“Good things come in small packages.” This age-old saying couldn’t be more true when it comes to cherries. These little red jewels don’t just taste divine—they pack a health punch powerful enough to rival the most hyped superfoods.
If you’ve been skipping past cherries at the market, it might be time to reconsider. Whether you’re looking to boost your recovery after workouts, sleep better at night, reduce inflammation, or support your heart, cherries might just be the missing piece in your wellness puzzle.
Let’s dig into what science has uncovered recently about cherries—and how you can make the most of this delicious fruit in your daily routine.
🧬 What Makes Cherries So Special?
Cherries—especially the Montmorency tart and Bing sweet varieties—are loaded with:
- Anthocyanins: Powerful antioxidants that give cherries their deep red color and fight inflammation.
- Melatonin: The same hormone your body produces to regulate sleep.
- Quercetin & Kaempferol: Natural plant compounds with anti-inflammatory and anti-allergy effects.
- Vitamins A, C, and K, and potassium for heart and bone health.
- Fiber: Supports digestion and blood sugar control.
🔬 The Science-Backed Benefits of Cherries
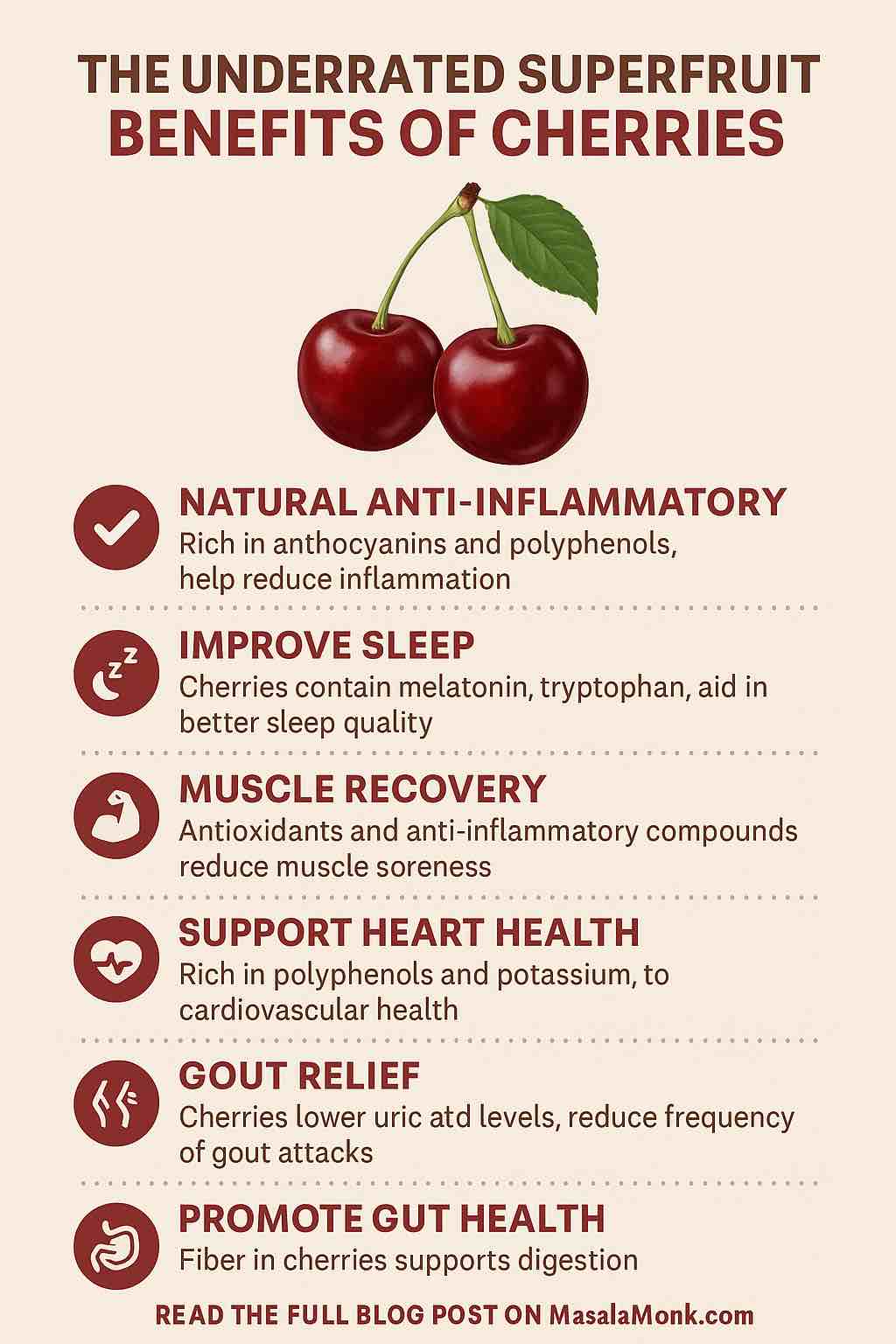
1. They’re Nature’s Anti-Inflammatory Pill
Chronic inflammation is a root cause of many diseases—from arthritis and diabetes to heart disease and cancer. Cherries, especially tart varieties, are rich in polyphenols and anthocyanins that help lower inflammation markers like CRP (C-reactive protein).
✅ Clinical highlight: A 2025 review of 20+ clinical trials found cherry consumption significantly reduced systemic inflammation and oxidative stress when consumed for at least 7–14 days.
🛠️ Practical tip: Include 1–2 cups of cherries (or ~60 mL tart cherry concentrate) daily during periods of stress or inflammation flare-ups.
2. They May Help You Sleep Like a Baby
Tart cherries contain natural melatonin, as well as tryptophan and serotonin precursors that work together to support your circadian rhythm.
✅ Study insight: A meta-analysis found that people who drank tart cherry juice twice daily improved their total sleep time and sleep efficiency—especially helpful for those with insomnia.
🛠️ Practical tip: Drink ~60 mL tart cherry juice 1–2 hours before bed for a gentle sleep boost. Pair it with a calming nighttime ritual (no screens, low lights).
3. Your Muscles Will Thank You
Strenuous workouts can leave your muscles sore for days. Cherry juice has become a go-to recovery drink for professional athletes, including Tour de France cyclists and ultramarathoners.
✅ Why it works: The combination of antioxidants and anti-inflammatory compounds reduces muscle soreness, minimizes damage, and speeds up recovery time.
🛠️ Practical tip: If you’re training hard, drink tart cherry juice 5–7 days before and 2–3 days after an intense event. Powdered cherry extract also works—just look for ~500 mg anthocyanin content per serving.
4. Heart Health in a Glass
Potassium, fiber, and polyphenols work together in cherries to help lower blood pressure, reduce LDL cholesterol, and improve vascular function.
✅ Clinical finding: A recent RCT showed participants who took tart cherry concentrate had a significant drop in systolic blood pressure after just 12 days.
🛠️ Practical tip: Add a small bowl of sweet cherries to your breakfast or snack on dried tart cherries post-lunch. Just be mindful of added sugars if dried.
5. Good for Your Gut and Immune System
New research shows tart cherry juice may reduce markers of gut inflammation and improve quality of life in people with ulcerative colitis.
✅ Emerging research: Drinking 130 mL of tart cherry juice twice daily reduced gut inflammation markers (like fecal calprotectin) by ~40% in a six-week study.
🛠️ Practical tip: If you have digestive issues or autoimmune-related inflammation, speak to your doctor about adding cherry juice to your routine.
6. A Natural Ally Against Gout and Arthritis
Cherries can help reduce uric acid levels and lower the risk of gout attacks.
✅ Study review: People who ate cherries regularly had up to a 35% lower risk of gout flare-ups compared to those who didn’t.
🛠️ Practical tip: 10–12 cherries a day, or 1–2 tablespoons of cherry concentrate, may offer protective benefits. Consistency is key.
🧠 Bonus: Cognitive & Metabolic Benefits on the Radar
While not yet as firmly proven, early data hints that cherry antioxidants might support brain function, help regulate blood sugar, and even improve mood and alertness in older adults.
✅ Why? Anthocyanins cross the blood-brain barrier, reducing inflammation in the brain and improving blood flow—two keys to better cognition.
🛠️ Practical tip: Eat whole cherries to get the added benefit of fiber, which slows sugar absorption and supports a healthy gut-brain connection.
🧾 Choosing the Right Cherry Products
| Form | Benefits | What to Watch |
|---|---|---|
| Fresh | Full spectrum of nutrients | Short shelf life |
| Frozen | Almost as nutritious as fresh | Watch for added sugar in some |
| Juice (unsweetened) | High melatonin & antioxidants | High natural sugar |
| Concentrate | Potent source, great for dosing | Needs dilution |
| Capsules/extracts | Convenient, standardized dosing | Choose standardized for polyphenols |
| Dried | Convenient snack | Check sugar levels |
🧠 Pro tip: Always look for Montmorency or Balaton tart cherry labels for the highest polyphenol content. If using supplements, check for 250–500 mg standardized anthocyanins.
⚠️ A Few Things to Keep in Mind
- Too much juice = too much sugar. Stick with 4–6 oz daily unless you’re offsetting with high activity.
- Allergic reactions are rare but possible.
- Digestive issues? Cherries are high in sorbitol, which may cause bloating or gas in sensitive individuals (e.g. IBS).
- Medication interactions: Cherry polyphenols may slightly interact with blood thinners—check with your healthcare provider.
💬 Final Thoughts: Small Fruit, Big Results
Cherries aren’t a magic bullet—but when combined with a healthy diet and lifestyle, they offer real, clinically-backed benefits for inflammation, recovery, sleep, heart health, and more.
If you’re looking for a simple way to level up your wellness without reaching for pills or powders—just toss a handful of cherries into your day.
Your joints, heart, muscles, and maybe even your dreams will thank you.
📦 Sample Daily Cherry Routine
| Time | Cherry Form | Purpose |
|---|---|---|
| Breakfast | ½ cup sweet cherries | Antioxidants, fiber |
| Pre-workout | Tart cherry juice | Endurance, reduced soreness |
| Evening snack | Cherry concentrate | Sleep support |
🍒 Frequently Asked Questions (FAQs)
1. What’s the difference between sweet and tart cherries?
Sweet cherries (like Bing or Rainier) are typically eaten fresh and are higher in sugar. Tart cherries (especially Montmorency) are more sour and often found in juice, powder, or supplement form. Tart cherries generally have higher concentrations of melatonin and anthocyanins, making them more effective for sleep and inflammation.
2. How much cherry juice should I drink per day?
A common effective dose is 60–120 mL (2–4 oz) of unsweetened tart cherry juice daily. For specific benefits (like sleep or exercise recovery), split this into two servings—morning and evening—for best results.
3. Can cherries really help me sleep better?
Yes, especially Montmorency tart cherries, which are rich in natural melatonin and tryptophan. Clinical studies show improved sleep duration and efficiency, particularly in people with mild insomnia.
4. Are there side effects from eating too many cherries?
Cherries are generally safe, but large amounts can cause bloating or digestive discomfort due to their sorbitol and fiber content. Moderation is key—stick to 1–2 servings daily, and adjust based on how your body responds.
5. Is cherry juice safe for diabetics?
Cherries have a low glycemic index, but tart cherry juice still contains natural sugars. Diabetics should:
- Choose unsweetened versions.
- Limit servings (½ cup juice max).
- Prefer whole cherries for fiber and better glucose control.
Always consult your doctor before making regular use.
6. What’s better: cherry juice, supplements, or fresh cherries?
It depends on your goal:
- For sleep & inflammation: Tart cherry juice or concentrate is more potent.
- For everyday wellness: Fresh or frozen whole cherries offer fiber and balanced nutrients.
- For convenience: Choose capsules with 250–500 mg standardized anthocyanins.
7. Can cherries really reduce gout or arthritis pain?
Yes. Cherries help lower uric acid levels and inflammation, reducing the frequency and intensity of gout attacks. Studies show a 35% lower risk of flare-ups in those who consume cherries regularly.
8. What’s the best time to take cherry juice for sleep?
Consume it about 1 to 2 hours before bedtime. That gives the melatonin time to take effect. If you’re splitting doses for other benefits, take one in the morning and one in the evening.
9. Are dried cherries just as healthy?
Dried cherries retain many nutrients but often have added sugar and lower melatonin. Look for unsweetened varieties, and eat in small amounts (¼ cup max).
10. How long does it take to see results from cherry intake?
It varies:
- For sleep: Effects may appear in 3–5 days.
- For muscle soreness: 1–2 days post-exercise.
- For joint/gut inflammation: 2–6 weeks of consistent use.
Track your response and adjust based on your needs.










