When you think of Multiple Sclerosis (MS), symptoms like muscle weakness, fatigue, or balance problems might spring to mind. But did you know that your digestive system—especially issues like acid reflux—can also become part of your MS journey?
Let’s unpack the connection between MS and acid reflux (GERD), explore the science, and offer practical tips you can use starting today.
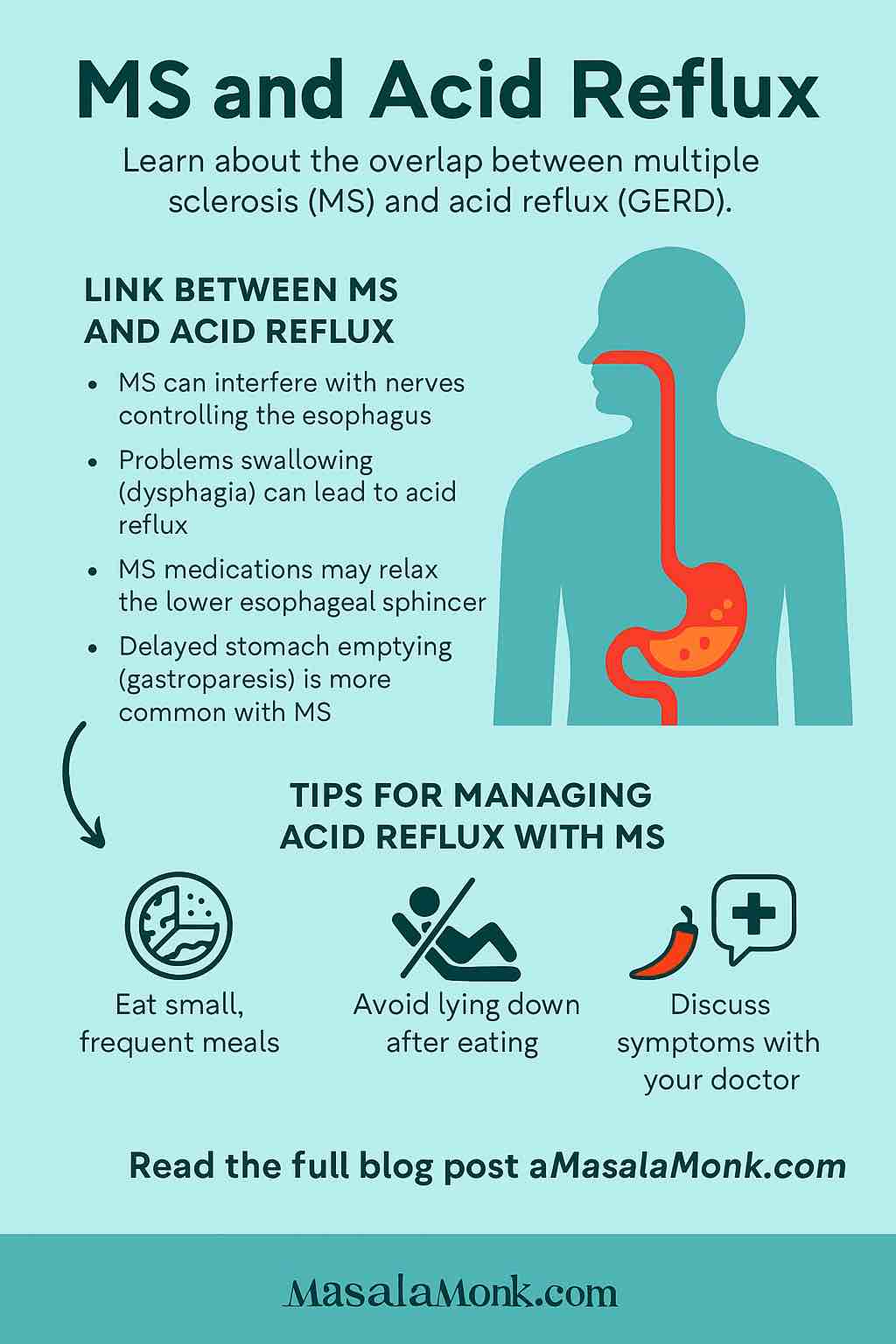
What’s the Connection Between MS and Acid Reflux?
Acid reflux (also known as gastroesophageal reflux disease or GERD) happens when stomach acid backs up into the esophagus, causing symptoms like heartburn, regurgitation, and even a chronic cough.
But how does MS get involved?
MS is a condition where your immune system mistakenly attacks the nerves in your brain and spinal cord. This can disrupt the way signals travel throughout your body—including the nerves that control your digestive tract.
- Nerves and Digestion:
The muscles in your throat and esophagus rely on precise nerve signals to swallow food and move it toward your stomach. MS lesions can interfere with these signals, slowing things down or causing muscles to spasm. - Swallowing Problems (Dysphagia):
MS can make it harder to swallow, which means food might not clear the esophagus as quickly, allowing acid to linger and cause irritation. - Stomach Emptying:
Sometimes MS affects how quickly your stomach empties (a condition called gastroparesis), increasing pressure and risk of reflux. - Medications:
Many MS medications, especially those for bladder control or muscle spasms, can relax the lower esophageal sphincter (LES)—the “valve” that normally keeps stomach acid out of your esophagus.
Recent Research: What’s New in 2025?
Higher Risk Confirmed
A recent study (May 2025) confirmed that people with MS report more GI symptoms—including acid reflux—than the general population. Severity of reflux symptoms even tracked with MS progression.
- Motility Matters:
National research shows that MS patients are 2–3 times more likely to have esophageal motility disorders like achalasia or spasms. These can mimic or worsen typical GERD.
Prodrome: A Gut Feeling?
Emerging studies suggest that GI symptoms may show up even years before MS is diagnosed. So, if you have unexplained and persistent acid reflux alongside other subtle neurological changes, it’s important to talk to your doctor.
Practical Tips for Managing Acid Reflux with MS
While you can’t “cure” acid reflux, you can absolutely make it more manageable. Here’s how:
1. Tweak Your Habits
- Eat Small, Frequent Meals:
Large meals put pressure on your stomach and LES. Opt for smaller portions throughout the day. - Stay Upright:
Don’t lie down within 2-3 hours after eating. If reflux is a problem at night, elevate the head of your bed by 6–8 inches. - Identify Triggers:
Keep a food diary. Common culprits include coffee, chocolate, citrus, tomato, spicy foods, and alcohol.
2. Work With Your Medical Team
- Discuss Symptoms Openly:
Mention reflux, swallowing difficulty, or persistent cough to your neurologist and primary care provider. - Review Medications:
Some drugs for MS can worsen reflux. Your doctor may have alternatives or suggestions for timing doses. - Ask About Swallowing Evaluations:
If food sticks or you cough while eating, a speech-language pathologist can assess your swallow and suggest safer ways to eat.
3. Use Medications Wisely
- Antacids and Acid Suppressors:
Over-the-counter options like antacids, H₂-blockers, or proton pump inhibitors (PPIs) can help, but always use under medical guidance—especially if you take multiple prescriptions. - Prokinetics:
In rare cases, drugs that help food move through the GI tract faster may be recommended.
4. Move (as Much as You Can)
- Gentle Activity:
Even short walks after meals can aid digestion and reduce reflux. - Physical Therapy:
For those with advanced MS, a therapist can help with safe exercises tailored to your ability.
When to Seek Help
Red flags:
- Trouble swallowing or choking on food
- Weight loss without trying
- Vomiting blood or black stools
- Severe, persistent chest pain
If you experience any of these, call your doctor right away. Sometimes, reflux can cause or worsen aspiration (food or acid entering the lungs), which is especially risky in MS patients with swallowing problems.
Key Takeaways
- MS increases the risk of acid reflux and other GI symptoms by affecting the nerves and muscles that control your digestive system.
- Don’t ignore digestive issues. They’re common in MS, can worsen quality of life, and are treatable.
- Teamwork is essential: Work with your medical providers, and be open about ALL your symptoms—even those that feel embarrassing.
- Practical habits, medication tweaks, and exercise can make a real difference.
Living with MS is a journey full of surprises. By staying curious, proactive, and honest about every symptom—from head to gut—you can take charge of your health and find relief for acid reflux and beyond.
FAQs: MS & Acid Reflux
1. Can MS directly cause acid reflux?
Yes, MS can contribute to acid reflux by disrupting the nerves that control the muscles in your esophagus and stomach, leading to swallowing difficulties and slower stomach emptying, which increase reflux risk.
2. Are acid reflux symptoms different in people with MS?
The symptoms (heartburn, regurgitation, chest discomfort) are similar to those in the general population, but MS patients may also experience swallowing problems or choking due to nerve involvement.
3. Can acid reflux be an early sign of MS?
Some studies suggest GI symptoms, including reflux, may appear before MS is diagnosed, but acid reflux alone is common and not usually an early indicator of MS without other neurological symptoms.
4. What MS medications can worsen acid reflux?
Certain medications used in MS—such as anticholinergics (for bladder issues), muscle relaxants, and some antidepressants—can relax the lower esophageal sphincter, increasing the risk of reflux.
5. Is there a specific diet recommended for MS patients with acid reflux?
No single diet fits all, but eating smaller meals, avoiding trigger foods (like spicy or acidic items), and staying upright after eating can help manage both MS and reflux symptoms.
6. How can I tell if my swallowing problems are from MS or acid reflux?
MS-related swallowing issues usually stem from nerve damage, while reflux-related issues often occur after meals or at night. A speech-language pathologist or gastroenterologist can help differentiate and diagnose the cause.
7. Is it safe to use over-the-counter reflux medications with MS?
Generally, yes, but always consult your doctor or pharmacist, as some reflux medications can interact with MS drugs or mask other problems.
8. When should I see a specialist for my symptoms?
If you have persistent heartburn, trouble swallowing, frequent choking, unexplained weight loss, or chest pain, see your doctor or a GI specialist for evaluation.
9. Can exercise help reduce acid reflux if I have MS?
Gentle activity after meals (like walking) can help digestion and reduce reflux episodes, but exercise should always be adapted to your abilities and MS symptoms.
10. Are there long-term complications of untreated acid reflux in MS?
Yes. Chronic reflux can lead to esophagitis, strictures, Barrett’s esophagus, or aspiration pneumonia—risks that may be higher in MS due to swallowing problems. Treating reflux and working with your care team is crucial.










