Gaining weight might sound simple — just eat more, right? But anyone who has struggled with being underweight knows it’s not always that easy. Some people can eat and eat yet still find the number on the scale barely moving. Others may want to put on weight for health reasons, to recover from illness, or to build strength and muscle. In all these cases, the right weight gain foods can make the difference between frustration and steady progress.
And here’s the truth: it’s not just about eating more calories — it’s about eating the right calories. A giant bag of chips or endless fried food might give you quick energy, but it doesn’t nourish your body in the long run. On the other hand, healthy weight gain foods not only help you add pounds but also give your body the nutrients it needs to stay strong, energized, and balanced.
Think of it this way: if your body were a house, calories would be the bricks, and nutrients would be the cement holding everything together. You need both to build something solid.
Weight gain can feel as challenging as weight loss. And just like with weight loss, the approach matters. Crash diets, unhealthy shortcuts, or overeating the wrong foods may deliver quick results, but they rarely last. Worse, they can leave you with health problems you didn’t bargain for. The smarter route is to embrace calorie-dense foods that help you eat more without overwhelming your stomach, and that provide vitamins, minerals, protein, and healthy fats your body needs.
Why Choosing the Right Weight Gain Foods Matters
Many people assume gaining weight is easier than losing it. But ask anyone with a naturally fast metabolism, a small appetite, or a history of being underweight — it can feel just as challenging as shedding extra pounds. And just like weight loss, weight gain comes with its own pitfalls.
One common trap? Relying too heavily on processed junk food. Yes, these foods are high in calories, but they’re also high in sugar, unhealthy fats, and additives. They might add weight quickly, but they don’t support your overall health. In fact, a clinical trial on ultra-processed diets (Hall et al., 2019) showed that participants who ate highly processed foods consumed about 500 extra calories per day and gained nearly 1 kg in just two weeks — but much of it was fat, not lean muscle.
That’s why it’s so important to choose calorie-dense foods that combine energy with nutrition. Foods like nuts and seeds — protein-packed superfoods, dairy, whole grains, lean proteins, and healthy fats give your body both the extra calories it needs and the nutrients to build strength, improve immunity, and keep your energy steady throughout the day. As researchers explain in a review of overfeeding and body composition (Leaf et al., 2017), the quality of calories determines whether you mostly gain muscle or fat.
Another key reason to be mindful? How you feel while gaining weight matters. Eating heavy, greasy meals may leave you sluggish or uncomfortable, while a balanced mix of high calorie foods — spread across meals and snacks — can make the process feel sustainable and even enjoyable. Instead of forcing yourself to overeat, you can create a daily rhythm where adding extra calories feels natural.
In other words, the journey to a healthier weight isn’t about stuffing yourself with anything in sight. It’s about being strategic — choosing foods that are rich, satisfying, and good for you. This way, each bite brings you closer not just to your weight goals, but also to better health overall.
And now that we know why the right choices matter, let’s dive into the most effective weight gain foods — the ones that will help you add pounds while still feeling your best.
Top High-Calorie Foods for Weight Gain
When you’re trying to gain weight, you need foods that give you more “bang for your bite” — meaning lots of calories and nutrients in a reasonable portion. These are often called calorie-dense foods, and they make it easier to increase your daily intake without feeling like you’re constantly stuffed.
Nutrition science confirms that dietary energy density — how many calories are packed into each gram of food — strongly influences calorie intake. In fact, a review on energy density and appetite (Rolls et al., 2017) showed that calorie-dense foods help people eat more without overwhelming their appetite, which is especially helpful for underweight individuals.
Below are some of the best categories of weight gain foods to build your meals around. Each category has its own role to play — staples for energy, protein for muscle, fats for calorie boosts, and dairy for variety.
Calorie-Dense Staple Foods
Some foods form the foundation of a healthy weight gain diet. They’re versatile, affordable, and easy to prepare in countless ways.

- Rice – A simple cup of cooked white rice has about 200 calories, and it pairs well with curries, stir-fries, or beans. Brown rice adds fiber but is slightly less calorie-dense, so if your goal is purely weight gain, white rice can be an easier option.
- Oats – A warm bowl of oats at breakfast can keep you full for hours, especially when made with whole milk and topped with nuts or dried fruits. Oats also work brilliantly in smoothies.
- Potatoes & Sweet Potatoes – Starchy, filling, and nutrient-rich. Potatoes can be mashed, roasted, or turned into hearty curries, while sweet potatoes bring fiber and antioxidants along with the calories.
- Whole Grain Pasta & Bread – These are quick to cook and adapt to nearly any cuisine. Whole grain options add extra nutrition, while regular pasta or bread still delivers plenty of energy. Whole grains like quinoa are equally versatile — see these plant-based meal prep ideas using quinoa.
These calorie-dense foods provide steady energy and can be combined with proteins and fats to build balanced meals. For example, a bowl of rice with chicken curry and a drizzle of ghee instantly transforms into a calorie powerhouse.
Protein-Rich Foods for Weight Gain
Protein is the building block of muscle. If you want your weight gain to be more than just fat, you need plenty of it.
Research shows that adequate protein intake supports lean mass gains. A meta-analysis on protein intake (Nunes et al., 2022) concluded that eating 1.2–1.6 g of protein per kg bodyweight per day improves lean body mass outcomes. The International Society of Sports Nutrition (Jäger et al., 2017) also recommends spreading protein across meals (1.4–2.0 g/kg/day total) to maximize results. Here are some tips on how to get more protein in your diet to make that easier.
And more recently, a trial in young men (Hatamoto et al., 2024) showed that combining a calorie surplus with protein supplementation increased body protein mass, not just fat. Similarly, a global nutrition review (Smith et al., 2024) emphasized that meeting protein needs is still a challenge in many regions — making protein-rich foods a cornerstone of healthy weight gain.

Some of the best protein-rich foods for weight gain include:
- Eggs – Affordable, versatile, and packed with high-quality protein. A boiled egg, an omelette, or scrambled eggs with cheese are all excellent choices.
- Chicken & Turkey – Lean meats that help you grow muscle without excess fat. Adding a little cooking oil or butter while preparing them can easily boost calorie counts.
- Fish – Salmon, tuna, and mackerel provide not just protein but also healthy omega-3 fats that support brain and heart health.
- Beans & Lentils – Plant-based proteins that work well in curries, soups, or salads. Pairing them with rice or bread gives you complete protein combinations.
💡 Tip: Include a source of protein in every meal so that your extra calories go toward building muscle and strength.
Healthy Fats & Oils
Here’s a secret: fat has more than twice the calories of carbs or protein. That means a small serving goes a long way in boosting your intake. But not all fats are created equal. Focus on the ones that are both calorie-rich and heart-healthy.
Health authorities like Harvard’s Nutrition Source (Healthy Fats Guide) emphasize choosing unsaturated fats (nuts, seeds, olive oil, avocados) over trans fats or heavily processed oils. These calorie-dense but nourishing foods can support weight gain without increasing long-term health risks.

Some of the best options:
- Nuts & Seeds – Almonds, cashews, walnuts, chia seeds, flaxseeds. Snack on them raw, add them to salads, or blend them into shakes. You can learn more about the benefits of nuts and seeds here.
- Nut Butters – Peanut butter, almond butter, or mixed nut spreads are perfect on toast, in oatmeal, or even by the spoonful.
- Avocados – Creamy, versatile, and loaded with healthy fats. Try them on toast, in smoothies, or as guacamole.
- Olive Oil, Coconut Oil, Ghee – Perfect for cooking or drizzling over meals. A tablespoon of olive oil adds about 120 calories instantly.
Sprinkling seeds on your oats or adding a spoonful of peanut butter to a smoothie is a simple way to turn a snack into a high-calorie boost.
Dairy & Cheese
If you tolerate dairy well, it can be one of the easiest and tastiest ways to add calories and protein.
Research shows that dairy proteins like whey and casein are especially effective for muscle recovery and growth (Jäger et al., 2017, ISSN Position Stand). Whole milk and full-fat dairy also provide calcium and vitamin D, making them excellent foods for weight gain and overall nutrition.
- Milk – Whole milk adds richness to shakes and cereals and delivers about 150 calories per cup.
- Yogurt – Greek yogurt is higher in protein, while regular yogurt is great for blending into smoothies or eating with granola.
- Cheese – From cheddar to mozzarella to paneer, cheese is calorie-dense and adds flavor to almost any dish.
- Paneer (Cottage Cheese) – Popular in many Indian diets, paneer is full of protein and fat. A paneer curry with rice is both satisfying and calorie-rich.
These are some of the best foods to gain weight because they combine protein, fat, and carbs all in one. For example, a cheese omelette with toast or a bowl of yogurt with nuts can add hundreds of nutritious calories in minutes.
💡 Tip: Try combining foods from each group — rice (staple) + chicken (protein) + olive oil (fat) + yogurt (dairy) = a calorie-dense, balanced meal.
High-Calorie Snacks for Weight Gain
One of the easiest ways to increase your daily calorie intake is through snacks. Think of them as “mini meals” that bridge the gap between breakfast, lunch, and dinner. Instead of reaching for processed junk, you can stock up on nutritious, high-calorie snacks that give you both energy and nutrients. The trick is to make every bite count.

Research confirms that snacking can significantly influence weight status. A study on energy-dense snacking in adults (Skoczek-Rubińska et al., 2021, Appetite via ScienceDirect) found that high-calorie snack foods increased overall energy intake and were associated with higher body weight. Similarly, a review of discretionary snack habits (Cooke et al., 2024, Obesity Reviews via Wiley) concluded that large portion sizes and frequent “extra” snacks raise the risk of overeating and fat gain.
The message? Snacks are powerful tools — but choosing the right ones ensures those extra calories work for you, not against you.
Nut Butters & Spreads
Few foods are as simple and effective for weight gain as nut butters. A couple of tablespoons of peanut butter or almond butter can add over 200 calories — and that’s before you spread it on bread or blend it into a smoothie.
- Spread peanut butter on whole-grain toast and top with banana slices.
- Add almond butter to oatmeal for a creamy, filling breakfast.
- Stir a spoonful into your protein shake for an instant calorie boost.
These snacks aren’t just calorie-dense; they’re also rich in healthy fats and protein. A jar of nut butter is like a secret weapon in your kitchen for quick, nutritious calories.
Energy Bars & Trail Mix
If you’re busy and always on the go, energy bars and trail mix can be lifesavers.
- Energy Bars: Look for ones with nuts, dried fruits, and oats instead of sugary fillers.
- Trail Mix: A simple mix of cashews, raisins, almonds, sunflower seeds, and dark chocolate chunks makes for a tasty, calorie-rich snack.
A small handful of trail mix can pack 200–300 calories, making it one of the most convenient foods to eat to gain weight. Toss a bag into your work bag or keep some at your desk — no excuses to miss out on extra calories.
Studies show that frequent snacking occasions are strongly linked with calorie intake. For example, a U.S. study on snack frequency (Cowan et al., 2020, PLOS One) found that adults who snacked more often consumed significantly more total energy across the day. That means trail mix isn’t just convenient — it’s a proven way to sneak in extra calories without overstuffing at mealtimes.
Homemade Snack Ideas
Sometimes, the best snacks are the ones you make yourself — fresh, customizable, and much cheaper.
- Granola with Greek yogurt – a combo of carbs, protein, and fats.
- Roasted chickpeas – crunchy, spiced, and full of plant protein.
- Stuffed dates with walnuts or peanut butter – a naturally sweet, high-calorie treat.
- Cheese cubes with whole-grain crackers – simple but satisfying.
The beauty of homemade snacks is that you control the ingredients. Want more calories? Add extra nuts, seeds, or a drizzle of honey. Prefer lighter? Scale back slightly. Flexibility makes this approach sustainable.
💡 Tip: Plan snacks like you plan meals. Keeping them ready means you’ll always have something calorie-dense to reach for, instead of skipping or settling for empty calories.
Bananas, mangoes, dates, and dried fruits like raisins or apricots are calorie-dense fruit choices. Mangoes are especially powerful — discover more about mango for weight gain.
Protein Shakes and Drinks for Weight Gain
Sometimes chewing through another plate of food feels impossible. That’s where drinks come in — they’re easy to prepare, quick to consume, and surprisingly effective at helping you reach your calorie goals. Whether it’s a smoothie, a milkshake, or a custom protein blend, these weight gain drinks make it easier to add both calories and nutrients to your day.
Why Liquid Calories Work
Unlike solid foods, liquid calories often don’t trigger the same fullness signals. This means you can drink extra calories without losing your appetite for meals. In fact, a classic trial comparing liquid vs solid carbs (DiMeglio & Mattes, 2000, International Journal of Obesity via PubMed) found that liquid carbohydrate intake led to greater overall calorie consumption and weight gain compared to solids. More recent research backs this up: a study on liquid calories and energy compensation (Allison et al., 2013, Current Obesity Reports via PubMed Central) showed that sugary drinks add surplus calories because the body doesn’t fully compensate by eating less later.
For underweight individuals, this is actually an advantage. Shakes, smoothies, and milk-based drinks can boost calorie intake without making you feel uncomfortably stuffed.
Homemade Protein Shakes
Store-bought shakes can be expensive and often loaded with sugar, but making your own at home is not only cheaper — it’s healthier too.

Try this simple combo:
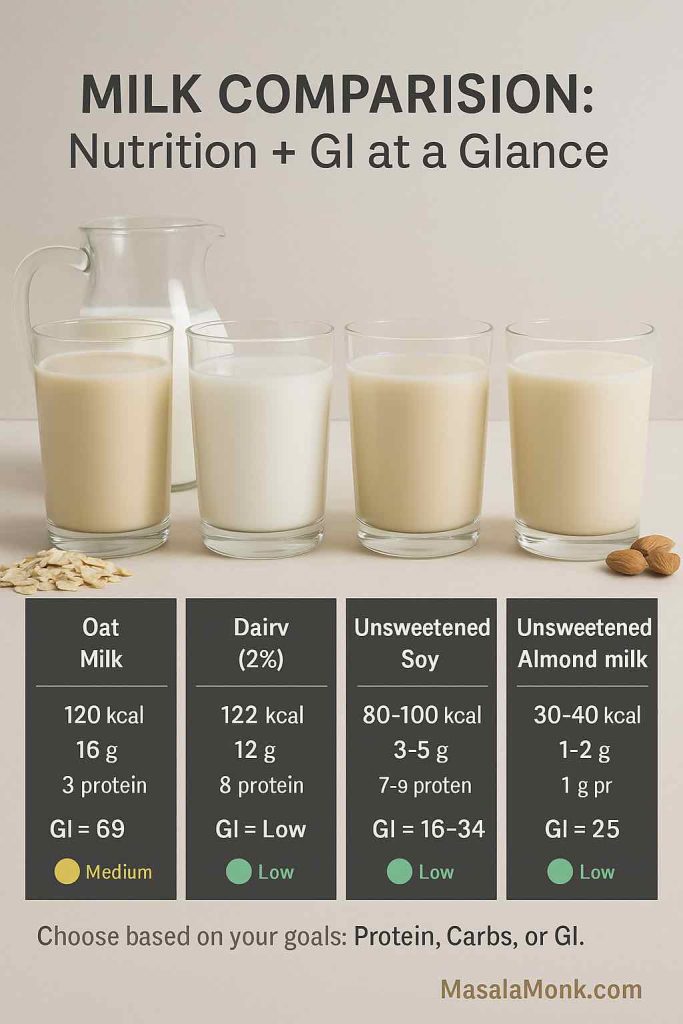
- Base: Whole milk or almond milk (200 calories per cup).
- Protein: A scoop of whey or plant protein powder (100–150 calories).
- Carbs: A banana or oats (100–150 calories).
- Fats: A spoonful of peanut butter or almond butter (100 calories).
Blend it all together, and you’ve got a protein shake for weight gain that can easily cross 500 calories. If you want even more, toss in some honey or dates for natural sweetness.
Weight Gain Milkshakes
If you want something richer, milkshakes are a delicious way to sneak in calories. They’re especially helpful for people with low appetites — it’s easier to drink a milkshake than to eat another meal.
- Classic weight gain milkshake: whole milk + ice cream + nut butter + cocoa powder.
- Fruit-based version: whole milk + mango or banana + Greek yogurt + honey.
Each serving can give you anywhere from 400 to 800 calories depending on ingredients, making them one of the fastest weight gain foods in liquid form.
Smoothies for Weight Gain
Smoothies are a lighter, fresher option but can still be packed with calories if you choose the right ingredients.
- Green smoothie: spinach + avocado + banana + protein powder.
- Tropical smoothie: mango + coconut milk + oats + chia seeds.
- Chocolate smoothie: cocoa + oats + almond butter + milk.
These are nutrient-dense weight gain drinks that combine vitamins, minerals, protein, and healthy fats — perfect for boosting calories without relying on junk.
💡 Tip: If you’re struggling to hit your calorie target, try adding one protein shake or milkshake between meals every day. That alone could mean an extra 500+ calories daily, which adds up fast over time.
Appetite feeling low? Along with calorie-dense foods, certain herbs and spices can help. Fenugreek, for example, has appetite-boosting effects — see the benefits of fenugreek for weight gain.
Sample Weight Gain Meal Plan
Knowing what to eat is one thing, but seeing it all come together in a daily routine can make the process feel much more doable. A meal plan doesn’t just provide structure — it also helps you make sure you’re hitting your calorie and protein goals without leaving it to chance.
Why Meal Structure Matters
Weight gain isn’t just about piling on calories randomly. How you distribute those calories — across meals, snacks, and even timing in the day — can influence both how much you eat and what kind of weight you gain.
A large prospective study of over 50,000 adults (Blazey et al., 2023, IJBNPA via BioMed Central) found that people who ate more frequently were more likely to gain weight over time. For those struggling to put on weight, that’s good news: splitting food into 5–6 meals and snacks instead of just 2–3 makes it easier to hit calorie goals. Similarly, a review on meal frequency and timing (Paoli et al., 2019, Nutrients via PubMed Central) highlighted that higher meal frequency helps distribute calories more evenly and may support energy balance.
Protein distribution matters too. Overfeeding research shows that when calories come with enough protein, more of the weight gain is lean mass rather than fat. For example, an overfeeding trial (Bray et al., 2012, JAMA) found that participants consuming extra protein gained muscle along with fat, while those on very low-protein diets mostly gained fat. In athletes, increasing meal occasions also helped maintain appetite and improved body composition during weight gain (Taguchi et al., 2020, IJSNEM via Human Kinetics).
Finally, when you eat may matter almost as much as what you eat. A systematic review (Liu et al., 2024, JAMA Network Open) found that front-loading calories earlier in the day (bigger breakfast and lunch, lighter dinner) supports healthier weight distribution and reduces fat accumulation. For someone aiming to gain weight, this means don’t skip breakfast and try to build meals consistently through the day, not just at night.
With those principles in mind, here’s a sample plan.
Breakfast Ideas
Start your day with something hearty and energizing. Skipping breakfast means missing a big opportunity to add calories.
- Oats with whole milk, banana, and peanut butter – rich in carbs, fats, and protein.
- Cheese omelette with whole-grain toast and avocado – savory, calorie-dense, and full of healthy fats.
- Greek yogurt with granola and nuts – a mix of protein and healthy fats for lasting energy.
These options are calorie-dense without feeling heavy, making them ideal for mornings.
Lunch & Dinner Ideas
Main meals are where you can really load up. The goal is to have a good balance of carbs, protein, and fats — every plate should include all three.
- Rice or quinoa with chicken curry, paneer, or lentils – add a drizzle of ghee or olive oil for extra calories.
- Pasta with olive oil, cheese, and grilled vegetables – simple, high-calorie, and customizable.
- Grilled salmon with roasted potatoes and avocado salad – protein, carbs, and healthy fats in one plate.
Remember, protein should be spread across the day. Following the evidence from Bray et al. (2012, JAMA), a portion of protein in every main meal helps ensure more of your weight gain is lean mass.
Snack & Shake Suggestions
Snacks and shakes are where you can add “bonus calories” throughout the day. Think of them as bridges between your main meals.
- Trail mix with nuts, seeds, and dried fruit – 200–300 calories in just a handful.
- Stuffed dates with nut butter – naturally sweet and calorie-dense.
- Homemade protein shake or milkshake – at least one per day can boost intake by 500+ calories.
- Nut butter on whole-grain crackers or toast – quick, simple, and satisfying.
Shakes are especially helpful if you struggle with appetite, since liquids often don’t suppress hunger as much as solid food. That’s exactly why studies like DiMeglio & Mattes (2000, Int. J. Obesity) found that liquid calories can promote greater overall energy intake.
Timing Tips
- Front-load calories – make breakfast and lunch hearty, instead of leaving the bulk for dinner.
- Snack smart – keep trail mix, granola bars, or nut butter handy so you never miss a chance for calories.
- Spread protein – aim for 20–30 g of protein per meal, as recommended by sports nutrition research.
- Consistency > perfection – even if you miss a snack or undershoot one day, hitting your plan most days will add up over weeks.
💡 Tip: If your appetite is low in the evening, don’t force a huge late dinner. Instead, build your day so most calories are eaten earlier, when your body can use them more efficiently.
To make your journey easier, here are some vegetarian high protein meal prep ideas that fit beautifully into a structured weight gain meal plan.
Weight Gain Foods for Women
For many women, gaining weight isn’t just about adding calories — it’s about doing so in ways that support strength, hormonal balance, and body composition. What works best will depend on life stage (young adult, midlife, pregnancy), activity levels, and metabolism. The following foods and strategies are especially helpful for women who want healthy, balanced weight gain.
Key Principles for Women
- Protein spread throughout the day: A protein distribution study in women (Johnson et al., 2022, Nutrients via PubMed Central) found that women who consumed at least 25 grams of protein across different eating periods (morning, midday, or evening) had higher lean mass and greater strength. This means it’s best not to save all your protein for dinner — include it in breakfast and lunch too.
- Meeting energy needs, especially if active: A review on female-specific nutrition (Wohlgemuth et al., 2021, JISSN via BioMed Central) emphasized that women, especially athletes, often under-consume calories relative to their needs. For healthy weight gain, women need to be intentional about fueling adequately with calorie-dense, nutrient-rich foods.
- Maintain protein during life transitions: During menopause, appetite regulation changes and protein intake often drops, which can lead to fat gain instead of lean mass. A study on menopause and protein leverage (Simpson et al., 2023, BJOG via Wiley) highlighted the importance of keeping protein intake steady to support healthy body composition.
Foods Especially Helpful for Women
- Whole milk, full-fat dairy, cheese, and yogurt — In a long-term cohort study of Swedish women (Mozaffarian et al., 2011, NEJM), higher whole milk and cheese intake was associated with more stable weight. For women worried about “bad fats,” this shows dairy can be a safe, nourishing calorie source.
- Pulses & legumes, eggs, lean meats, fish — Excellent protein sources to spread across meals, supporting lean mass development.
- Nuts, seeds, nut butters — Convenient and rich in healthy fats, protein, and calories. Great as snacks or toppings.
- Complex carbs & healthy fats — Whole grains, potatoes, olive oil, and avocados provide sustained energy and balance, especially when paired with protein.

Practical Tips & Strategies for Women
- Eat protein at breakfast: Many women skimp on protein early in the day. Adding eggs, Greek yogurt, or a protein shake ensures muscle synthesis starts from the morning.
- Use hunger cues: A study on women’s appetite and body composition (Wang et al., 2025, Nutrients via PubMed Central) showed that appetite signals correlate with body composition. If you feel hungrier earlier in the day, plan your bigger meals then.
- Don’t fear full-fat dairy: As shown in the Swedish women’s study (Mozaffarian et al., 2011, NEJM), whole milk and cheese can support steady weight gain while also providing essential nutrients.
- Adjust for life stage: During menopause, focus on higher protein and strength training to avoid fat-only gain. During pregnancy, calorie-dense but nutrient-rich foods (whole grains, nuts, dairy, lean proteins) are essential for both mother and baby.
💡 Tip: Women often underestimate how much protein and energy they need. Aiming for a mix of calorie-dense staples, protein-rich foods, and healthy fats spread throughout the day ensures weight gain is gradual, empowering, and supportive of long-term health.
Healthy Ways to Gain Weight (Without Junk Food)
Gaining weight quickly by leaning on fried snacks and sugary treats is easy — but it often leaves you sluggish and can raise long-term health risks. The smarter path is to build a steady calorie surplus with nutrient-dense whole foods so you feel stronger, not just heavier.
Why “quality calories” matter
A tightly controlled, inpatient trial showed that people eating an ultra-processed diet consumed ~500 extra kcal/day and gained weight within two weeks compared with a minimally processed diet — even though meals were matched for macros and palatability (Hall et al., 2019, NIH trial). A broader meta-analysis also links higher ultra-processed food intake with greater odds of overweight and obesity across diverse populations (Lane et al., 2023, Obesity Reviews).
Takeaway: junky, highly processed calories tend to drive overeating and fat gain. You’ll gain weight, but not in the way you want.
Focus on Whole, Calorie-Dense Foods
Energy density — calories per gram — is a key driver of how much we end up eating. For healthy weight gain, use calorie-dense foods that also carry vitamins, minerals, fiber, and healthy fats: nuts, seeds, avocados, olive oil, whole-fat dairy, whole grains, potatoes/sweet potatoes. The science supports using energy density intentionally, not accidentally.
How to apply it: add a tablespoon of olive oil to cooked grains, sprinkle nuts and seeds onto yogurt/oats/salads, and pair starchy staples with protein and a fat source.

Make Every Meal Work Harder
Think of each plate as an opportunity. Simple tweaks can turn an ordinary meal into a calorie-dense powerhouse:
- Add olive oil or ghee when cooking rice or vegetables.
- Sprinkle nuts and seeds onto oatmeal, yogurt, or salads.
- Blend fruits with milk, protein powder, and nut butter for shakes.
These small upgrades add hundreds of calories without making your meal feel overwhelming.
Balance Calories with Nutrients
Calories matter, but so does quality. Combining carbs, proteins, and fats in every meal ensures your weight gain is steady and balanced. For example: rice + lentils + ghee; or chicken + potatoes + avocado salad. This approach helps you gain not just fat, but muscle and strength too.
Be Consistent, Not Extreme
Weight gain takes time. Just as losing weight doesn’t happen overnight, building healthy mass is a gradual process. Aim for slow, steady progress — around 0.5 to 1 kg per week is a safe and sustainable goal.
Consistency matters more than perfection. Even if you can’t hit your calorie target every single day, staying close most of the time will move you toward your goal.
💡 Remember: food is fuel, but it’s also joy. Explore new recipes, experiment with shakes, and celebrate small wins along the way. Healthy weight gain is not just about the number on the scale — it’s about feeling stronger, more confident, and more energized in your own skin.
Conclusion: Building a Healthier You, One Bite at a Time
Gaining weight doesn’t have to feel like a battle or a burden. With the right approach, it can actually be enjoyable — a chance to explore new foods, create satisfying meals, and nourish your body in ways that make you feel stronger and more energized. By focusing on weight gain foods that are calorie-dense yet wholesome, you’re not just adding numbers to the scale — you’re building better health from the inside out.
Whether it’s a creamy shake between meals, a hearty bowl of oats in the morning, or a paneer curry at dinner, each choice adds up. Remember, consistency is the secret ingredient. Small, intentional steps taken daily will move you closer to your goal, without leaving you feeling stuffed, sluggish, or deprived.
Most importantly, give yourself patience and kindness along the way. Just as losing weight is a journey, so is gaining it. Celebrate the progress, however small, and trust that every nourishing bite is bringing you closer to the healthier, fuller version of yourself.
Frequently Asked Questions About Weight Gain Foods
1. What are the best foods to gain weight naturally?
The best foods for healthy weight gain are calorie-dense, nutrient-rich choices like nuts, seeds, avocados, full-fat dairy, whole grains, potatoes, and protein-rich foods such as eggs, chicken, and beans. These add calories while also nourishing your body.
2. How much protein should I eat if I want to gain weight?
Protein is crucial for building muscle as you gain weight. Aiming for 1.6–2.2 grams per kilogram of body weight per day works well for most people. Spreading protein across meals helps your body absorb it more effectively.
3. Can women eat the same weight gain foods as men?
Yes, but women often need to be more intentional about protein and calorie intake. Foods like dairy, nuts, legumes, and whole grains are excellent choices, especially during active years, pregnancy, or menopause.
4. Are weight gain shakes healthy?
They can be — if you make them with whole ingredients. Blending milk or yogurt with oats, bananas, nut butter, and protein powder creates a balanced shake that supports both calorie and nutrient needs.
5. How fast can I expect to gain weight?
A steady and safe pace is about 0.25–0.5 kg (0.5–1 lb) per week. This rate allows your body to build lean mass while minimizing excess fat gain.
6. Do I need supplements to gain weight?
Not always. Whole foods should be your foundation, but supplements like whey protein or mass-gainer powders can help if you struggle to eat enough. They’re useful as a boost, not a replacement for meals.
7. What’s the healthiest way to snack for weight gain?
Opt for calorie-dense snacks that also bring nutrients: trail mix, stuffed dates, peanut-butter toast, or granola with yogurt. These snacks help you eat more without relying on processed junk food.
8. Should I eat more meals or bigger portions?
Both can work, but many people find it easier to eat 5–6 smaller meals and snacks rather than forcing large plates. Frequent meals keep your energy steady and calories high without discomfort.
9. Is rice good for gaining weight?
Yes. Rice is inexpensive, easy to digest, and pairs well with proteins and fats. For extra calories, cook it with ghee, olive oil, or pair with beans, paneer, or chicken.
10. Which fruits help with weight gain?
Bananas, mangoes, dates, and dried fruits like raisins or apricots are calorie-dense fruit choices. Pairing them with nut butter or yogurt makes them even more filling and nutritious.
11. Can I gain weight while eating healthy?
Absolutely. The key is to focus on calorie-dense whole foods instead of relying on processed fast food. By choosing nuts, dairy, whole grains, and healthy oils, you’ll gain weight that supports strength and energy.
12. What drinks are good for weight gain?
Homemade shakes and smoothies are best. Try milk or yogurt with fruit, oats, nut butter, and optional protein powder. Avoid sodas and sugary drinks, since they add empty calories without real nutrition.
13. Are high-calorie foods bad for me?
Not if you choose the right ones. Foods like nuts, seeds, avocado, olive oil, and whole-fat dairy are calorie-rich but also provide essential nutrients. It’s the ultra-processed, low-nutrient foods you want to limit.
14. How can I increase appetite to eat more?
Start with smaller, more frequent meals, use herbs and spices to make food more appealing, and try liquid calories like smoothies if solid meals feel heavy. Gentle exercise like walking can also stimulate appetite.
15. What’s the difference between gaining weight and gaining muscle?
Gaining weight just means adding mass — but without enough protein and strength training, it’s mostly fat. To gain lean muscle, combine calorie-dense foods with resistance exercise and spread protein intake throughout the day.