In the realm of natural health remedies, clove water emerges as a powerful ally for anyone looking to enhance their weight loss journey and overall well-being. Steeped in both tradition and modern wellness practices, this simple yet potent concoction harnesses the myriad benefits of cloves—a spice revered for its medicinal properties. Let’s dive into how clove water can be the key to unlocking a healthier, more vibrant version of yourself.
The Mighty Clove: A Spice with a Punch
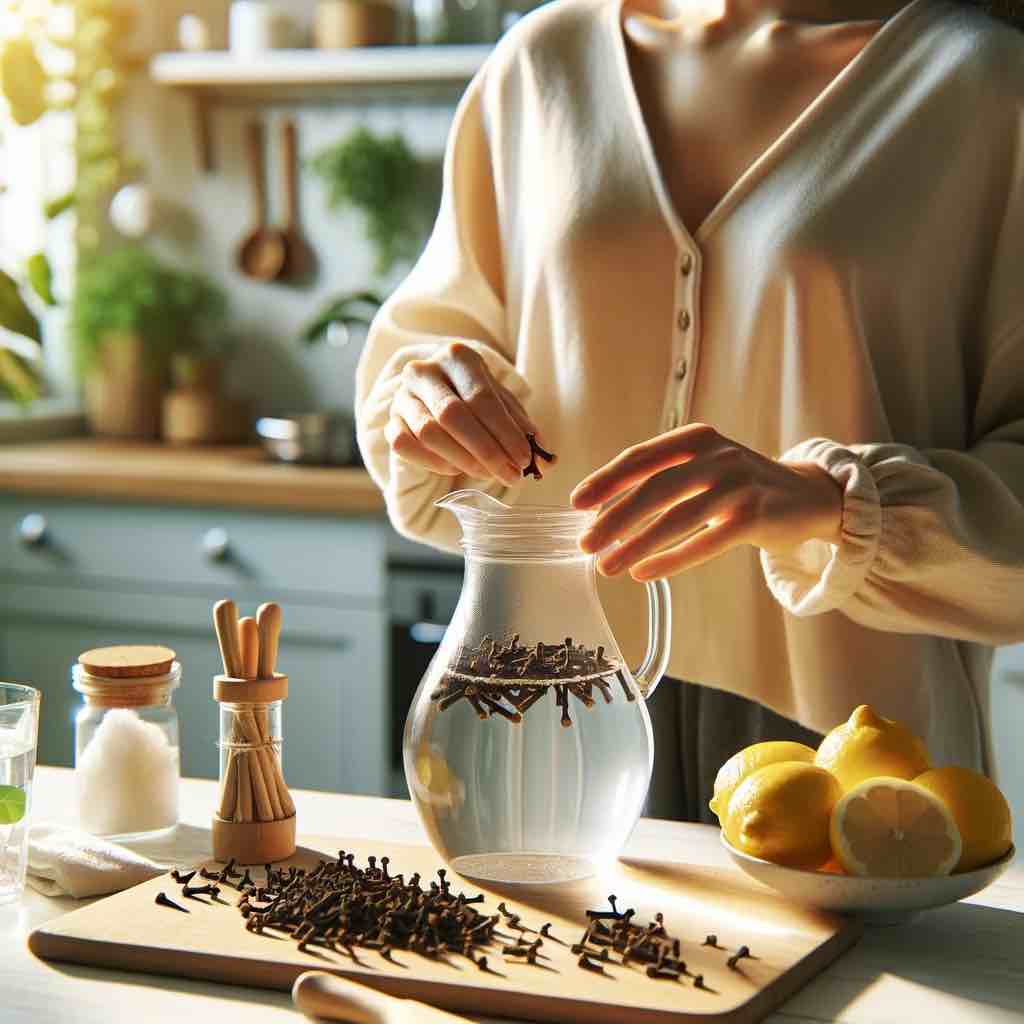
Cloves, the aromatic flower buds of the clove tree, have been utilized in culinary and medicinal contexts for centuries, prized for their ability to impart intense flavor and promote health. Rich in antioxidants and compounds like eugenol, cloves offer anti-inflammatory, antibacterial, and analgesic properties. When infused in water, these benefits translate into a refreshing beverage that not only tantalizes the taste buds but also contributes to physical wellness.
Unleashing the Benefits: Clove Water for Weight Loss
1. Metabolic Boost: Clove water can kickstart your metabolism, thanks to eugenol’s thermogenic properties. A more active metabolism means your body becomes more efficient at burning calories, paving the way for sustainable weight loss.
2. Appetite Control: Struggling with snacking urges or overeating? Clove water might just be the remedy. Its natural components help regulate hunger signals, making it easier to stick to healthy portion sizes.
3. Blood Sugar Balance: Fluctuations in blood sugar levels can lead to cravings and weight gain. Regular consumption of clove water helps maintain steady blood sugar levels, reducing cravings and supporting overall weight management.
4. Digestive Health: A healthy gut is crucial for effective weight loss. Clove water aids digestion and combats gastrointestinal issues, ensuring that your digestive system runs smoothly.
5. Detoxification: Cloves are a natural detoxifier. Clove water helps cleanse the liver, flush out toxins, and improve your body’s natural detoxification processes, contributing to better health and aiding weight loss efforts.
How to Incorporate Clove Water into Your Diet
Making Clove Water: Simply steep a teaspoon of whole cloves in a cup of boiling water for 8-10 minutes. For a stronger infusion, let it sit covered overnight. Strain before drinking, and consider adding a slice of lemon or a dash of honey for extra flavor.
When to Drink: For best results, consume clove water first thing in the morning on an empty stomach or 30 minutes before meals to aid digestion and control appetite.
Beyond Weight Loss: Holistic Health Benefits
Clove water’s benefits extend far beyond weight management. Its antibacterial and anti-inflammatory properties can enhance oral health, reduce pain and inflammation, and even improve cardiovascular health by lowering blood pressure and cholesterol levels.
A Word of Caution
While clove water is generally safe for consumption, moderation is key. High doses of cloves can lead to adverse effects, and pregnant or breastfeeding women, as well as individuals on certain medications, should consult with a healthcare provider before adding clove water to their regimen.
Embracing Clove Water: A Step Towards Holistic Wellness
Incorporating clove water into your daily routine is more than just a step towards achieving your weight loss goals; it’s a commitment to enhancing your overall health naturally. As you embark on this flavorful journey, remember that the best results come from a balanced approach that includes a nutritious diet, regular physical activity, and adequate rest. Here’s to unlocking the power of nature with clove water and toasting to a healthier, happier you.