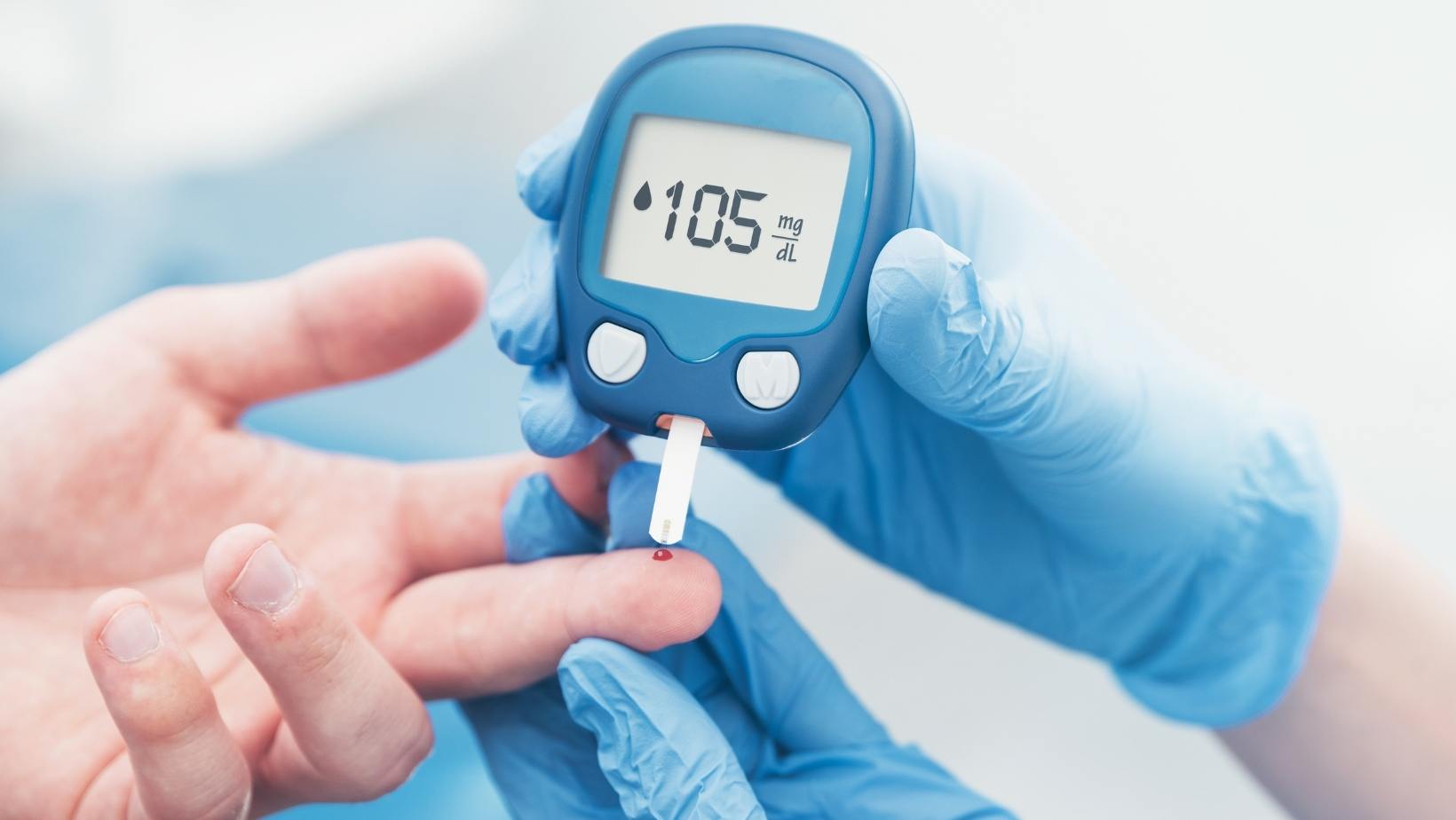
The ketogenic diet, characterized by low carbohydrate and high fat intake, has gained significant popularity over the years. As individuals strive to achieve and maintain a state of ketosis for weight loss or health reasons, the need for accurate and reliable ketone monitoring devices has become paramount. These devices, which measure ketone levels in blood, breath, or urine, have evolved significantly since their inception, offering users a range of options to suit their unique needs and preferences. This guide delves into the history of ketone meters, their effectiveness, and provides detailed insights into some of the top devices on the market.
2024 Update: Latest Advancements in Ketone Monitoring Technology
As we move into 2024, the landscape of ketone monitoring continues to evolve with innovative technologies and advanced devices. This update delves into the latest and most effective ketone meters available, along with groundbreaking developments in the field.
New Entrants in Ketone Meters
- Keto-Mojo GK+ Blood Glucose & Ketone Meter: A dual-function device that stands out for its accuracy in measuring both ketone and blood glucose levels. Its user-friendly interface and companion phone app make monitoring trends over time more accessible than ever.
- Kiss My Keto Ketone Blood Meter Kit: This meter is not just reliable but also visually appealing. It offers a unique combination of a 30-day money-back guarantee and a lifetime warranty, making it a risk-free investment for health enthusiasts.
- Nova Max Plus Glucose and Ketone Testing Meter: Offering dual functionality, this device is known for its precise readings and small blood sample requirement, catering to those who need consistent and accurate monitoring.
- BKT Keto Starter Kit: Tailored for beginners on a keto diet, this kit includes educational materials and a ketone meter with Bluetooth connectivity, allowing seamless tracking of both blood ketone and glucose levels.
- Biosense Fat Burn Tracker & Mobile App: Revolutionizing non-invasive ketone monitoring, this breath analyzer is a medical-grade device that measures breath acetone levels, accompanied by a comprehensive app.
- KETONIX Breath Ketone Analyzer: A compact and reliable breath analyzer, perfect for those on the go. It’s a long-term investment with no additional purchases required, making it a cost-effective option for regular monitoring.
Technological Breakthroughs
- Continuous Ketone Monitoring (CKM): Emerging technologies are bringing us closer to continuous ketone monitoring, potentially integrated into CGMs and automated insulin delivery systems. This advancement could provide crucial insights for individuals on insulin, those at risk of diabetic ketoacidosis, or anyone following a ketogenic diet.
- Non-Invasive Glucose Monitoring: Devices like GWave are leading the way in non-invasive glucose monitoring, using radiofrequency technology and AI algorithms. This technology offers a painless and convenient way to track glucose levels, showing promise for future integration with ketone monitoring.
Looking Ahead
The future of ketone monitoring looks bright, with technological advancements making these devices more accurate, user-friendly, and integrated with other health monitoring systems. These developments not only enhance the convenience of monitoring but also promise a more holistic approach to managing health and wellness on a ketogenic diet.
History of Ketone Meters
The first ketone meters were introduced in the early 1990s as a tool for diabetics to monitor their ketone levels and prevent ketoacidosis. Initially, these devices were primarily designed to measure blood glucose levels, with the ability to measure ketones being a secondary function. Over time, with the rise of the ketogenic diet, manufacturers began to produce dedicated ketone meters. These devices have since evolved, with modern meters offering features such as digital displays, memory storage, and even smartphone connectivity.
Top Ketone Meters and Ketosis Measuring Devices
Ketone meters have proven to be an effective tool for monitoring ketosis. Blood ketone meters are considered the gold standard due to their high accuracy. Breath ketone meters, while less accurate, offer a non-invasive alternative and can be more cost-effective in the long run as they do not require test strips. Urine test strips are the least accurate but are a cheap and easy way for beginners to start monitoring their ketone levels.
1. Keto Mojo Meter
The Keto Mojo Meter is a popular choice among those following a ketogenic diet. It’s a dual-function device that measures both glucose and ketones. The meter is known for its accuracy and ease of use. It provides results in seconds and uses separate test strips for glucose and ketones. The Keto Mojo Meter also has a companion app that allows you to track and monitor your results over time, making it easier to manage your diet and health.
2. Precision Xtra Meter
The Precision Xtra Meter, manufactured by Abbott, is a reliable and precise device that measures both glucose and ketones. It’s compact and portable, making it easy to use anywhere. The meter uses separate test strips for glucose and ketones. It’s a great tool for those who need to monitor their ketone levels regularly.
3. Biosense Breath Ketone Meter
The Biosense Breath Ketone Meter offers a non-invasive way to measure ketone levels. Instead of using blood, this device measures acetone levels in your breath, a byproduct of ketosis. It’s a great option for those who prefer not to use blood samples. The Biosense meter is also equipped with a mobile app for easy tracking and monitoring.
4. Freestyle Precision Neo
The Freestyle Precision Neo is another excellent product from Abbott. This meter measures both blood glucose and ketone levels. It’s known for its accuracy and the convenience of having a backlit screen and a sleek design. The device uses Freestyle Precision Neo test strips, which are easy to handle and require a small blood sample.
5. Ketonix Breath Ketone Analyzer
The Ketonix Breath Ketone Analyzer is a reusable breath analyzer that measures ketones. It’s a good option for those who want to avoid the ongoing cost of test strips. The Ketonix connects to your computer or mobile device, allowing you to track and record your ketone levels over time.
6. Fora 6 Connect
The Fora 6 Connect is a versatile 6-in-1 device that can measure both ketones and glucose, as well as hemoglobin, hematocrit, and uric acid levels. It’s particularly useful for people who need to monitor multiple health metrics. The device is easy to use and provides accurate results.
These are some of the top ketone meters and measuring devices available in the market. Each device has its unique features and advantages, so it’s important to choose the one that best fits your needs and lifestyle.
Other Solutions for Ketone Monitoring
While ketone meters and measuring devices provide a direct and accurate way to monitor ketone levels, there are other solutions available that can also help individuals track their state of ketosis.
Urine Test Strips
Urine test strips are a simple and cost-effective way to measure ketone levels. These strips change color when dipped in urine based on the concentration of ketones present. While not as accurate as blood ketone meters, they can be a good starting point for beginners or for those who prefer a non-invasive method of testing.
Breath Analyzers
In addition to the Biosense and Ketonix devices mentioned earlier, there are other breath analyzers available in the market. These devices measure the amount of acetone, a type of ketone, in your breath. While they may not be as accurate as blood tests, they are non-invasive and can be used multiple times without the need for additional supplies.
Diet and Symptom Tracking
Monitoring your diet closely and being aware of the symptoms of ketosis can also serve as a method of tracking. Symptoms of ketosis can include weight loss, increased focus and energy, suppressed appetite, and bad breath. However, this method is subjective and may not be as reliable as using a ketone meter or test strip.
Digital Apps
There are numerous digital apps available that can help you track your macronutrient intake and ensure you’re maintaining a ketogenic diet. While these apps don’t measure ketone levels directly, they can be a useful tool in managing your diet and ensuring you’re likely to be in a state of ketosis based on your food intake.
Regular Medical Check-ups
Regular medical check-ups and blood tests can also help monitor your ketone levels, especially if you have a medical condition like diabetes. This should be done under the guidance of a healthcare professional.
Remember, while these solutions can help monitor ketone levels, they may not be as accurate as a dedicated ketone meter. The best solution will depend on your personal preferences, budget, and specific health needs.
Warnings and Considerations When Using Ketone Meters
While ketone meters and other monitoring solutions can be extremely helpful for those following a ketogenic diet or managing conditions like diabetes, it’s important to be aware of certain warnings and considerations:
- Accuracy: Not all ketone meters and monitoring solutions provide the same level of accuracy. Blood ketone meters are generally considered the most accurate, while breath and urine tests may be less precise.
- Cost: The cost of ketone meters and test strips can add up over time. Consider the ongoing cost of test strips when choosing a meter. Breath analyzers and urine test strips may be more cost-effective options.
- Over-reliance: While these devices can provide valuable data, they should not replace professional medical advice. If you have a medical condition or are starting a new diet, it’s important to consult with a healthcare professional.
- Ketoacidosis: If you have diabetes, especially type 1, high levels of ketones can lead to a dangerous condition called ketoacidosis. If your ketone levels are consistently high, seek medical attention immediately.
- Hydration Levels: Hydration levels can affect the accuracy of urine test strips. If you’re dehydrated, the test may show higher ketone levels than are actually present in your body.
- Device Maintenance: Make sure to properly maintain your device according to the manufacturer’s instructions to ensure its longevity and accuracy. This can include regular cleaning and calibration.
- Interpretation of Results: Understanding what the results mean can sometimes be confusing. It’s important to educate yourself on how to interpret the results or seek guidance from a healthcare professional.
Remember, while ketone monitoring can be a useful tool, it’s just one piece of the puzzle. A balanced diet, regular exercise, and regular check-ups with your healthcare provider are also crucial for maintaining good health.
Frequently Asked Questions
- What is the purpose of a ketone meter in a ketogenic diet? A ketone meter is used in a ketogenic diet to measure the level of ketones in your blood, breath, or urine. This helps to ensure that you’re in a state of ketosis, which is the goal of the ketogenic diet. Being in ketosis means your body is burning fat for energy instead of carbohydrates.
- How does the Keto Mojo Meter work? The Keto Mojo Meter is a dual-function device that measures both glucose and ketones. It uses separate test strips for each measurement. After applying a small blood sample to the test strip, the meter will provide a reading within seconds.
- What makes the Precision Xtra Meter a reliable choice? The Precision Xtra Meter, manufactured by Abbott, is known for its reliability and precision. It measures both glucose and ketones, providing accurate readings that can help users manage their ketogenic diet or diabetes.
- How does the Biosense Breath Ketone Meter measure ketones? The Biosense Breath Ketone Meter measures acetone levels in your breath. Acetone is a byproduct of ketosis and can be detected in your breath. This device provides a non-invasive way to monitor ketone levels.
- What are the benefits of using the Freestyle Precision Neo? The Freestyle Precision Neo is known for its accuracy and convenience. It has a backlit screen and a sleek design, making it easy to use. It measures both blood glucose and ketone levels using Freestyle Precision Neo test strips.
- Why might someone choose the Ketonix Breath Ketone Analyzer? The Ketonix Breath Ketone Analyzer is a reusable breath analyzer that measures ketones. It’s a good option for those who want to avoid the ongoing cost of test strips. The Ketonix connects to your computer or mobile device, allowing you to track and record your ketone levels over time.
- What makes the Fora 6 Connect a versatile choice? The Fora 6 Connect is a versatile 6-in-1 device that can measure both ketones and glucose, as well as hemoglobin, hematocrit, and uric acid levels. It’s particularly useful for people who need to monitor multiple health metrics.
- How accurate are urine test strips for measuring ketones? While urine test strips are a simple and cost-effective way to measure ketone levels, they are generally less accurate than blood ketone meters. Hydration levels can also affect the accuracy of urine test strips.
- What are the benefits of using digital apps for ketone monitoring? Digital apps can help you track your macronutrient intake and ensure you’re maintaining a ketogenic diet. While these apps don’t measure ketone levels directly, they can be a useful tool in managing your diet and ensuring you’re likely to be in a state of ketosis based on your food intake.
- Why is it important to have regular medical check-ups when using ketone meters? Regular medical check-ups and blood tests can help monitor your ketone levels, especially if you have a medical condition like diabetes. High levels of ketones can lead to a dangerous condition called ketoacidosis. Regular check-ups ensure you’re using the ketone meter correctly and that your ketone levels are safe.
Conclusion
Ketone meters and other monitoring solutions are valuable tools for those following a ketogenic diet or managing conditions like diabetes. They provide a way to measure the level of ketones in your blood, breath, or urine, helping you ensure you’re in a state of ketosis. While these devices can provide valuable data, they should not replace professional medical advice. Always consult with a healthcare professional before starting a new diet or health regimen.
Blog Tags
Ketogenic Diet, Ketone Meters, Keto Mojo Meter, Precision Xtra Meter, Biosense Breath Ketone Meter, Freestyle Precision Neo, Ketonix Breath Ketone Analyzer, Fora 6 Connect, Ketosis, Diabetes Management, Health and Wellness, Diet and Nutrition, Ketone Monitoring, Blood Glucose Monitoring, Health Technology.