In Ayurveda, sesame oil (tila taila) is considered one of the most revered and widely used oils. It holds a prominent place both as a therapeutic agent and a base oil for many medicinal preparations. Here’s a detailed Ayurvedic perspective:
🔹 Qualities of Sesame Oil in Ayurveda
According to classical Ayurvedic texts (like Charaka Samhita and Sushruta Samhita), sesame oil has the following properties:
- Rasa (taste): Sweet (madhura) and slightly bitter/astringent
- Guna (qualities): Heavy (guru), unctuous (snigdha), and penetrating (sukshma)
- Virya (potency): Hot (ushna)
- Vipaka (post-digestive effect): Sweet (madhura)
- Dosha effects:
- Pacifies Vata effectively (very grounding and warming)
- Can mildly increase Pitta and Kapha if overused due to its heat and heaviness
🔹 Therapeutic Uses in Ayurveda
- Abhyanga (Oil Massage):
- Sesame oil is the gold standard for abhyanga, especially for calming Vata.
- Improves circulation, nourishes skin, strengthens tissues.
- Nasya (Nasal Therapy):
- Used in oil form for lubricating and clearing nasal passages.
- Helps with headaches, sinus congestion, and Vata disorders of the head.
- Shirodhara and Head Massage:
- Warm sesame oil poured on the forehead calms the nervous system.
- Reduces stress, insomnia, and mental agitation (especially Vata imbalance).
- Internal Use (when properly medicated and advised):
- Sometimes used as a base for medicated ghee or oil in internal detox protocols (panchakarma).
- Used in small quantities to improve digestion and promote joint health (under guidance).
- Wound Healing & Skin Disorders:
- Topical use promotes healing and soothes dry or irritated skin.
- Often used in herbal wound oils (Jatyadi Taila, etc.).
🔹 Cautions According to Ayurveda
- People with high Pitta (inflammation, skin rashes, excess heat) may need to avoid or modify its use—e.g., mixing with cooling herbs or oils.
- Overuse may aggravate Kapha (causing heaviness, sluggishness).
Summary Table:
| Aspect | Description |
|---|---|
| Dosha Action | ↓ Vata, ↗ (mildly) Pitta and Kapha |
| Key Uses | Massage, Nasya, Skin care, Wound healing |
| Ayurvedic Qualities | Heavy, Unctuous, Warming, Penetrating |
| Ideal For | Dry skin, Joint issues, Vata imbalance |
Here are some classical Sanskrit references and verses related to sesame oil (tila taila) from authoritative Ayurvedic texts:
🔹 1. Charaka Samhita – Sutrasthana 27.249–250
तिलतैलं गुरु स्थैर्यबलवर्णकरं सरम् |
श्रोत्र्यं बुद्धिदं मेध्यं बृंहणं रक्तपित्तजित् ||कृमिशोषविषच्छर्दिहिक्काश्वासज्वरापहम् |
वातासृग्दोषघ्नं दीपनीयं च चक्षुष्यम् ||
Transliteration:
Tilatailaṁ guru, sthairya-bala-varṇa-karaṁ, saram |
Śrotryaṁ buddhidaṁ medhyaṁ, bṛṁhaṇaṁ rakta-pittajit ||
Kṛmi-śoṣa-viṣa-chardi-hikkā-śvāsa-jvarāpaham |
Vātāsṛg-doṣaghnaṁ dīpanīyaṁ ca cakṣuṣyam ||
Meaning:
Sesame oil is:
- Heavy, improves stability, strength, complexion
- Beneficial for ears, intelligence, and mental faculties
- Nourishing, and helpful in blood and Pitta disorders
- Treats worms, emaciation, poisoning, vomiting, hiccup, dyspnea, fever
- Alleviates Vata and blood-related disorders, enhances digestion, and is good for eyes
🔹 2. Sushruta Samhita – Sutrasthana 45.97
तिलतैलं गुरु स्थैर्यबलवर्णकरं सरम् |
स्निग्धोष्णं विषदं तीक्ष्णं बृंहणं वातनाशनम् ||
Meaning:
Sesame oil is:
- Heavy, promotes stability, strength, and complexion
- Unctuous, hot, clear, penetrating
- Nourishing and alleviates Vata
🔹 3. Ashtanga Hridaya – Sutrasthana 5.41
सर्वेषां तैलानां तिलतैलं श्रेष्ठतमं स्मृतम् |
बलवर्णकरं दीपनं स्निग्धं गुरु च वातनुत् ||
Transliteration & Meaning:
Sarveṣāṁ tailānāṁ tilatailaṁ śreṣṭhatamaṁ smṛtam |
Bala-varṇa-karaṁ dīpanaṁ snigdhaṁ guru ca vātanut ||
Among all oils, sesame oil is considered the best.
It improves strength and complexion, enhances digestion, is unctuous and heavy, and removes Vata.
These verses form the classical Ayurvedic foundation for the use of sesame oil in external and internal therapies.
Here’s a summary connecting classical Ayurvedic attributes of sesame oil to modern therapeutic applications across key physiological systems:
🔹 Modern Therapeutic Translation of Classical Properties
| Ayurvedic Attribute | Classical Meaning | Modern Correlation / Application |
|---|---|---|
| Guru (Heavy) | Provides grounding, stability | Deeply nourishing for tissues; promotes muscle and joint recovery |
| Snigdha (Unctuous) | Lubricates tissues, counters dryness | Effective emollient for dry skin, joints; improves skin barrier and elasticity |
| Ushna (Hot potency) | Warming and stimulating | Improves circulation; relaxes stiff muscles; enhances metabolic activity locally |
| Saram (Flowing) | Penetrates fine channels | Excellent for transdermal absorption; carries herbs into deeper tissues |
| Vatahara (Alleviates Vata) | Calms movement, dryness, cold | Used for anxiety, insomnia, joint pain, nervous system imbalances |
| Medhya (Supports intellect) | Enhances cognitive function | May support brain function via oleic acid and antioxidant activity |
| Bṛṃhaṇa (Nourishing) | Builds tissues | Helps in recovery from fatigue, undernourishment, and emaciation |
| Dīpanīya (Enhances digestion) | Stimulates agni (digestive fire) | Used in medicated oils to support digestion, especially in weak Vata types |
| Cakṣuṣya (Good for eyes) | Supports eye health | May benefit eye massage (Netra Tarpana); reduces dry eyes and fatigue |
| Raktapittajit (Pacifies blood and Pitta) | Controls heat/inflammation | In combination with cooling herbs, helps in inflammatory skin issues |
| Śrotryaṁ (Good for ears) | Benefits auditory functions | Used in Karṇapūraṇa (ear oiling) to relieve tinnitus and dryness |
🔹 Applications by Body System
1. 🧠 Nervous System
- Abhyanga (Oil massage) with warm sesame oil reduces stress, supports sleep, and stabilizes mood.
- Shirodhara, head massage, and nasya therapies calm the mind and reduce anxiety or restlessness.
2. 🦴 Musculoskeletal System
- Relieves joint stiffness and pain due to its warming and lubricating properties.
- Often used as a base for herbal pain-relief oils (e.g., Mahanarayan Taila).
3. 🩺 Digestive & Metabolic System
- In small amounts, it supports Agni (digestive fire), especially in Vata-dominant types.
- Used internally under supervision in Snehapana (internal oleation) during Panchakarma.
4. 🧴 Skin & Integumentary System
- Soothes dry, flaky, and aging skin.
- Acts as a carrier for herbal extracts with antimicrobial or anti-inflammatory effects.
- Rich in Vitamin E, sesamol, and fatty acids – supports antioxidant defense.
5. 👂 ENT Health
- Used in Nasya (nasal instillation) and Karṇapūraṇa (ear oiling) to soothe dryness, improve clarity, and calm the senses.
🧪 Supporting Modern Findings (Briefly)
- Antioxidant & Anti-inflammatory: Due to sesamin, sesamol, and tocopherols.
- Antimicrobial: Traditional use in wound healing finds support in some modern studies.
- Transdermal Carrier: High permeability makes it ideal for delivering herbal actives through the skin.
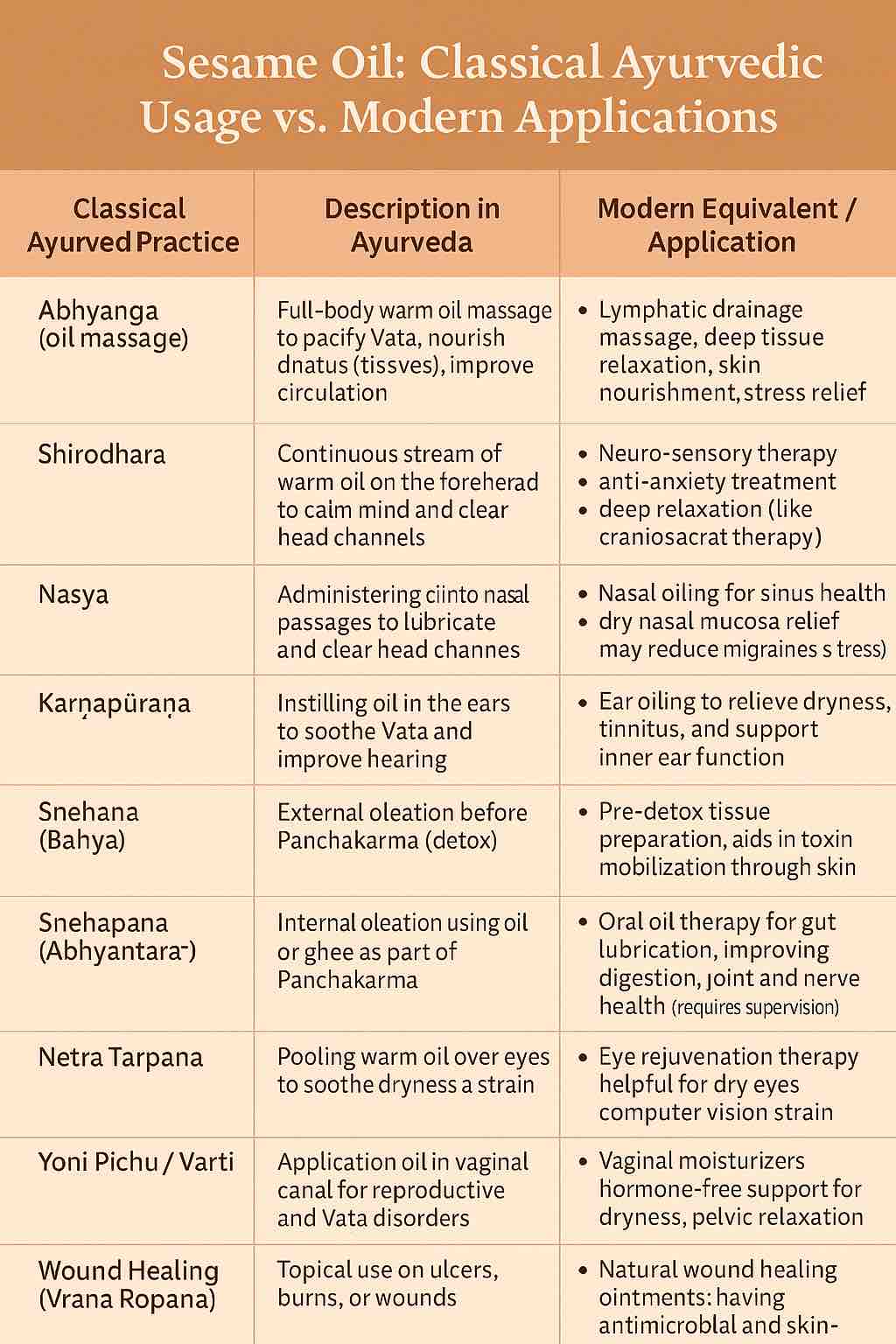
Here’s a comparative table mapping classical Ayurvedic uses of sesame oil to their modern therapeutic equivalents or interpretations:
🔁 Sesame Oil: Classical Ayurvedic Usage vs. Modern Applications
| Classical Ayurvedic Practice | Description in Ayurveda | Modern Equivalent / Application |
|---|---|---|
| Abhyanga (oil massage) | Full-body warm oil massage to pacify Vata, nourish dhatus (tissues), improve circulation | Lymphatic drainage massage, deep tissue relaxation, skin nourishment, stress relief |
| Shirodhara | Continuous stream of warm oil on the forehead to calm mind and balance doshas | Neuro-sensory therapy, anti-anxiety treatment, deep relaxation (like craniosacral therapy) |
| Nasya | Administering oil into nasal passages to lubricate and clear head channels | Nasal oiling for sinus health, dry nasal mucosa relief, may reduce migraines and stress |
| Karṇapūraṇa | Instilling oil in the ears to soothe Vata and improve hearing | Ear oiling to relieve dryness, tinnitus, and support inner ear function |
| Snehana (Bahya) | External oleation before Panchakarma (detox) | Pre-detox tissue preparation, aids in toxin mobilization through skin and lymph |
| Snehapana (Abhyantara) | Internal oleation using oil or ghee as part of Panchakarma | Oral oil therapy for gut lubrication, improving digestion, joint and nerve health (requires supervision) |
| Netra Tarpana | Pooling warm oil over the eyes to soothe dryness and strain | Eye rejuvenation therapy, helpful for dry eyes, computer vision strain |
| Yoni Pichu / Varti | Application of oil in vaginal canal for reproductive and Vata disorders | Vaginal moisturizers, hormone-free support for dryness, pelvic relaxation therapy |
| Wound Healing (Vrana Ropana) | Topical use on ulcers, burns, or wounds | Used in natural wound healing ointments; antimicrobial and skin-regenerative properties |
| Murdha Taila (Head oiling) | Application of oil on scalp for nervous system and hair health | Scalp oiling for hair growth, mental relaxation, nervous system regulation |
✅ Summary
Sesame oil’s traditional Ayurvedic roles align closely with modern wellness practices in:
- Neurotherapy
- Integrative dermatology
- Reproductive and ENT health
- Massage therapy
- Joint and musculoskeletal care
FAQs: Sesame Oil in Ayurveda – Classical Wisdom, Modern Use
1. Why is sesame oil considered the best in Ayurveda?
Ayurveda regards sesame oil (tila taila) as the most beneficial oil due to its nourishing, penetrating, warming, and Vata-pacifying properties. It enhances strength, complexion, and stability of the body.
2. What doshas does sesame oil balance?
Sesame oil primarily reduces Vata, and to some extent can aggravate Pitta or Kapha if overused or used without balancing herbs.
3. Can sesame oil be used daily for massage (abhyanga)?
Yes. Daily self-massage with warm sesame oil is highly recommended, especially for those with dry skin, stress, or Vata imbalance.
4. Is sesame oil safe to use on the face and hair?
Yes. It is excellent for the scalp and hair nourishment. For facial use, it suits dry or mature skin, but may be too heavy for oily/acne-prone skin.
5. How does sesame oil help the nervous system?
Its warming and grounding nature soothes the nervous system, reduces anxiety, supports deep sleep, and improves focus — especially when used in head massage or Shirodhara.
6. Can sesame oil be taken internally?
Yes, but only under the guidance of an Ayurvedic practitioner. It is used in Snehapana during detox and for gut lubrication, digestion, and joint support.
7. Is sesame oil used in wound care in Ayurveda?
Yes. Sesame oil is used in formulations like Jatyadi Taila for wound healing due to its antimicrobial and tissue-regenerating properties.
8. What is the modern equivalent of Nasya with sesame oil?
Nasal oiling for sinus health, dry nasal passages, and mental clarity. It may reduce migraines and tension when done correctly.
9. Can sesame oil be used for women’s reproductive health?
Yes. It’s used in therapies like Yoni Pichu to support vaginal dryness, pelvic muscle relaxation, and balance Vata in the reproductive system.
10. How does sesame oil benefit the eyes?
Through practices like Netra Tarpana, sesame oil soothes dry, fatigued eyes and may help with eye strain from screen use.









