Coffee lovers, take a seat! The classic debate between Arabica and Robusta coffee beans is hotter than ever—and the science has never been clearer. Whether you’re a café regular, a home barista, or just someone looking for that perfect cup, understanding the differences between these two beans can upgrade not only your coffee ritual but your overall wellness.
Let’s dig deep into the latest research, practical brewing tips, and the little-known ways your choice of bean could impact your body and mind.
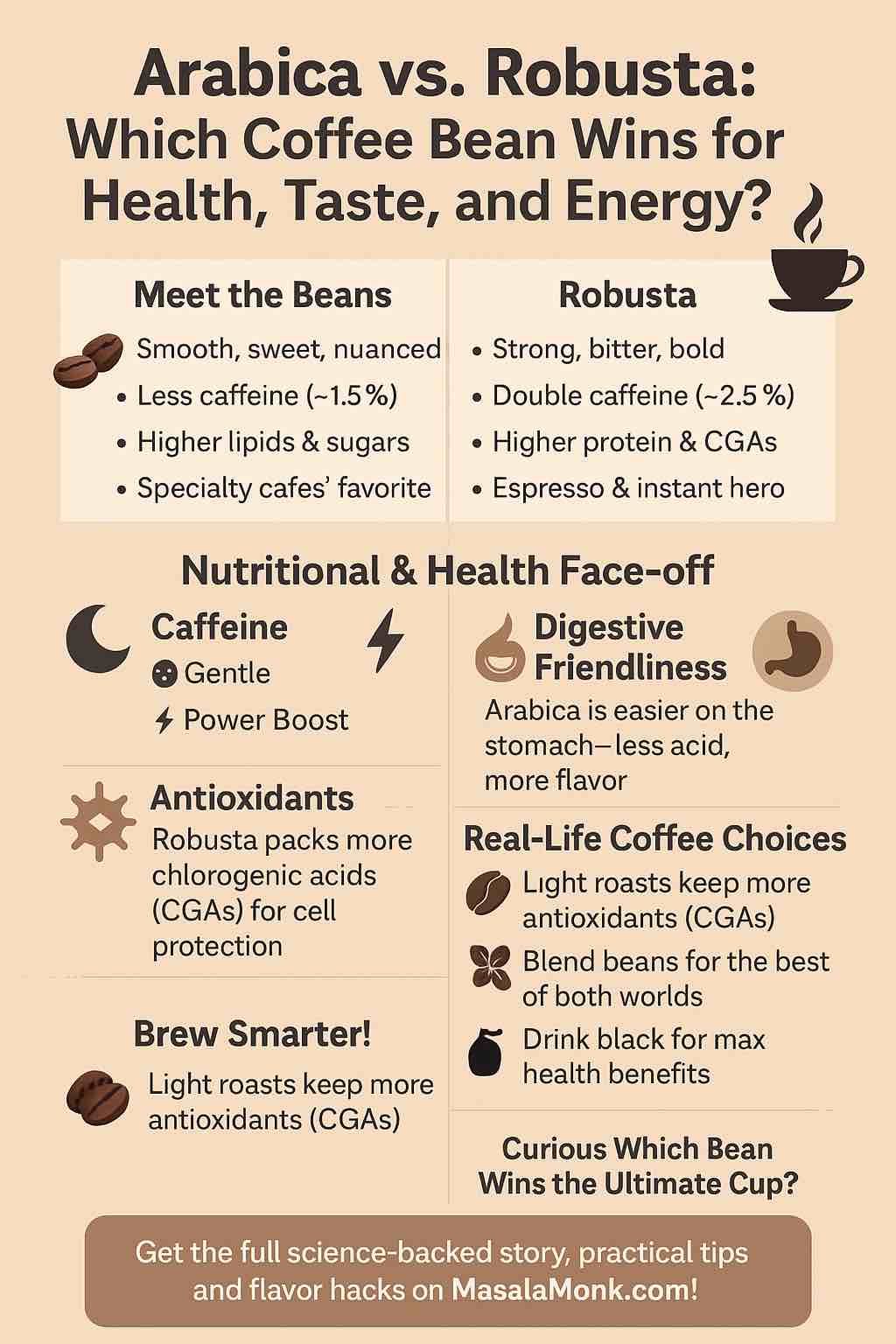
1. Meet the Beans: Arabica and Robusta
Before we get technical, let’s introduce our contenders:
- Arabica (Coffea arabica): Grown at higher altitudes, this bean delivers a sweeter, smoother, and often fruitier taste. It’s what you’ll find in most specialty cafes. Arabica is prized for its complex aroma and is generally gentler on the palate (and stomach).
- Robusta (Coffea canephora): Grown at lower altitudes, Robusta is the hardier bean—resistant to disease and climate stress, and producing higher yields at lower costs. Its flavor? Strong, bitter, and earthy. It’s the backbone of many espresso blends and instant coffees.
2. Nutritional Showdown: What’s Inside the Beans?
Here’s where the plot thickens. Modern research (2023–2025) has delivered new insights into what makes these beans tick:
| Nutrient/Compound | Arabica | Robusta |
|---|---|---|
| Caffeine | ~1.2–1.5% | ~2.2–2.7% |
| Chlorogenic Acids | ~65 mg/g (green) | ~140 mg/g (green) |
| After Roasting | Both drop below ~30 mg/g | Both drop below ~30 mg/g |
| Lipids/Fats | Higher | Lower |
| Sugars | Higher | Lower |
| Protein | Lower | Higher |
| Melanoidins | Lower | Higher |
| Trigonelline/Vitamin E | Higher | Lower |
Takeaway:
Robusta brings a heavy dose of caffeine and antioxidants, while Arabica leans on a richer, smoother taste profile and contains more compounds that support heart and liver health.
3. Health Benefits: What Does the Science Say in 2025?
A. Antioxidants: The Real Powerhouses
- Both beans are loaded with antioxidants, especially chlorogenic acids (CGAs).
- Robusta has the edge in CGA content pre-roast, but after roasting (especially dark roasts), the difference shrinks. Lighter roasts retain more CGAs, regardless of bean type.
- Practical Tip: For the best antioxidant punch, go for lightly roasted Robusta or Arabica.
B. Caffeine: Perk or Pitfall?
- Robusta can contain twice the caffeine of Arabica. Good news for those needing a big morning kick or long study night!
- But higher caffeine can mean more jitters, anxiety, or disrupted sleep—especially for sensitive individuals or those with high blood pressure.
- Practical Tip: Choose Arabica if you’re caffeine-sensitive, or want a cup later in the day.
C. Metabolic and Liver Health
- Recent studies show both Arabica and Robusta help with blood sugar regulation and fat metabolism—good news for metabolic wellness.
- In animal studies, Robusta slightly outperformed Arabica in improving cholesterol and supporting liver function.
D. Digestive Impact
- Robusta is more acidic post-roast and can be harsh on sensitive stomachs.
- Arabica’s higher lipid content gives a silkier mouthfeel and tends to be easier to digest.
- Practical Tip: If you have acid reflux or stomach sensitivity, stick with Arabica.
E. Cognitive and Mood Boosts
- Arabica seed extract (2025 human trial): Improved working memory and mood, likely due to a unique blend of caffeine, CGAs, and trigonelline.
- Robusta hasn’t been trialed as extensively in humans for cognition, but its higher caffeine and antioxidant load suggest potential benefits.
- Practical Tip: If you want a mental boost with less risk of jitters, try a high-quality Arabica, preferably light or medium roast.
4. Taste and Aroma: Beyond the Science
- Arabica is celebrated for its complex, nuanced flavors—think floral, fruity, chocolaty. It’s often the darling of specialty coffee.
- Robusta delivers a powerful, sometimes astringent, boldness with earthy and nutty undertones. It’s the hero of many espresso blends (think crema!) but less popular in pour-overs or single-origin offerings.
- Practical Tip: If you’re new to coffee or love black brews, start with Arabica. If you love espresso’s bite or want to cut through milk and sugar, try Robusta blends.
5. How to Choose: A Practical Guide
- Energy Seekers: Robusta for that double-caffeine punch.
- Flavor Adventurers: Arabica for complexity, or blend both for balance.
- Stomach Sensitive: Arabica, preferably light roast.
- Budget-Conscious: Robusta is usually cheaper and more sustainable in tough climates.
- Espresso Fans: Try blends—Robusta adds crema and body; Arabica brings sweetness.
Pro Tip: Roasting level matters more than bean type for antioxidant retention. Light-to-medium roasts maximize CGAs. Freshness, grind, and brew method also influence taste and health impact.
6. What’s Next in Coffee Science?
- Bioactive Extracts: New human trials are exploring CGA and trigonelline supplements for mental health, metabolism, and liver support.
- Sustainability: Robusta’s climate resilience is making it more important for the future of global coffee production as climate change advances.
- Flavor Innovation: Advances in fermentation and roasting are blurring the lines—expect more hybrid blends and exciting single-origin Robustas!
7. Final Word: Drink What You Love, But Drink It Smart
Whether you’re team Arabica, team Robusta, or somewhere in between, both beans offer compelling health benefits—so long as you drink your coffee in moderation and keep an eye on additives like sugar and cream.
The best cup is the one that fits your body, taste, and lifestyle. Armed with science, you can make every sip count!
FAQs
1. What is the main difference between Arabica and Robusta coffee?
Arabica beans are known for their smoother, sweeter, and more complex flavors, while Robusta beans are stronger, more bitter, and have almost double the caffeine. Robusta is also generally more affordable and easier to cultivate.
2. Which coffee bean is healthier: Arabica or Robusta?
Both beans offer health benefits. Robusta has more antioxidants and caffeine, while Arabica contains more trigonelline and healthy fats. Choosing light or medium roast and drinking coffee black maximizes health benefits for either bean.
3. Does Robusta coffee have more caffeine than Arabica?
Yes. Robusta beans typically contain 2–2.7% caffeine, almost twice as much as Arabica’s 1.2–1.5%. This makes Robusta more energizing but also riskier for those sensitive to caffeine.
4. Is Arabica coffee less acidic than Robusta?
Generally, yes. Arabica tends to be less acidic and is easier on sensitive stomachs, especially in lighter roasts. However, roast level and brewing method also play a big role in perceived acidity.
5. Which coffee is better for espresso?
Espresso blends often use a mix of both. Robusta adds body and crema, while Arabica provides sweetness and complexity. For a bold espresso, try blends with at least 20–30% Robusta.
6. Are there significant nutritional differences between Arabica and Robusta?
Yes. Arabica has more lipids and sugars, which create a richer flavor and mouthfeel. Robusta has higher protein and antioxidant (CGA) content, especially before roasting.
7. Does roasting affect the health benefits of coffee beans?
Absolutely. Lighter roasts retain more antioxidants and chlorogenic acids, while darker roasts enhance flavor at the cost of some healthful compounds. Roast level impacts the bean’s final nutrition more than bean type.
8. Which coffee is more sustainable or climate-resilient?
Robusta is more resistant to pests, diseases, and climate stress, making it a more sustainable option in regions facing unpredictable weather.
9. Is instant coffee made from Robusta or Arabica?
Most instant coffees use Robusta due to its cost and high caffeine, but some premium brands now offer Arabica or blended instant coffee for better flavor.
10. How much coffee is safe to drink per day?
Current research suggests 1–3 cups of black coffee daily is linked to health benefits and longevity. Limit added sugar and cream, and watch your total caffeine intake if you have health concerns.
Want more on brewing methods, new research, or taste hacks? Leave a comment below!
Brew well. Drink wisely. Explore bravely. Coffee’s story is just beginning.











