As Paxlovid becomes a common treatment for COVID-19, many people wonder about its side effects. If you’re asking questions like “Does Paxlovid cause diarrhea?”, “Can Paxlovid cause nausea?”, or want to know the worst side effects of Paxlovid, you’re not alone. This comprehensive guide breaks down everything you need to know about Paxlovid’s side effects — from common symptoms like diarrhea and nausea to rarer but serious issues.
What is Paxlovid?
Before diving into side effects, it helps to understand what Paxlovid is. Paxlovid is an antiviral medication prescribed to reduce the severity of COVID-19 in high-risk patients. It contains two drugs — nirmatrelvir and ritonavir — that work together to stop the virus from replicating. The treatment typically lasts five days.
Common Side Effects of Paxlovid
Like all medications, Paxlovid can cause side effects, but most are mild and temporary. Here are the most frequently reported:
1. Diarrhea and Stomach Issues
Diarrhea is one of the top side effects users report. You might also experience stomach pain, cramps, or an upset stomach. This happens because Paxlovid can irritate your gastrointestinal (GI) tract temporarily. Usually, diarrhea resolves on its own after treatment ends.
Quick Tip: Stay hydrated and eat bland foods like bananas or rice to ease symptoms.
2. Nausea and Vomiting
Feeling nauseous or actually vomiting is another common complaint. This can be unsettling but usually doesn’t last long. If nausea is severe, speak with your healthcare provider about possible remedies or if you should continue treatment.
3. Headaches
Many people experience headaches while taking Paxlovid. This is generally mild and can be managed with over-the-counter pain relievers, but consult your doctor if headaches worsen or don’t go away.
4. Altered or Metallic Taste
A weird metallic or bitter taste in the mouth, often called “Paxlovid mouth,” is very common. This strange taste sensation is harmless and typically fades soon after completing the treatment.
What Are the Worst Side Effects of Paxlovid?
While most side effects are manageable, some rare but serious side effects need urgent attention:
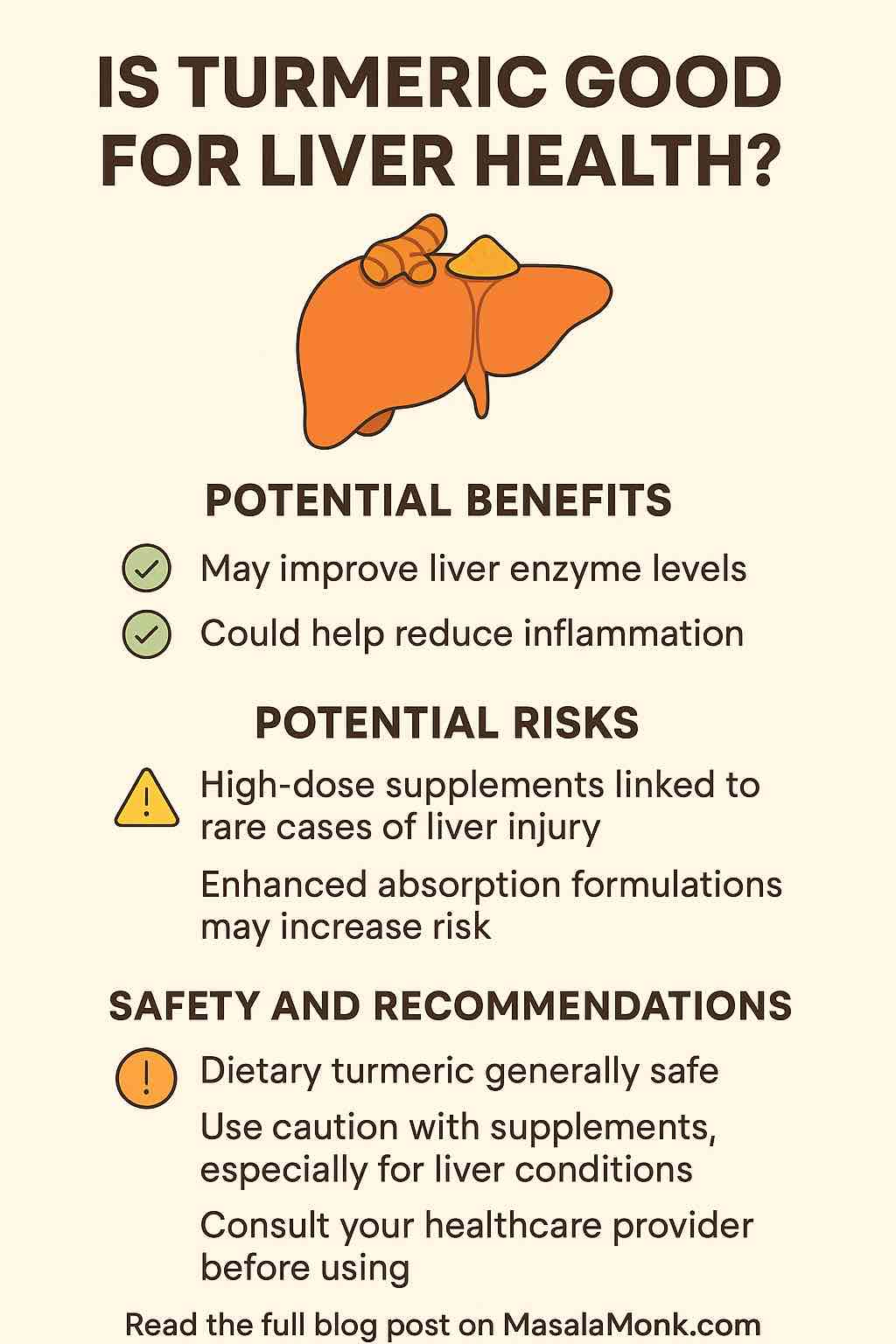
- Liver problems: Symptoms include yellowing skin or eyes, dark urine, severe abdominal pain, or itchy skin.
- Allergic reactions: Look out for rash, swelling of the face or throat, difficulty breathing, or hives.
- Bradycardia: An uncommon slow heart rate, though very rare.
- Severe electrolyte imbalances: Such as low sodium levels (hyponatremia).
If you experience any of these, seek emergency medical help immediately.
Does Paxlovid Cause Diarrhea and Nausea?
Short answer: Yes, it can.
Both diarrhea and nausea are among the most commonly reported side effects in clinical trials and real-world use. They are generally mild and temporary. Understanding these symptoms helps you prepare and manage them better, reducing the risk of dehydration or treatment interruption.
Can Paxlovid Cause Headaches?
Yes. Headaches are another relatively common side effect but are usually mild and short-lived. If your headache is severe or persistent, it’s important to discuss this with your healthcare provider.
How to Manage Paxlovid Side Effects
Here are practical tips to make your Paxlovid treatment more comfortable:
- Stay hydrated: Drink plenty of fluids, especially if you experience diarrhea or vomiting.
- Eat light meals: Bland foods like toast, bananas, or rice can reduce nausea and stomach upset.
- Use over-the-counter meds: For headaches, acetaminophen or ibuprofen (if not contraindicated) can help.
- Monitor symptoms: Keep track of side effects and talk to your doctor if they worsen or last beyond the treatment period.
Important Considerations: Drug Interactions & Contraceptives
Paxlovid can interact with certain medications due to ritonavir’s effect on liver enzymes. Always inform your doctor about all medicines and supplements you take.
For women using oral contraceptives, severe vomiting or diarrhea during Paxlovid treatment may reduce contraceptive effectiveness. Use backup contraception or consult your healthcare provider for advice.
When to Contact Your Doctor About Paxlovid Side Effects
Seek medical advice if you experience:
- Persistent or severe diarrhea, nausea, or vomiting.
- Signs of liver trouble: yellowing skin/eyes, dark urine.
- Allergic reactions: rash, swelling, difficulty breathing.
- Unusual fatigue, dizziness, or chest pain.
Final Thoughts
Paxlovid is a powerful tool against COVID-19 and is generally safe with mostly mild side effects. Knowing what to expect — from diarrhea and nausea to headaches and a strange taste — can ease anxiety and help you manage symptoms effectively. If in doubt, always consult your healthcare provider.
Have you experienced Paxlovid side effects? Share your story or ask questions in the comments below!
FAQs About Paxlovid Side Effects
1. Does Paxlovid cause diarrhea?
Yes, diarrhea is a common side effect of Paxlovid. It usually resolves shortly after completing the treatment.
2. Can Paxlovid cause nausea or vomiting?
Yes, many patients report nausea and sometimes vomiting during treatment. These symptoms are typically mild and temporary.
3. What are the most common side effects of Paxlovid?
Common side effects include diarrhea, nausea, headache, altered taste, vomiting, and stomach pain.
4. Are there any serious side effects of Paxlovid?
Rarely, Paxlovid can cause serious side effects such as liver problems, allergic reactions, slow heart rate, or severe low sodium levels.
5. How long do Paxlovid side effects last?
Most side effects last only during the 5-day treatment period and improve soon after.
6. Can Paxlovid cause headaches?
Yes, headaches are a reported side effect but are usually mild and manageable.
7. What should I do if I experience severe side effects?
Contact your healthcare provider immediately if you have symptoms like jaundice, rash, swelling, difficulty breathing, or severe abdominal pain.
8. Will Paxlovid affect my other medications?
Paxlovid can interact with some medications, especially due to ritonavir. Always inform your doctor about all medications you’re taking.
9. Can Paxlovid reduce the effectiveness of birth control pills?
Severe vomiting or diarrhea during treatment may reduce contraceptive effectiveness. Use backup contraception and consult your doctor.
10. Is it safe to take Paxlovid if I have pre-existing liver or kidney problems?
Patients with liver or kidney issues should discuss with their healthcare provider before starting Paxlovid, as dose adjustments may be needed.