When it comes to cardio training, one-size-fits-all doesn’t work. Your heart rate zones shift based on your age, gender, fitness level, and physiology. Understanding how your heart rate zones by age and gender evolve is the key to smarter workouts, better results, and reduced risk of injury or burnout.
In this detailed guide, we’ll break down exactly how to personalize your heart rate training zones based on your individual profile.
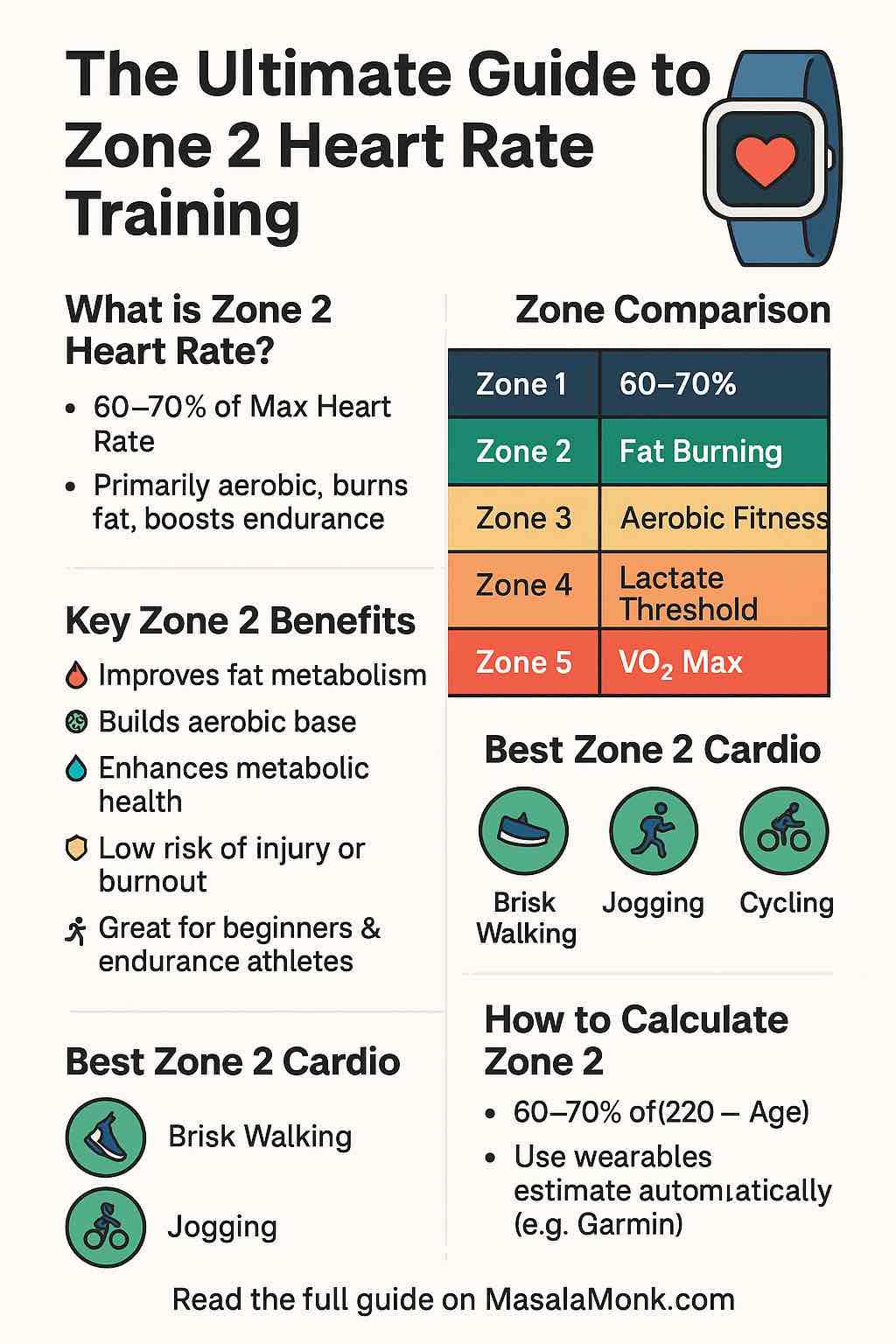
🔬 Why Heart Rate Zones Change With Age
As you age, your maximum heart rate (HRmax) naturally declines. This affects all your training zones. The formula most people start with is:
Max HR = 220 − Age
While simple, this formula doesn’t account for individual variation. Factors like genetics, fitness level, and gender play a major role in your actual heart rate performance.
As your Max HR lowers, your zone ranges also shift downward — meaning your Zone 2 heart rate at 50 won’t be the same as it was at 30.
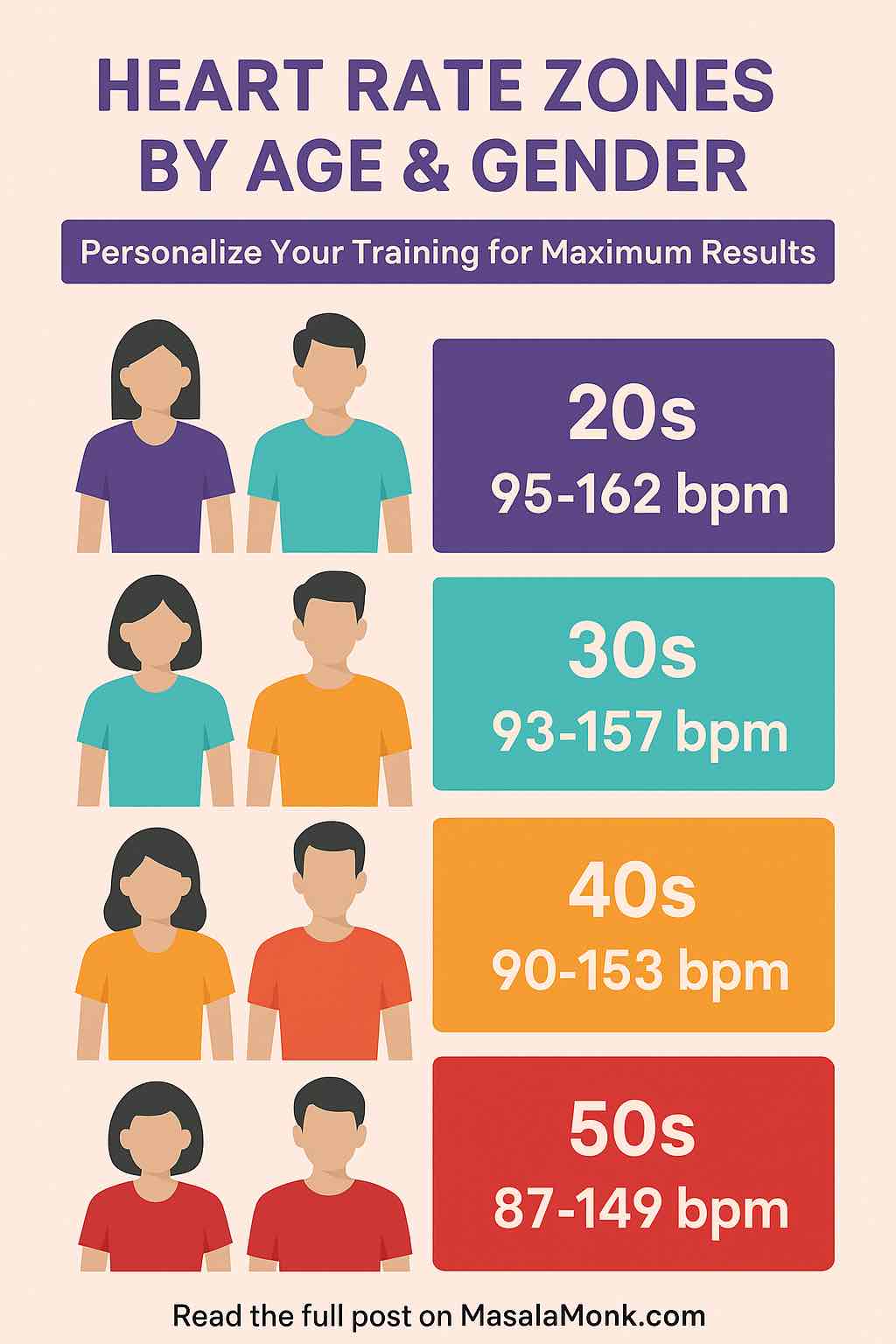
🧮 Heart Rate Zones By Age (General Chart)
| Age | Max HR | Zone 1 (50–60%) | Zone 2 (60–70%) | Zone 3 (70–80%) | Zone 4 (80–90%) | Zone 5 (90–100%) |
|---|---|---|---|---|---|---|
| 20 | 200 | 100–120 | 120–140 | 140–160 | 160–180 | 180–200 |
| 30 | 190 | 95–114 | 114–133 | 133–152 | 152–171 | 171–190 |
| 40 | 180 | 90–108 | 108–126 | 126–144 | 144–162 | 162–180 |
| 50 | 170 | 85–102 | 102–119 | 119–136 | 136–153 | 153–170 |
| 60 | 160 | 80–96 | 96–112 | 112–128 | 128–144 | 144–160 |
| 70 | 150 | 75–90 | 90–105 | 105–120 | 120–135 | 135–150 |
Note: Use these as starting points. Lab testing, wearables, and real-world data can fine-tune your exact zones.
🧬 Gender Differences in Heart Rate Zones
While men and women both benefit from heart rate training, some gender differences exist:
| Factor | Men | Women |
|---|---|---|
| Resting Heart Rate | Slightly lower | Slightly higher |
| Max HR Formula Adjustment | Slightly lower in some formulas | Often higher for same age |
| HRV (Heart Rate Variability) | Lower overall HRV | Typically higher HRV |
| Recovery Heart Rate | Faster HR drop-off | Slightly slower |
🧮 More accurate Max HR formulas:
For Women (Gulati Formula):
Max HR = 206 − (0.88 × Age)
Example for 40-year-old woman:
206 − (0.88 × 40) = 170.8 bpm
This provides a more precise starting point than the traditional 220−age formula for women.
🎯 Why Personalizing Heart Rate Zones Matters
- ✅ Prevents overtraining & burnout
- ✅ Optimizes fat burning (especially in Zone 2)
- ✅ Maximizes endurance adaptations
- ✅ Enhances VO2 max development
- ✅ Protects heart health long-term
- ✅ Makes every minute of training more efficient
🔍 How Wearables Help Personalize Zones
Modern fitness trackers like Garmin, WHOOP, Polar, COROS, Fitbit, and Apple Watch analyze:
- Resting HR
- HRV (Heart Rate Variability)
- VO2 max estimates
- Lactate thresholds
- Recovery readiness
They help fine-tune your zones in real-time as your fitness improves.
🏋️♂️ Sample Personalized Zone 2 Heart Rates
| Age | Male Zone 2 | Female Zone 2 |
|---|---|---|
| 30 | 114–133 bpm | 110–129 bpm |
| 40 | 108–126 bpm | 102–122 bpm |
| 50 | 102–119 bpm | 98–115 bpm |
| 60 | 96–112 bpm | 92–110 bpm |
👉 Key takeaway:
Your Zone 2 will likely sit lower as you age or depending on your gender — but its importance never fades.
🔬 Should You Test Your Zones?
Yes. If you want true precision:
- VO2 max lab testing
- Lactate threshold testing
- Metabolic cart tests
- Professional coaching assessments
If that’s not practical, a good wearable + consistent tracking will still get you 80% of the way there.
🧘 Final Thought: Smarter, Not Harder
Heart rate zones are your personal blueprint for sustainable, science-backed training.
- Younger? Build a strong base now.
- Older? Focus on longevity and metabolic health.
- Male or female? Personalize your formula and listen to your data.
The right intensity for you changes with age, gender, and fitness — and that’s exactly why heart rate zone training works so well.
✅ 10 FAQs for Heart Rate Zones by Age & Gender
1️⃣ How does age affect heart rate zones?
As you age, your maximum heart rate naturally decreases. This lowers all your training zones, meaning your target heart rate for fat burning or endurance shifts downward as you get older.
2️⃣ How do you calculate heart rate zones by age?
Use the formula:
Max HR = 220 − Age.
Then apply zone percentages (e.g., Zone 2 is 60–70% of Max HR). For more accuracy, adjust for gender and use heart rate reserve (HRR) calculations.
3️⃣ Do men and women have different heart rate zones?
Generally, women have slightly higher resting heart rates and HRV scores, while men may have slightly lower max heart rates. Formulas like Gulati’s (206 − 0.88 × age) are more accurate for women.
4️⃣ What is the best zone for fat burning?
Zone 2 (60–70% of Max HR) is optimal for fat burning and endurance building, as your body primarily burns fat for fuel in this range.
5️⃣ How does gender affect recovery heart rate?
Men often experience a slightly faster drop in heart rate after exercise. Women typically have higher resting HR but may show more stable HRV patterns.
6️⃣ Can wearables personalize my heart rate zones?
Yes. Devices like Garmin, Whoop, Polar, Coros Pace 2, and Apple Watch use continuous heart rate data, VO2 max estimates, HRV, and recovery metrics to fine-tune your zones.
7️⃣ Should I retest my zones as I get fitter?
Yes. As your fitness improves, your zones may shift. Retesting every 3–6 months ensures your training stays effective and individualized.
8️⃣ What happens if I use generic heart rate formulas?
Generic formulas give a starting point but may not reflect your true zones. Personalized data from wearables or lab tests provides better results.
9️⃣ Why is Zone 2 training emphasized for longevity?
Zone 2 improves mitochondrial health, metabolic flexibility, fat burning, and cardiovascular efficiency — all essential for long-term health and performance.
🔟 What is the Karvonen formula for heart rate zones?
Target HR = [(Max HR − Resting HR) × %Intensity] + Resting HR.
This formula personalizes zones by incorporating your resting heart rate.