Discover over 30 foods rich in Vitamin C (ascorbic acid), including fruits, vegetables, and fortified options. Learn how they benefit immunity, skin, and energy—plus tips for easy daily intake.
🧬 Why Your Body Loves Vitamin C
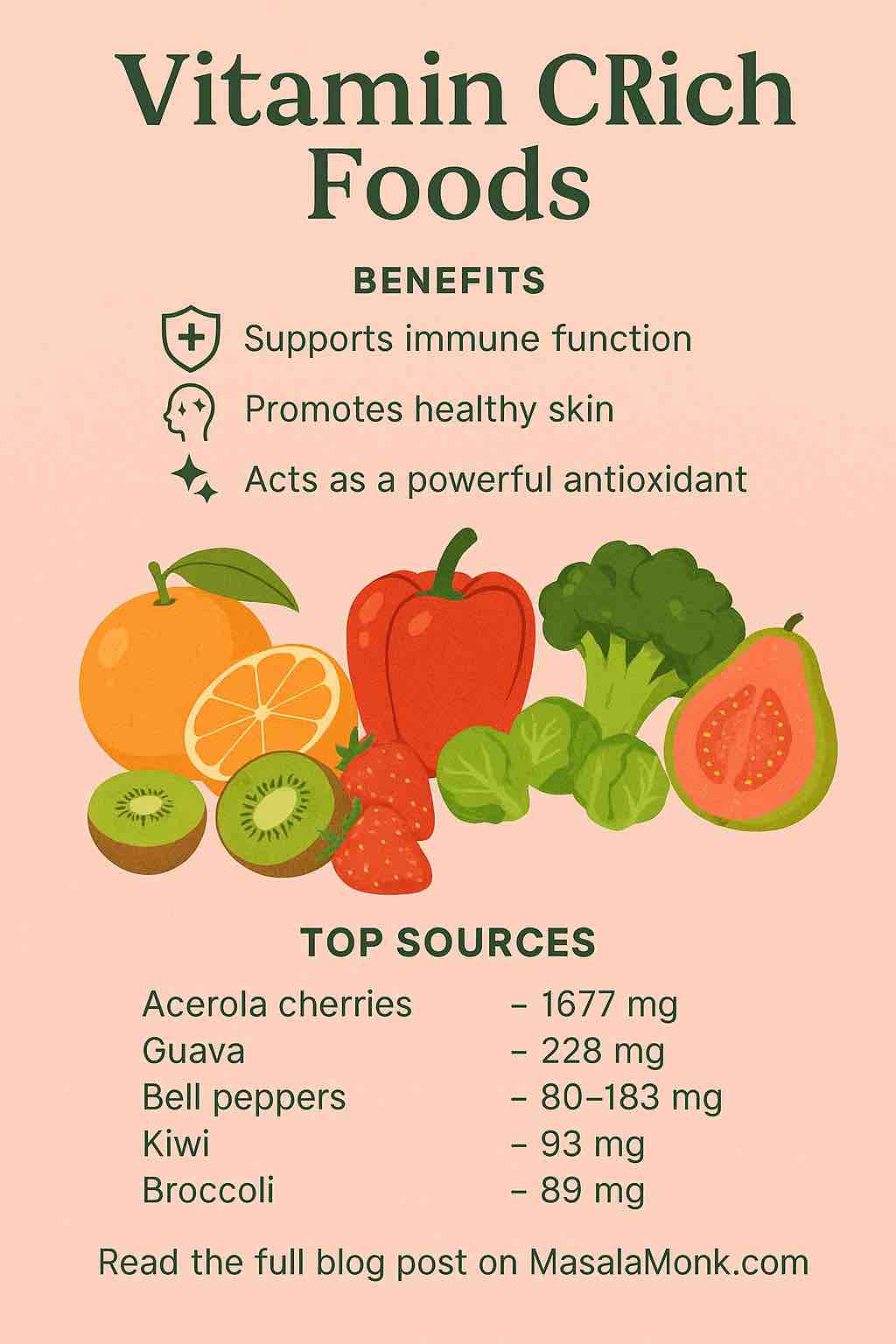
Vitamin C, also known as ascorbic acid, is a water-soluble vitamin that’s essential for numerous physiological processes:
- Supports immune function by stimulating white blood cells
- Promotes collagen production for healthy skin, joints, and blood vessels
- Aids iron absorption from plant-based foods, helping to prevent anemia
- Acts as a powerful antioxidant, neutralizing harmful free radicals
- Helps regenerate other antioxidants, like Vitamin E
What makes Vitamin C unique? Your body can’t produce it on its own—and since it’s water-soluble, excess amounts aren’t stored. That means you need to replenish it every single day.
🥇 Top 15 Vitamin C Rich Foods (per 100g)
| Food | Vitamin C (mg) | Key Benefits |
|---|---|---|
| Acerola Cherries | 1677 | Extreme C concentration, supports immune health |
| Camu Camu | ~2800 (fresh) | Amazonian fruit, powerful antioxidant |
| Guava | 228 | Excellent daily source, supports skin |
| Blackcurrants | 181 | Boosts immunity, rich in anthocyanins |
| Red Bell Peppers | 127 | High in C, versatile and low-calorie |
| Kiwi | 93 | Skin health, digestion support |
| Strawberries | 59 | Skin-friendly, anti-inflammatory |
| Oranges | 53 | Classic C source, easy to consume |
| Papaya | 61 | Skin glow, digestion aid |
| Pineapple | 48 | Combats inflammation (bromelain) |
| Mango | 36 | Tasty and nutrient-dense |
| Brussels Sprouts | 85 | Great for detox, rich in fiber |
| Broccoli | 89 | Cruciferous, great cooked or raw |
| Kale (raw) | 120 | Dense greens for iron + C combo |
| Yellow Bell Peppers | 183 | Highest among peppers, immunity hero |
🥬 Vegetables High in Vitamin C: Not Just Citrus!
While most people think of fruits when they hear “Vitamin C,” many vegetables are equally powerful.
🌿 Cruciferous Vegetables
These are anti-inflammatory, cancer-fighting, and rich in ascorbic acid:
- Kale – 120 mg
- Broccoli – 89 mg
- Cauliflower – 48 mg
- Brussels Sprouts – 85 mg
- Cabbage – 36 mg
🫑 Bell Peppers
Bright, crunchy, and sweet—bell peppers are incredibly Vitamin C-rich:
- Yellow Bell Peppers – 183 mg
- Red Bell Peppers – 127 mg
- Green Bell Peppers – 80 mg
🥗 Leafy Greens & Others
- Spinach (raw) – 28 mg
- Mustard Greens – 70 mg
- Swiss Chard – 30 mg
- Turnip Greens – 60 mg
✅ Tip: Raw or lightly steamed veggies retain more Vitamin C than boiling or overcooking.
🍊 Fruits Rich in Vitamin C
From tropical fruits to everyday options, here are some of the top Vitamin C sources in the fruit family:
- Acerola Cherry
- Camu Camu
- Guava
- Kiwi
- Strawberries
- Oranges
- Lemons & Limes
- Papaya
- Pineapple
- Mango
- Cantaloupe
- Raspberries
- Blackcurrants
- Grapefruit
These fruits are not just sweet and refreshing—they’re also powerful allies in your wellness routine.
🍇 Fruits Rich in Vitamin C and Zinc
Vitamin C and zinc together are a dynamic immune-supporting duo. Here are some fruits that naturally offer both or help enhance zinc absorption:
- Guava – Top for C and contains trace zinc
- Blackberries – Offers zinc, Vitamin C, and antioxidants
- Pomegranate – Packed with polyphenols and C
- Avocado – Contains zinc, Vitamin E, and some Vitamin C
- Kiwi – Enhances zinc absorption and supports collagen
💡 Zinc requires Vitamin C for better absorption and synergy in immune defense.
🧾 Complete Vitamin C Foods List
Here’s a handy categorized list of foods rich in Vitamin C:
🍉 Fruits:
- Guava
- Papaya
- Kiwi
- Oranges
- Strawberries
- Blackcurrants
- Cantaloupe
- Pineapple
- Mango
- Lychee
- Camu Camu
- Acerola Cherry
🥦 Vegetables:
- Red, Yellow, and Green Bell Peppers
- Broccoli
- Brussels Sprouts
- Cauliflower
- Kale
- Spinach
- Swiss Chard
- Mustard Greens
- Tomatoes
- Cabbage
🧂 Herbs & Others:
- Parsley (fresh)
- Thyme (fresh)
- Chili Peppers
- Rose Hips (dried, in tea)
- Sea Buckthorn Berries
🥗 Creative Ways to Add Vitamin C to Your Meals
Getting more Vitamin C doesn’t mean popping supplements—it can be both fun and flavorful.
🍹 Morning
- Green Smoothie: Spinach, kiwi, orange juice, mango
- Fruit Bowl: Strawberries, pineapple, papaya
- Infused Water: Lemon, mint, cucumber slices
🥗 Lunch
- Salad with Bell Peppers & Citrus Dressing
- Broccoli stir-fry with garlic and sesame
🍽️ Dinner
- Grilled chicken with roasted Brussels sprouts
- Stuffed bell peppers with quinoa and tomatoes
🥤 Snacks
- Guava slices
- Red pepper strips with hummus
- Fresh fruit smoothies
🌟 Remember: Fresh and raw beats processed when it comes to Vitamin C retention.
🛒 Fortified & Enriched Vitamin C Foods
Not all Vitamin C comes from whole produce. Many packaged or enriched foods can provide an added boost:
- Fortified breakfast cereals
- Vitamin C-enriched fruit juices
- Plant-based milks (almond, oat, soy)
- Multivitamin gummies
- Vitamin C water or electrolyte drinks
While whole foods are ideal, fortified options can help bridge nutritional gaps—especially for picky eaters, seniors, or those with dietary restrictions.
🧠 Final Thoughts: Build Immunity from the Inside Out
In a world full of supplements and health gimmicks, Vitamin C remains one of the most trusted, science-backed nutrients you can add to your day. From strengthening your immune system to keeping your skin youthful, the benefits are undeniable.
Whether you’re sipping a smoothie, crunching on a red pepper, or juicing oranges, remember: small daily choices lead to long-term health gains.
Eating a rainbow of Vitamin C rich foods ensures you’re not only covering your basic needs—but actively thriving.
❓ Frequently Asked Questions About Vitamin C Rich Foods
1. What is the best natural source of Vitamin C?
The best natural source of Vitamin C is acerola cherries, which contain up to 1677 mg per 100g—over 20 times more than oranges.
2. Can I get enough Vitamin C from food alone?
Yes, most people can get sufficient Vitamin C through a varied diet rich in fruits and vegetables. Guava, kiwi, bell peppers, and strawberries are excellent daily options.
3. How much Vitamin C do I need daily?
The recommended daily intake is:
- 90 mg for adult men
- 75 mg for adult women
Higher needs may apply during illness, pregnancy, or smoking.
4. What are signs of Vitamin C deficiency?
Common symptoms include:
- Fatigue
- Weak immune response
- Slow wound healing
- Bleeding gums
- Dry, rough skin
In severe cases, it can lead to scurvy.
5. Does cooking reduce Vitamin C content in foods?
Yes, Vitamin C is heat-sensitive. Boiling or overcooking can reduce content significantly. To preserve it, use steaming, stir-frying, or eating raw.
6. What’s the difference between Vitamin C and ascorbic acid?
They are essentially the same. Ascorbic acid is the chemical name for Vitamin C, whether it’s found in natural foods or synthetic supplements.
7. Can you take too much Vitamin C?
While it’s water-soluble and excess is usually excreted, very high doses (above 2000 mg/day) may cause:
- Stomach cramps
- Diarrhea
- Nausea
8. Are supplements as effective as food sources of Vitamin C?
Supplements can help, but whole foods also provide fiber, enzymes, and phytonutrients that aid absorption and overall health.
9. Which fruits contain both Vitamin C and Zinc?
Fruits like guava, kiwi, blackberries, and pomegranate offer Vitamin C and trace amounts of zinc, supporting immune and skin health.
10. Is it safe to take Vitamin C daily?
Yes, daily intake from food is safe and recommended. Consistency matters more than quantity—regular small doses are more effective than occasional megadoses.










[…] citrus, kiwi, strawberries, or peppers into the same meal. To make pairings effortless, skim vitamin C–rich foods and match them to the veg list […]