You might want to read: Decaf Coffee and GERD: Is Decaf Coffee Better for Acid Reflux?
When Acidity Becomes a Problem
- Concentrated forms: Ginger shots, lemon-ginger water, or spicy raw ginger may be too acidic for sensitive stomachs.
- Personal tolerance: Some people handle small doses fine but react poorly when combining ginger with other acidic foods.
As highlighted in MasalaMonk’s piece on Baking Soda for Heartburn, Acid Reflux, & GERD, the key isn’t always pH alone — it’s how foods interact with your body and whether they soothe or aggravate reflux triggers.
Ginger vs. Other Natural Remedies for Acid Reflux
While ginger is one of the most talked-about natural options, it isn’t the only one. Many people with reflux explore herbal and traditional remedies — sometimes finding even better relief by combining them.
Chamomile: Calming and Soothing
Chamomile tea is a classic bedtime remedy for reflux. It helps relax the digestive tract, reduce stress (a hidden reflux trigger), and calm inflammation. Interestingly, MasalaMonk features chamomile and ginger together in 21 Remedies for Acid Reflux, Heartburn, and GERD, recommending the two as a soothing blend. For many, this combo is gentler than ginger alone.
Aloe Vera: Cooling Relief
Aloe vera juice is often described as a “coolant” for the esophagus. It helps soothe irritation caused by acid and may promote healing. It’s best consumed in small amounts and in purified, food-safe form.
Licorice Root: Protecting the Esophagus
Deglycyrrhizinated licorice (DGL) is used in natural medicine for coating and protecting the esophageal lining. Like ginger, it’s anti-inflammatory, but it works more by creating a protective barrier than by aiding motility.
Slippery Elm and Probiotics
- Slippery elm forms a gel-like substance that coats the digestive tract, reducing irritation.
- Probiotics improve gut balance, which may indirectly ease reflux symptoms for some people.
Where Ginger Fits in the Mix
Compared to these remedies, ginger’s strength lies in supporting digestion and reducing nausea. But if your main issue is esophageal burning and irritation, you might find more relief from slippery elm, aloe vera, or licorice root.
That’s why experts often suggest trying ginger alongside other natural aids. For example, MasalaMonk’s guide on Managing Acid Reflux: Foods to Avoid for a Soothing Digestive Experience emphasizes balancing trigger avoidance with gentle, calming foods — ginger included, but not in isolation.
Ginger for Heartburn: Natural Relief or Digestive Myth? (The Final Verdict)
So where does all this leave us? Is ginger a natural relief or just another wellness myth?
The Takeaway on Benefits
- In small amounts, ginger can reduce nausea, calm bloating, and speed up digestion — all of which may help reduce reflux symptoms.
- Tea or lightly cooked ginger are the gentlest forms, offering comfort without being too harsh.
- Ginger pairs well with other soothing remedies like chamomile or alkaline foods, making it part of a reflux-friendly routine.
The Risks You Can’t Ignore
- Too much ginger (above 4–6 grams daily) may cause heartburn, diarrhea, or stomach upset.
- Concentrated forms (shots, lemon-ginger detox drinks) are more likely to irritate.
- People with chronic GERD should use ginger cautiously, tracking symptoms closely.
MasalaMonk reinforces this balance in Foods That Worsen Acid Reflux and Heartburn, reminding readers that even natural remedies can tip into “too much of a good thing.”
Practical Bottom Line
- Yes, ginger can help — especially as tea or a mild infusion.
- Yes, ginger can hurt — especially in raw, concentrated, or excessive forms.
- The deciding factor is your body’s response. Start small, track your symptoms, and always pair ginger with an overall reflux-friendly lifestyle.
If you want a simple first step, try replacing that after-dinner coffee (a notorious reflux trigger) with a mild ginger-chamomile tea. You’ll support digestion, avoid acid build-up, and maybe even sleep better.
In the end, ginger isn’t a miracle cure for acid reflux, but it’s far from a myth. Used wisely, it can be a supportive tool in your natural reflux toolkit.
Frequently Asked Questions About Ginger and Acid Reflux
Does ginger root help with acid reflux?
Yes — in small amounts, ginger root may help with acid reflux by speeding up digestion, calming inflammation, and reducing nausea. Many people find ginger tea or lightly cooked ginger gentler than raw ginger. However, the effect isn’t universal, so track your symptoms.
Can ginger cause heartburn?
It can. While ginger is often soothing, higher doses or concentrated forms (like ginger shots or ginger chews) may relax the lower esophageal sphincter, allowing acid to escape upward. This can cause or worsen heartburn in sensitive people.
Is ginger good for GERD?
Ginger can provide relief for some people with mild GERD by easing digestion and bloating. But for chronic GERD sufferers, large or frequent doses may backfire. Moderation is key, and forms like tea are usually better tolerated than raw ginger.
Is ginger tea good for acid reflux?
Yes — ginger tea is one of the safest ways to consume ginger if you have reflux. A warm, diluted tea can soothe the stomach and reduce bloating. Just avoid adding lemon if you’re sensitive, as that may increase acidity.
Is ginger acidic?
Ginger is slightly acidic on the pH scale, but its overall effect in the body isn’t as simple as “acidic food = more reflux.” In many cases, ginger’s anti-inflammatory and digestive benefits outweigh its mild acidity.
How much ginger is safe for reflux?
Most experts recommend 1–2 grams per day for digestive support. More than 4–6 grams daily can cause heartburn, diarrhea, or stomach upset. Start small, see how your body responds, and adjust.
Can ginger chews or candy help reflux?
Sometimes — but often they contain sugar and concentrated ginger, which may worsen reflux. If you want to try them, start with a small amount and avoid before bedtime. Ginger tea or infused water is usually a better option.
Will ginger help with indigestion too?
Yes. Ginger has long been used to ease indigestion by relaxing the stomach and speeding up emptying. This can also help reduce the pressure that leads to reflux. MasalaMonk’s article on 21 Remedies for Acid Reflux, Heartburn, and GERD even suggests ginger as part of Ayurvedic blends for indigestion relief.
Final Word
Ginger isn’t a magic bullet for acid reflux, but it’s not a myth either. In small, gentle forms — like tea or light cooking — it may provide real relief. In large or harsh doses, it can easily tip the other way.
The key is moderation, mindful preparation, and paying attention to your own triggers. Pair ginger with other reflux-friendly habits, and it can be a helpful ally in calming heartburn naturally.










