When we think of spices that shaped history, ginger always stands near the top. From ancient Ayurvedic texts in India to trade routes that connected Asia with Europe, ginger wasn’t just valued for its fiery kick in food—it was treasured as a healing root. Even today, you’ll find it everywhere: fresh ginger root in your kitchen, ginger tea at your grandma’s, pickled ginger with sushi, gingerbread during the holidays, or even craft ginger brews at the local market.
But beyond its flavor and cultural charm, ginger has an impressive body of research behind it. Science keeps confirming what our ancestors knew—ginger can truly transform your health when consumed regularly. Let’s dive into the stunning health benefits of ginger, backed by the latest studies and practical ways to include it in your life.
1. Ginger for Digestion and Gut Health
One of the most well-documented benefits of ginger is its ability to support digestion. The root contains natural compounds like gingerols and shogaols that stimulate saliva and bile production, helping your body break down food more efficiently.
- If you suffer from bloating, indigestion, or a “heavy” feeling after meals, sipping on ginger tea or adding fresh grated ginger to warm water can make a noticeable difference.
- A 2024 review in Nutrients showed that ginger can speed up gastric emptying, meaning food leaves the stomach faster, reducing discomfort and acid reflux.
👉 If you want to explore this further, check out our deep dive: Ginger for Heartburn and Acid Reflux: Natural Relief or Digestive Myth?
2. Anti-Inflammatory and Pain-Relief Power
Ginger has been called “nature’s ibuprofen” for a reason. Its bioactive compounds fight inflammation at the cellular level. Research published in The Journal of Pain Research (2023) found ginger supplements effective in reducing muscle soreness after exercise.
- People with osteoarthritis reported reduced pain and stiffness when taking ginger regularly.
- Athletes use ginger shots or ginger tea post-workout for faster recovery.
This isn’t just folk wisdom—it’s clinically significant. Daily ginger intake can lower inflammatory markers like CRP (C-reactive protein), which is linked to chronic diseases.
3. Immunity and Respiratory Benefits
From grandma’s “ginger kadha” to modern herbal syrups, ginger has always been a go-to for colds and coughs. And now science explains why:
- Ginger relaxes airway muscles, which can ease breathing difficulties.
- A 2022 study in Frontiers in Pharmacology showed that fresh ginger extract helped suppress viral activity in respiratory infections.
This makes ginger especially useful during seasonal flu outbreaks or when your immunity feels compromised.
👉 You can learn more in our post: Ginger for Your Lungs: 5 Benefits and Practical Uses
4. Heart and Metabolic Health
Beyond the stomach and lungs, ginger has cardiovascular benefits too. Studies suggest it helps reduce LDL cholesterol and improve blood circulation. Its anti-inflammatory properties support arterial health, while its warming effect naturally stimulates blood flow.
- A 2023 Clinical Nutrition study reported that people who consumed ginger daily had improved blood sugar regulation—key for preventing type 2 diabetes.
- Combining ginger with turmeric, cinnamon, or lemon creates even more powerful effects on metabolism and weight management.
👉 Related read: Exploring the Science Behind Turmeric and Ginger for Effective Weight Loss
5. Everyday Ways to Enjoy Ginger
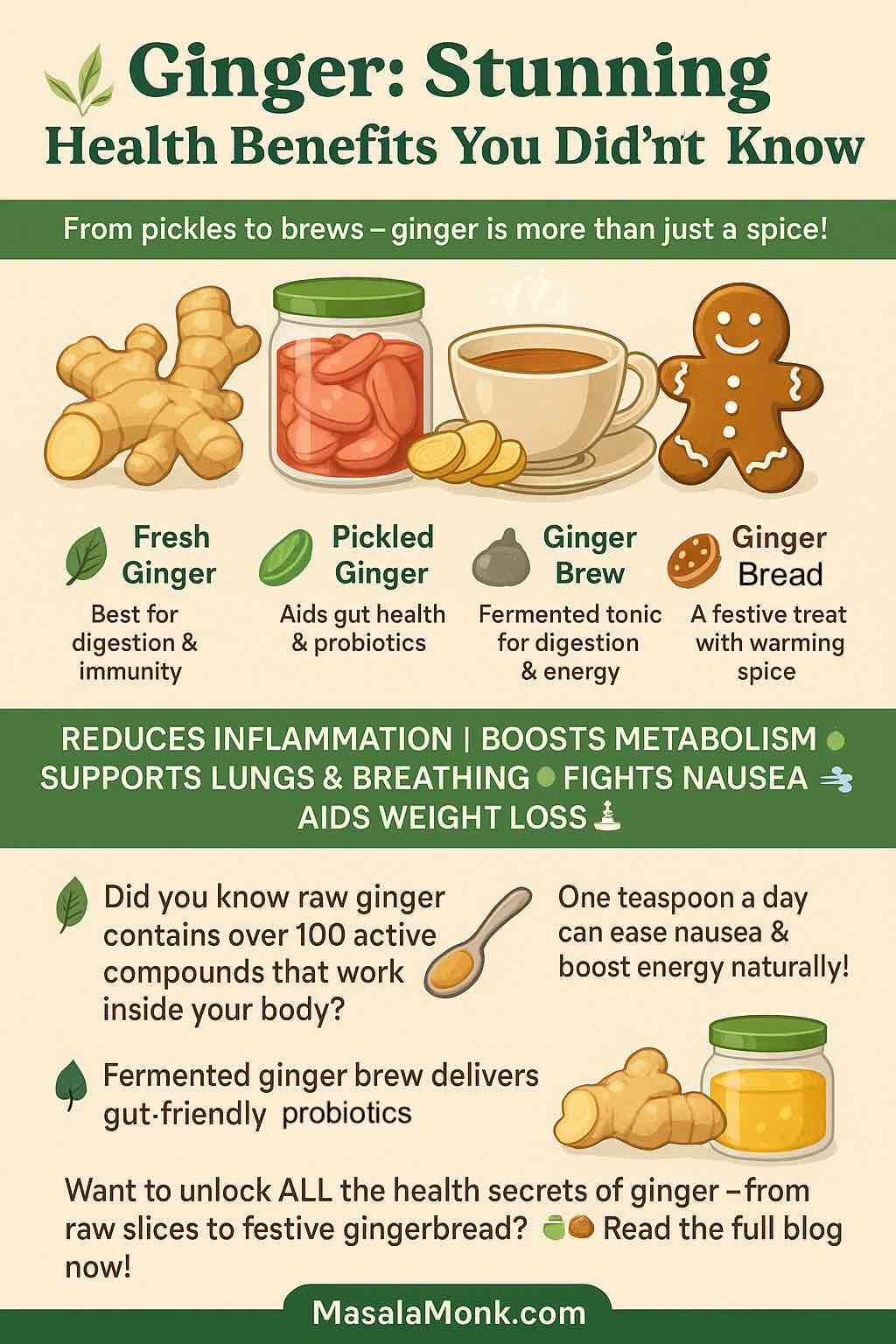
Now here’s where ginger shines: it’s versatile. Whether you like it raw, fresh, pickled, or brewed—there’s a way for everyone to bring it into daily life.
- Raw ginger: Spicy and pungent, excellent for smoothies or chewing small slices to fight nausea.
- Fresh ginger: Add to teas, curries, soups, or stir-fries for digestive comfort and flavor.
- Pickled ginger: Popular with sushi, but also excellent for gut health—fermented pickles provide probiotics plus ginger’s bioactive compounds. Pickling Your Way to Health: A Guide to Ginger Pickle Variations and Benefits
- Ginger brews & drinks: From homemade lemon-ginger teas to trendy ginger kombuchas and craft sodas, they hydrate while delivering antioxidants. 7 Ginger Drinks for Weight Loss and Well-Being
- Gingerbread & treats: While gingerbread cookies might not be a “superfood,” they still provide trace benefits from ginger—just balance them with healthier forms.
6. Skin, Topical, and Beauty Uses of Ginger
Ginger isn’t just for eating or drinking—it also has topical benefits. Traditional practices like the Pechoti method (applying oils to the belly button) have recently resurfaced in modern wellness trends. Ginger oil, when diluted properly, can be applied to the skin or used in massage blends for its warming and circulation-boosting properties.
- Skin glow: Ginger’s antioxidants help fight oxidative stress, reducing dullness and protecting against skin damage.
- Topical pain relief: Massaging ginger oil into sore muscles or stiff joints can reduce pain and stiffness, especially when paired with turmeric or black pepper oils.
- Stress relief: Aromatherapy with ginger essential oil has shown calming effects on the nervous system.
👉 For a full guide, read: Ginger Oil and the Belly Button: Benefits, Myths, and How to Use
7. Ginger for Weight Loss & Metabolic Boost
If you’re aiming to manage weight naturally, ginger deserves a place in your diet. It works in multiple ways:
- Thermogenic effect: Ginger slightly raises body temperature, which helps burn more calories.
- Appetite control: Research in Metabolism (2022) showed that drinking hot ginger tea reduced hunger between meals.
- Fat metabolism: Gingerols can enhance fat breakdown and prevent fat storage in animal studies.
No wonder ginger is featured in so many detox and weight-loss drinks:
- Pineapple + Cucumber + Ginger water for hydration and metabolism
- Lemon + Ginger water for digestion and cleansing
- Turmeric + Ginger + Cinnamon tea for fat-burning synergy
👉 Explore more here:
- Pineapple, Cucumber, and Ginger for Weight Loss: Myth and Facts
- Benefits of Cucumber, Lemon, and Ginger Water
- The Benefits of Turmeric Ginger Cinnamon Tea for Weight Loss and Overall Well-Being
8. Ginger and Pickling: Flavor + Health
Pickled ginger, or “gari,” isn’t just a sushi sidekick. Pickling ginger can actually enhance some of its digestive properties while adding probiotics (if fermented naturally).
- Digestive aid: Pickled ginger helps cleanse the palate and aid digestion during meals.
- Gut health: When prepared as a fermented pickle, ginger introduces beneficial bacteria to the gut.
- Low-calorie snack: A tangy, healthy option compared to processed snacks.
👉 Discover more recipes and benefits in: Pickling Your Way to Health: A Guide to Ginger Pickle Variations and Benefits
9. Ginger in Traditional and Festive Foods
While raw and fresh ginger are the healthiest, don’t dismiss its role in festive treats like gingerbread. Gingerbread may not be a “health tonic,” but it still carries microdoses of gingerols, and the warming aroma has a psychological comfort that boosts mood.
- Pairing gingerbread with ginger tea or a ginger brew can make the experience both tasty and mildly beneficial.
- Ginger beers and brews (including kombucha-based ones) are now backed by studies showing antioxidant and digestive perks.
👉 For more inspiration: 7 Ginger Drinks for Weight Loss and Well-Being
10. Fresh vs Raw Ginger: What’s the Difference?
This is a common question we see. “Fresh” and “raw” ginger are often used interchangeably—but there’s a nuance:
- Raw ginger: Simply uncooked ginger root, often chewed directly or added to smoothies/juices.
- Fresh ginger: Typically refers to the whole ginger root (as opposed to powdered/dried).
Both retain the maximum amount of antioxidants, enzymes, and vitamins. In contrast, powdered or dried ginger is convenient but slightly less potent.
11. Ginger for Whole-Body Wellness
Finally, ginger isn’t about one single benefit—it’s a holistic superfood. Regular use supports digestion, immunity, circulation, skin, weight management, and even mood. Whether you’re sipping on warm ginger tea in winter, crunching pickled ginger with sushi, or mixing up a summer ginger-cucumber detox water—this root adapts to every season and every lifestyle.
And science continues to uncover new angles: from cardiovascular health to anti-cancer potential. What’s exciting is that ginger remains one of the most accessible, affordable, and versatile natural remedies in the world.
Frequently Asked Questions About Ginger
1. Is raw ginger good for you?
Yes—raw ginger is the most potent form since it contains the highest amount of gingerols and enzymes. Chewing a small slice can relieve nausea, freshen breath, and support digestion. Just don’t overdo it, as raw ginger can be quite spicy on the stomach.
2. What are the benefits of fresh ginger vs dried?
Fresh ginger is best for digestion, immunity, and anti-inflammatory effects. Dried ginger is more warming in Ayurvedic use and often used for colds. Both have unique strengths, but fresh retains more antioxidants.
3. Does pickled ginger have health benefits?
Yes—pickled ginger aids digestion, especially when eaten with heavy or protein-rich meals. If fermented, it may also deliver probiotic benefits. Just watch for added sugar or excess salt in commercial versions.
4. What about ginger brew or ginger beer?
Homemade ginger brew (or naturally fermented versions) contains antioxidants and supports digestion. Commercial ginger beer often has added sugar, so it’s best enjoyed occasionally rather than daily.
5. Is gingerbread good for you?
Not exactly a superfood—but gingerbread does deliver a touch of real ginger’s warming properties. While the sugar content makes it a treat, pairing gingerbread with fresh ginger tea can balance indulgence with wellness.
6. Can ginger help with heartburn or acid reflux?
Yes—ginger is known to relax the gastrointestinal tract, which may reduce acid reflux symptoms. But in some sensitive people, too much raw ginger can trigger irritation. Moderation is key.
👉 Read more: Ginger for Heartburn and Acid Reflux: Natural Relief or Digestive Myth?
7. Can ginger boost weight loss?
Yes—ginger has thermogenic and appetite-suppressing effects, plus it supports fat metabolism. Combined with turmeric, cinnamon, or lemon, ginger drinks can naturally support weight goals.
8. How much ginger should you eat per day?
Most research suggests 2–4 grams per day (about a teaspoon of fresh grated ginger) is safe and effective for health benefits.
9. Does ginger really help your lungs?
Yes—gingerols help relax airway muscles, reduce inflammation, and improve circulation to the lungs. This is why ginger teas are often recommended for colds or respiratory discomfort.
👉 Read more: Ginger for Your Lungs: 5 Benefits and Practical Uses
10. Are there side effects of too much ginger?
Yes—excessive amounts (over 6–8 grams daily) may cause stomach upset, heartburn, or interact with blood-thinning medications. Always listen to your body.
Final Thoughts
Ginger is one of those rare foods that blends flavor, tradition, and modern science into one root. From calming an upset stomach to supporting heart health, from spicing up a pickle jar to lighting up holiday gingerbread, ginger finds a way to fit into every part of our lives.
What makes ginger so powerful is its versatility:
- Digestive health with fresh, raw, or pickled ginger
- Immunity and lung health with teas and brews
- Weight management with detox waters and spice blends
- Topical wellness with ginger oil massages
- Festive joy with gingerbread and ginger drinks
So the next time you slice into fresh ginger or sip on a warm brew, remember—you’re not just enjoying a spice, you’re fueling your body with centuries of wisdom and modern science combined.
✨ Whether you choose raw slices, soothing teas, refreshing pickles, or even festive gingerbread, this humble root has something to offer everyone.
👉 Dive deeper into more spice wisdom and practical recipes at MasalaMonk.com










